+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5yph | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | p62/SQSTM1 ZZ domain with Ile-peptide | ||||||
 Components Components | 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein,Sequestosome-1 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN / Complex / p62/SQSTM1 / ZZ domain / Autophagy / N-end rule | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of ATF6-mediated unfolded protein response / regulation of PERK-mediated unfolded protein response / regulation of protein folding in endoplasmic reticulum / cerebellum structural organization / brown fat cell proliferation / ATF6 (ATF6-alpha) activates chaperones / ATF6B (ATF6-beta) activates chaperones / protein localization to perinuclear region of cytoplasm / maintenance of protein localization in endoplasmic reticulum / protein targeting to vacuole involved in autophagy ...regulation of ATF6-mediated unfolded protein response / regulation of PERK-mediated unfolded protein response / regulation of protein folding in endoplasmic reticulum / cerebellum structural organization / brown fat cell proliferation / ATF6 (ATF6-alpha) activates chaperones / ATF6B (ATF6-beta) activates chaperones / protein localization to perinuclear region of cytoplasm / maintenance of protein localization in endoplasmic reticulum / protein targeting to vacuole involved in autophagy / regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / IRE1alpha activates chaperones / ATF6 (ATF6-alpha) activates chaperone genes / endoplasmic reticulum chaperone complex / aggrephagy / response to mitochondrial depolarisation / Lewy body / negative regulation of IRE1-mediated unfolded protein response / negative regulation of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway / regulation of IRE1-mediated unfolded protein response / amphisome / PERK regulates gene expression / protein folding in endoplasmic reticulum / regulation of protein complex stability / cerebellar Purkinje cell layer development / endosome organization / misfolded protein binding / autophagy of mitochondrion / pexophagy / membraneless organelle assembly / post-translational protein targeting to membrane, translocation / phagophore assembly site / ubiquitin-modified protein reader activity / regulation of mitochondrion organization / regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / Modulation of host responses by IFN-stimulated genes / Nuclear events mediated by NFE2L2 / aggresome / endosomal transport / intracellular membraneless organelle / K63-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / ER overload response / negative regulation of ferroptosis / cellular response to stress / temperature homeostasis / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment / negative regulation of PERK-mediated unfolded protein response / : / non-chaperonin molecular chaperone ATPase / autolysosome / molecular sequestering activity / Regulation of HSF1-mediated heat shock response / immune system process / protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity / negative regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response / cellular response to glucose starvation / mitophagy / energy homeostasis / heat shock protein binding / ERAD pathway / inclusion body / protein folding chaperone / ionotropic glutamate receptor binding / positive regulation of autophagy / signaling adaptor activity / negative regulation of protein ubiquitination / substantia nigra development / protein sequestering activity / cellular response to interleukin-4 / autophagosome / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / SH2 domain binding / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / Pexophagy / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / response to endoplasmic reticulum stress / protein kinase C binding / ubiquitin binding / positive regulation of protein ubiquitination / response to ischemia / sarcomere / positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / PINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / Antigen Presentation: Folding, assembly and peptide loading of class I MHC / macroautophagy / protein catabolic process / negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / P-body / ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone / molecular condensate scaffold activity / PML body / receptor tyrosine kinase binding / autophagy / Interleukin-1 signaling / protein import into nucleus / Signaling by ALK fusions and activated point mutants / melanosome / unfolded protein binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.629 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.629 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Kwon, D.H. / Kim, L. / Song, H.K. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2018 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2018Title: Insights into degradation mechanism of N-end rule substrates by p62/SQSTM1 autophagy adapter. Authors: Kwon, D.H. / Park, O.H. / Kim, L. / Jung, Y.O. / Park, Y. / Jeong, H. / Hyun, J. / Kim, Y.K. / Song, H.K. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5yph.cif.gz 5yph.cif.gz | 35.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5yph.ent.gz pdb5yph.ent.gz | 22.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5yph.json.gz 5yph.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yp/5yph https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yp/5yph ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yp/5yph ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yp/5yph | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5yp7SC  5yp8C  5ypaC  5ypbC  5ypcC  5ypeC  5ypfC  5ypgC S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 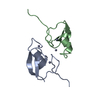
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 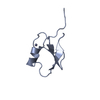
| ||||||||
| 2 | 
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 6469.278 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HSPA5, GRP78, SQSTM1, ORCA, OSIL / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HSPA5, GRP78, SQSTM1, ORCA, OSIL / Production host:  #2: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #3: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | Sequence details | Ile (-3 position) is synthetic residue generated by special enzyme | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density % sol: 16.77 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 293 K / Method: vapor diffusion / Details: sodium phosphate, potassium phosphate, MgCl2 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 293 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  Photon Factory Photon Factory  / Beamline: BL-17A / Wavelength: 1 Å / Beamline: BL-17A / Wavelength: 1 Å |
| Detector | Type: ADSC QUANTUM 270 / Detector: CCD / Date: Feb 17, 2016 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.629→17.91 Å / Num. obs: 9011 / % possible obs: 94 % / Redundancy: 3.3 % / Net I/σ(I): 34.7 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 5YP7 Resolution: 1.629→17.909 Å / SU ML: 0.14 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.37 / Phase error: 18
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 1.629→17.909 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj














