+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6hts | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
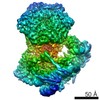
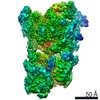
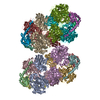
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the human INO80 complex bound to nucleosome | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN / Chromatin / Remodeller / Nucleosome / DNA Binding / Histones / DNA repair / ATPase / Helicase / Sliding / Complex | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of nuclear cell cycle DNA replication / promoter-enhancer loop anchoring activity / telomerase RNA localization to Cajal body / regulation of DNA strand elongation / positive regulation of telomere maintenance in response to DNA damage / establishment of protein localization to chromatin / R2TP complex / dynein axonemal particle / RPAP3/R2TP/prefoldin-like complex / Swr1 complex ...positive regulation of nuclear cell cycle DNA replication / promoter-enhancer loop anchoring activity / telomerase RNA localization to Cajal body / regulation of DNA strand elongation / positive regulation of telomere maintenance in response to DNA damage / establishment of protein localization to chromatin / R2TP complex / dynein axonemal particle / RPAP3/R2TP/prefoldin-like complex / Swr1 complex / Ino80 complex / ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity / regulation of double-strand break repair / box C/D snoRNP assembly / UV-damage excision repair / regulation of chromosome organization / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / TFIID-class transcription factor complex binding / regulation of DNA replication / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / MLL1 complex / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / regulation of embryonic development / Telomere Extension By Telomerase / protein folding chaperone complex / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / alpha-tubulin binding / RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / regulation of DNA repair / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / spindle assembly / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / telomere organization / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Interleukin-7 signaling / TBP-class protein binding / DNA helicase activity / telomere maintenance / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / positive regulation of DNA repair / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / cellular response to ionizing radiation / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / innate immune response in mucosa / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / Defective pyroptosis / Negative Regulation of CDH1 Gene Transcription / HDACs deacetylate histones / cellular response to estradiol stimulus / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / lipopolysaccharide binding / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / euchromatin / negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / HDMs demethylate histones / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / ADP binding / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / beta-catenin binding / chromatin DNA binding / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / DNA Damage Recognition in GG-NER / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / Meiotic recombination / spindle / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Metalloprotease DUBs / nuclear matrix / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / RMTs methylate histone arginines Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.8 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ayala, R. / Willhoft, O. / Aramayo, R.J. / Wilkinson, M. / McCormack, E.A. / Ocloo, L. / Wigley, D.B. / Zhang, X. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 3items United Kingdom, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2018 Journal: Nature / Year: 2018Title: Structure and regulation of the human INO80-nucleosome complex. Authors: Rafael Ayala / Oliver Willhoft / Ricardo J Aramayo / Martin Wilkinson / Elizabeth A McCormack / Lorraine Ocloo / Dale B Wigley / Xiaodong Zhang /  Abstract: Access to DNA within nucleosomes is required for a variety of processes in cells including transcription, replication and repair. Consequently, cells encode multiple systems that remodel nucleosomes. ...Access to DNA within nucleosomes is required for a variety of processes in cells including transcription, replication and repair. Consequently, cells encode multiple systems that remodel nucleosomes. These complexes can be simple, involving one or a few protein subunits, or more complicated multi-subunit machines . Biochemical studies have placed the motor domains of several chromatin remodellers in the superhelical location 2 region of the nucleosome. Structural studies of yeast Chd1 and Snf2-a subunit in the complex with the capacity to remodel the structure of chromatin (RSC)-in complex with nucleosomes have provided insights into the basic mechanism of nucleosome sliding performed by these complexes. However, how larger, multi-subunit remodelling complexes such as INO80 interact with nucleosomes and how remodellers carry out functions such as nucleosome sliding , histone exchange and nucleosome spacing remain poorly understood. Although some remodellers work as monomers , others work as highly cooperative dimers. Here we present the structure of the human INO80 chromatin remodeller with a bound nucleosome, which reveals that INO80 interacts with nucleosomes in a previously undescribed manner: the motor domains are located on the DNA at the entry point to the nucleosome, rather than at superhelical location 2. The ARP5-IES6 module of INO80 makes additional contacts on the opposite side of the nucleosome. This arrangement enables the histone H3 tails of the nucleosome to have a role in the regulation of the activities of the INO80 motor domain-unlike in other characterized remodellers, for which H4 tails have been shown to regulate the motor domains. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
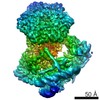
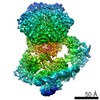
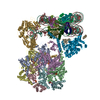
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6hts.cif.gz 6hts.cif.gz | 994.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6hts.ent.gz pdb6hts.ent.gz | 760.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6hts.json.gz 6hts.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ht/6hts https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ht/6hts ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ht/6hts ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ht/6hts | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3954MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 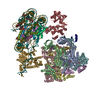
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 9 types, 17 molecules ACEBDFGHIMJNKOLPR
| #1: Protein | Mass: 50296.914 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RUVBL1, INO80H, NMP238, TIP49, TIP49A / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RUVBL1, INO80H, NMP238, TIP49, TIP49A / Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 51222.465 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RUVBL2, INO80J, TIP48, TIP49B, CGI-46 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RUVBL2, INO80J, TIP48, TIP49B, CGI-46 / Production host:  #3: Protein | | Mass: 146390.703 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INO80, INO80A, INOC1, KIAA1259 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INO80, INO80A, INOC1, KIAA1259 / Production host:  References: UniProt: Q9ULG1, Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement #4: Protein | | Mass: 68372.336 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ACTR5, ARP5 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ACTR5, ARP5 / Production host:  #5: Protein | Mass: 15437.167 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: HIST1H3A, H3FA, HIST1H3B, H3FL, HIST1H3C, H3FC, HIST1H3D, H3FB, HIST1H3E, H3FD, HIST1H3F, H3FI, HIST1H3G, H3FH, HIST1H3H, H3FK, HIST1H3I, H3FF, HIST1H3J, H3FJ Production host:  #6: Protein | Mass: 11394.426 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: HIST1H4A, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4B, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4C, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4D, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4E, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4F, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4H, H4/H, H4FH, HIST1H4I, H4/M, H4FM, HIST1H4J, H4/E, ...Gene: HIST1H4A, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4B, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4C, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4D, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4E, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4F, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4H, H4/H, H4FH, HIST1H4I, H4/M, H4FM, HIST1H4J, H4/E, H4FE, HIST1H4K, H4/D, H4FD, HIST1H4L, H4/K, H4FK, HIST2H4A, H4/N, H4F2, H4FN, HIST2H4, HIST2H4B, H4/O, H4FO, HIST4H4 Production host:  #7: Protein | Mass: 14165.551 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2AB, H2AFM, HIST1H2AE, H2AFA / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2AB, H2AFM, HIST1H2AE, H2AFA / Production host:  #8: Protein | Mass: 13935.239 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2BJ, H2BFR / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2BJ, H2BFR / Production host:  #9: Protein | | Mass: 38704.172 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INO80B, HMGA1L4, PAPA1, ZNHIT4 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INO80B, HMGA1L4, PAPA1, ZNHIT4 / Production host:  |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules XY
| #10: DNA chain | Mass: 70604.938 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #11: DNA chain | Mass: 70199.641 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 7 molecules 


| #12: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / #13: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has protein modification | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 80 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.10.1_2155: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 58145 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj















































