[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6i0y: TnaC-stalled ribosome complex with the titin I27 domain folding c... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6i0y | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | TnaC-stalled ribosome complex with the titin I27 domain folding close to the ribosomal exit tunnel | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOME / Protein folding / ribosomal exit tunnel / nascent chain / titin I27 domain | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / transcriptional attenuation by ribosome / sarcomerogenesis / titin-telethonin complex / structural molecule activity conferring elasticity / skeletal muscle myosin thick filament assembly / telethonin binding / detection of muscle stretch / : / muscle alpha-actinin binding ...: / transcriptional attenuation by ribosome / sarcomerogenesis / titin-telethonin complex / structural molecule activity conferring elasticity / skeletal muscle myosin thick filament assembly / telethonin binding / detection of muscle stretch / : / muscle alpha-actinin binding / L-tryptophan catabolic process / cardiac myofibril assembly / cardiac muscle hypertrophy / cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis / mitotic chromosome condensation / protein kinase regulator activity / Striated Muscle Contraction / muscle filament sliding / M band / actinin binding / I band / cardiac muscle cell development / structural constituent of muscle / sarcomere organization / stringent response / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / transcriptional attenuation / endoribonuclease inhibitor activity / positive regulation of ribosome biogenesis / RNA-binding transcription regulator activity / striated muscle contraction / translational termination / negative regulation of cytoplasmic translation / skeletal muscle contraction / cardiac muscle contraction / DnaA-L2 complex / translation repressor activity / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / mRNA regulatory element binding translation repressor activity / muscle contraction / assembly of large subunit precursor of preribosome / cytosolic ribosome assembly / response to reactive oxygen species / ribosome assembly / condensed nuclear chromosome / positive regulation of protein secretion / regulation of cell growth / DNA-templated transcription termination / response to radiation / response to calcium ion / mRNA 5'-UTR binding / Z disc / actin filament binding / Platelet degranulation / large ribosomal subunit / transferase activity / ribosome binding / protease binding / ribosomal large subunit assembly / 5S rRNA binding / protein tyrosine kinase activity / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / calmodulin binding / tRNA binding / non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase / protein kinase activity / negative regulation of translation / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / protein serine kinase activity / response to antibiotic / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / protein serine/threonine kinase activity / mRNA binding / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / protein kinase binding / enzyme binding / protein homodimerization activity / DNA binding / RNA binding / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / zinc ion binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Su, T. / Kudva, R. / von Heijne, G. / Beckmann, R. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Sweden, 1items Sweden, 1items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2018 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2018Title: Folding pathway of an Ig domain is conserved on and off the ribosome. Authors: Pengfei Tian / Annette Steward / Renuka Kudva / Ting Su / Patrick J Shilling / Adrian A Nickson / Jeffrey J Hollins / Roland Beckmann / Gunnar von Heijne / Jane Clarke / Robert B Best /     Abstract: Proteins that fold cotranslationally may do so in a restricted configurational space, due to the volume occupied by the ribosome. How does this environment, coupled with the close proximity of the ...Proteins that fold cotranslationally may do so in a restricted configurational space, due to the volume occupied by the ribosome. How does this environment, coupled with the close proximity of the ribosome, affect the folding pathway of a protein? Previous studies have shown that the cotranslational folding process for many proteins, including small, single domains, is directly affected by the ribosome. Here, we investigate the cotranslational folding of an all-β Ig domain, titin I27. Using an arrest peptide-based assay and structural studies by cryo-EM, we show that I27 folds in the mouth of the ribosome exit tunnel. Simulations that use a kinetic model for the force dependence of escape from arrest accurately predict the fraction of folded protein as a function of length. We used these simulations to probe the folding pathway on and off the ribosome. Our simulations-which also reproduce experiments on mutant forms of I27-show that I27 folds, while still sequestered in the mouth of the ribosome exit tunnel, by essentially the same pathway as free I27, with only subtle shifts of critical contacts from the C to the N terminus. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6i0y.cif.gz 6i0y.cif.gz | 2.3 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6i0y.ent.gz pdb6i0y.ent.gz | 1.8 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6i0y.json.gz 6i0y.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/i0/6i0y https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/i0/6i0y ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/i0/6i0y ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/i0/6i0y | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  0322MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
+50S ribosomal protein ... , 31 types, 31 molecules h01234568CDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTWXYZ
-RNA chain , 3 types, 3 molecules ABV
| #11: RNA chain | Mass: 941306.188 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #12: RNA chain | Mass: 38177.762 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #31: RNA chain | Mass: 24876.777 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Protein/peptide / Protein , 2 types, 2 molecules 7z
| #36: Protein | Mass: 9794.193 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TTN / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TTN / Production host:  References: UniProt: Q8WZ42, non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase |
|---|---|
| #9: Protein/peptide | Mass: 2899.416 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 584 molecules 

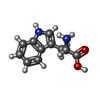




| #37: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #38: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / | #39: Chemical | ChemComp-TRP / | #40: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has protein modification | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 0.926 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 2613 |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 30 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 468015 | ||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 301510 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj