[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6bbm: Mechanisms of Opening and Closing of the Bacterial Replicative He... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6bbm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
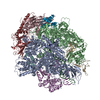
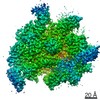
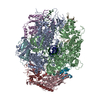
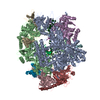
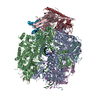
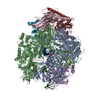
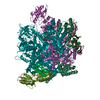
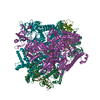
| Title | Mechanisms of Opening and Closing of the Bacterial Replicative Helicase: The DnaB Helicase and Lambda P Helicase Loader Complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | REPLICATION / Helicase Loader / Helicase / DNA replication / ATPase / DNA Replication Initiation / Bacteriophage Lambda | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationDnaB-DnaC complex / DnaB-DnaC-Rep-PriC complex / DnaB-DnaG complex / DnaB-DnaC-DnaT-PriA-PriC complex / DnaB-DnaC-DnaT-PriA-PriB complex / DNA helicase complex / primosome complex / DNA 5'-3' helicase / bidirectional double-stranded viral DNA replication / DNA replication, synthesis of primer ...DnaB-DnaC complex / DnaB-DnaC-Rep-PriC complex / DnaB-DnaG complex / DnaB-DnaC-DnaT-PriA-PriC complex / DnaB-DnaC-DnaT-PriA-PriB complex / DNA helicase complex / primosome complex / DNA 5'-3' helicase / bidirectional double-stranded viral DNA replication / DNA replication, synthesis of primer / replisome / response to ionizing radiation / replication fork processing / DNA replication initiation / DNA helicase activity / helicase activity / 5'-3' DNA helicase activity / DNA helicase / DNA replication / hydrolase activity / ATP hydrolysis activity / DNA binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Escherichia phage lambda (virus) Escherichia phage lambda (virus) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.1 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chase, J. / Catalano, A. / Noble, A.J. / Eng, E.T. / Olinares, P.D.B. / Molloy, K. / Pakotiprapha, D. / Samuels, M. / Chain, B. / des Georges, A. / Jeruzalmi, D. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 12items United States, 12items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2018 Journal: Elife / Year: 2018Title: Mechanisms of opening and closing of the bacterial replicative helicase. Authors: Jillian Chase / Andrew Catalano / Alex J Noble / Edward T Eng / Paul Db Olinares / Kelly Molloy / Danaya Pakotiprapha / Martin Samuels / Brian Chait / Amedee des Georges / David Jeruzalmi /   Abstract: Assembly of bacterial ring-shaped hexameric replicative helicases on single-stranded (ss) DNA requires specialized loading factors. However, mechanisms implemented by these factors during opening and ...Assembly of bacterial ring-shaped hexameric replicative helicases on single-stranded (ss) DNA requires specialized loading factors. However, mechanisms implemented by these factors during opening and closing of the helicase, which enable and restrict access to an internal chamber, are not known. Here, we investigate these mechanisms in the DnaB helicase•bacteriophage λ helicase loader (λP) complex. We show that five copies of λP bind at DnaB subunit interfaces and reconfigure the helicase into an open spiral conformation that is intermediate to previously observed closed ring and closed spiral forms; reconfiguration also produces openings large enough to admit ssDNA into the inner chamber. The helicase is also observed in a restrained inactive configuration that poises it to close on activating signal, and transition to the translocation state. Our findings provide insights into helicase opening, delivery to the origin and ssDNA entry, and closing in preparation for translocation. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6bbm.cif.gz 6bbm.cif.gz | 525.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6bbm.ent.gz pdb6bbm.ent.gz | 434.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6bbm.json.gz 6bbm.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  6bbm_validation.pdf.gz 6bbm_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  6bbm_full_validation.pdf.gz 6bbm_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  6bbm_validation.xml.gz 6bbm_validation.xml.gz | 87.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  6bbm_validation.cif.gz 6bbm_validation.cif.gz | 134.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bb/6bbm https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bb/6bbm ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bb/6bbm ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bb/6bbm | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7076MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 52450.945 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   References: UniProt: A0A365Q7M1, UniProt: P0ACB0*PLUS, DNA helicase #2: Protein | Mass: 23141.221 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Escherichia phage lambda (virus) / Plasmid: pET24a / Cell line (production host): BL21(DE3) / Production host: Escherichia phage lambda (virus) / Plasmid: pET24a / Cell line (production host): BL21(DE3) / Production host:  #3: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / Sequence details | The complete sequence of Bacteriophage Lambda P is ...The complete sequence of Bacteriophage Lambda P is MKNIAAQMVN | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 Details: Concentrated BP sample (18mg/mL) was diluted with freshly prepared buffer to desired concentration (~1.5 micromolar) for grid preparation. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.48 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: The sample was monodisperse. Side views were more electron weak than top or bottom views creating challenges for particle picking. This issue was overcome with cryo-electron tomography ...Details: The sample was monodisperse. Side views were more electron weak than top or bottom views creating challenges for particle picking. This issue was overcome with cryo-electron tomography techniques used for 1) initial model generation and 2) template generation for particle picking. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: The grid was coated with 50 nm of evaporated gold prior to use. All remaining carbon was removed by plasma cleaning for 5 minutes in a Gatan Solarus plasma cleaner. Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R0.6/1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K Details: 3uL of sample was adhered to a fresh plasma cleaned grid and allowed to adsorb for 30 seconds, blotted for 3 seconds with a blot force of 4 and plunge frozen into liquid nitrogen-cooled ethane. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS Details: Preliminary grid screening was performed prior to Krios data collections. All microscope alignments were completed by the New York Structural Biology SEMC team. |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 22500 X / Nominal defocus max: -3 nm / Nominal defocus min: -1 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 70 K / Temperature (min): 70 K |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 10 sec. / Electron dose: 8 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 3 / Num. of real images: 2426 Details: Single particle movies were recorded at a pixel size of 1.07 angstroms/pixel. Three 24-hour sessions produced 2,426 micrograph movies. In addition, five tilt series were collected from the ...Details: Single particle movies were recorded at a pixel size of 1.07 angstroms/pixel. Three 24-hour sessions produced 2,426 micrograph movies. In addition, five tilt series were collected from the same grids bi-directionally over a tilt range of -45 degrees to +45 degrees in 3 degree increments at a dose of 2.57 to 3.3 electrons per angstrom squared (total accumulated dose of 90 electrons per angstrom squared). Tilt series were collected at a pixel size of 1.76 angstroms and at defocus values of -2.8um, -6.1um and -9.3um. |
| EM imaging optics | Spherical aberration corrector: The Krios this data was collected on has a Cs of 2.7. |
| Image scans | Width: 3838 / Height: 3710 / Movie frames/image: 50 / Used frames/image: 1-50 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.14_3260: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj

