+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6skf | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
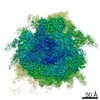
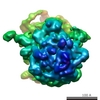
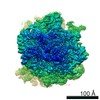
| Title | Cryo-EM Structure of T. kodakarensis 70S ribosome | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOME / T. kodakarensis / ac4C / cryo-EM | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationribonuclease P activity / tRNA 5'-leader removal / maturation of LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / ribosomal large subunit biogenesis / maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / maturation of SSU-rRNA / ribosome biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit assembly / small ribosomal subunit ...ribonuclease P activity / tRNA 5'-leader removal / maturation of LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / ribosomal large subunit biogenesis / maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / maturation of SSU-rRNA / ribosome biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit assembly / small ribosomal subunit / small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / 5S rRNA binding / ribosomal large subunit assembly / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / tRNA binding / negative regulation of translation / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / ribonucleoprotein complex / mRNA binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / metal ion binding / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Thermococcus kodakarensis (archaea) Thermococcus kodakarensis (archaea) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.95 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Matzov, D. / Sas-Chen, A. / Thomas, J.M. / Santangelo, T. / Meier, J.L. / Schwartz, S. / Shalev-Benami, M. | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2020 Journal: Nature / Year: 2020Title: Dynamic RNA acetylation revealed by quantitative cross-evolutionary mapping. Authors: Aldema Sas-Chen / Justin M Thomas / Donna Matzov / Masato Taoka / Kellie D Nance / Ronit Nir / Keri M Bryson / Ran Shachar / Geraldy L S Liman / Brett W Burkhart / Supuni Thalalla Gamage / ...Authors: Aldema Sas-Chen / Justin M Thomas / Donna Matzov / Masato Taoka / Kellie D Nance / Ronit Nir / Keri M Bryson / Ran Shachar / Geraldy L S Liman / Brett W Burkhart / Supuni Thalalla Gamage / Yuko Nobe / Chloe A Briney / Michaella J Levy / Ryan T Fuchs / G Brett Robb / Jesse Hartmann / Sunny Sharma / Qishan Lin / Laurence Florens / Michael P Washburn / Toshiaki Isobe / Thomas J Santangelo / Moran Shalev-Benami / Jordan L Meier / Schraga Schwartz /    Abstract: N-acetylcytidine (acC) is an ancient and highly conserved RNA modification that is present on tRNA and rRNA and has recently been investigated in eukaryotic mRNA. However, the distribution, dynamics ...N-acetylcytidine (acC) is an ancient and highly conserved RNA modification that is present on tRNA and rRNA and has recently been investigated in eukaryotic mRNA. However, the distribution, dynamics and functions of cytidine acetylation have yet to be fully elucidated. Here we report acC-seq, a chemical genomic method for the transcriptome-wide quantitative mapping of acC at single-nucleotide resolution. In human and yeast mRNAs, acC sites are not detected but can be induced-at a conserved sequence motif-via the ectopic overexpression of eukaryotic acetyltransferase complexes. By contrast, cross-evolutionary profiling revealed unprecedented levels of acC across hundreds of residues in rRNA, tRNA, non-coding RNA and mRNA from hyperthermophilic archaea. AcC is markedly induced in response to increases in temperature, and acetyltransferase-deficient archaeal strains exhibit temperature-dependent growth defects. Visualization of wild-type and acetyltransferase-deficient archaeal ribosomes by cryo-electron microscopy provided structural insights into the temperature-dependent distribution of acC and its potential thermoadaptive role. Our studies quantitatively define the acC landscape, providing a technical and conceptual foundation for elucidating the role of this modification in biology and disease. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6skf.cif.gz 6skf.cif.gz | 3.5 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6skf.ent.gz pdb6skf.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6skf.json.gz 6skf.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  6skf_validation.pdf.gz 6skf_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  6skf_full_validation.pdf.gz 6skf_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.8 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  6skf_validation.xml.gz 6skf_validation.xml.gz | 286.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  6skf_validation.cif.gz 6skf_validation.cif.gz | 478.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sk/6skf https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sk/6skf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sk/6skf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sk/6skf | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 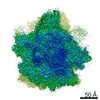 10223MC 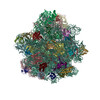 6skgC  6th6C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 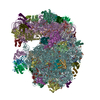
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-RNA chain , 3 types, 3 molecules AaBABB
| #1: RNA chain | Mass: 488234.531 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermococcus kodakarensis (archaea) Thermococcus kodakarensis (archaea) |
|---|---|
| #27: RNA chain | Mass: 990337.312 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermococcus kodakarensis (archaea) Thermococcus kodakarensis (archaea) |
| #28: RNA chain | Mass: 40744.309 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermococcus kodakarensis (archaea) / References: GenBank: 57158259 Thermococcus kodakarensis (archaea) / References: GenBank: 57158259 |
+30S ribosomal protein ... , 24 types, 24 molecules AbAcAdAeAfAgAhAiAjAkAlAmAnAoApAqArAsAtAuAvAwAxAy
+50S ribosomal protein ... , 32 types, 34 molecules BCBDBEBFBGBHBIBJBKBLBMBNBOBPBQBRBSBTBUBVBWBXBYBZBaBbBcBdBeBg...
-Protein / Protein/peptide , 2 types, 2 molecules AzBk
| #26: Protein | Mass: 7001.247 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermococcus kodakarensis (archaea) / References: UniProt: Q5JFE2 Thermococcus kodakarensis (archaea) / References: UniProt: Q5JFE2 |
|---|---|
| #60: Protein/peptide | Mass: 5051.409 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermococcus kodakarensis (archaea) / References: UniProt: Q5JEV0 Thermococcus kodakarensis (archaea) / References: UniProt: Q5JEV0 |
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 2379 molecules 


| #62: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #63: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: 70S ribosome from Thermococcus kodakarensis / Type: RIBOSOME / Entity ID: #1-#61 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermococcus kodakarensis (archaea) Thermococcus kodakarensis (archaea) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.25 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Calibrated magnification: 29000 X / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 34 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.95 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 53737 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



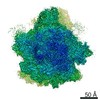




 PDBj
PDBj































