[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-5vho: Conformational Landscape of the p28-Bound Human Proteasome Regula... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5vho | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
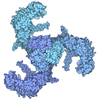
| Title | Conformational Landscape of the p28-Bound Human Proteasome Regulatory Particle | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / p28 / 26S proteasome / regulatory particle / 19S / gankyrin | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcytoplasmic sequestering of NF-kappaB / positive regulation of inclusion body assembly / proteasome regulatory particle assembly / thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor binding / modulation by host of viral transcription / proteasome accessory complex / proteasome regulatory particle / cytosolic proteasome complex / positive regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / proteasome-activating activity ...cytoplasmic sequestering of NF-kappaB / positive regulation of inclusion body assembly / proteasome regulatory particle assembly / thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor binding / modulation by host of viral transcription / proteasome accessory complex / proteasome regulatory particle / cytosolic proteasome complex / positive regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / proteasome-activating activity / proteasome regulatory particle, base subcomplex / negative regulation of programmed cell death / Regulation of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) / intermediate filament cytoskeleton / Cross-presentation of soluble exogenous antigens (endosomes) / Somitogenesis / negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity / negative regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria / transcription factor binding / regulation of protein catabolic process / proteasome storage granule / negative regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator / blastocyst development / positive regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / general transcription initiation factor binding / positive regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex assembly / negative regulation of MAPK cascade / enzyme regulator activity / SARS-CoV-1 targets host intracellular signalling and regulatory pathways / inclusion body / ERAD pathway / cytoskeletal protein binding / proteasome complex / Regulation of activated PAK-2p34 by proteasome mediated degradation / positive regulation of protein ubiquitination / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / protein localization to plasma membrane / Asymmetric localization of PCP proteins / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / NIK-->noncanonical NF-kB signaling / Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Cyclin D / AUF1 (hnRNP D0) binds and destabilizes mRNA / TNFR2 non-canonical NF-kB pathway / Vpu mediated degradation of CD4 / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Degradation of DVL / Ubiquitin Mediated Degradation of Phosphorylated Cdc25A / Cdc20:Phospho-APC/C mediated degradation of Cyclin A / Dectin-1 mediated noncanonical NF-kB signaling / Hh mutants are degraded by ERAD / Degradation of AXIN / Activation of NF-kappaB in B cells / Degradation of GLI1 by the proteasome / Hedgehog ligand biogenesis / Defective CFTR causes cystic fibrosis / G2/M Checkpoints / Negative regulation of NOTCH4 signaling / GSK3B and BTRC:CUL1-mediated-degradation of NFE2L2 / Autodegradation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 / Vif-mediated degradation of APOBEC3G / P-body / Regulation of RUNX3 expression and activity / Hedgehog 'on' state / Degradation of GLI2 by the proteasome / GLI3 is processed to GLI3R by the proteasome / FBXL7 down-regulates AURKA during mitotic entry and in early mitosis / MAPK6/MAPK4 signaling / APC/C:Cdh1 mediated degradation of Cdc20 and other APC/C:Cdh1 targeted proteins in late mitosis/early G1 / Degradation of beta-catenin by the destruction complex / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / Oxygen-dependent proline hydroxylation of Hypoxia-inducible Factor Alpha / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) signaling / SCF(Skp2)-mediated degradation of p27/p21 / Regulation of expression of SLITs and ROBOs / FCERI mediated NF-kB activation / Regulation of PTEN stability and activity / Interleukin-1 signaling / cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule / Orc1 removal from chromatin / osteoblast differentiation / Regulation of RAS by GAPs / Separation of Sister Chromatids / Regulation of RUNX2 expression and activity / The role of GTSE1 in G2/M progression after G2 checkpoint / UCH proteinases / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / Downstream TCR signaling / positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / Neddylation / protein-macromolecule adaptor activity / ER-Phagosome pathway / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / cytoplasmic vesicle / positive regulation of cell growth / secretory granule lumen Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 8.3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Lu, Y. / Wu, J. / Dong, Y. / Chen, S. / Sun, S. / Ma, Y.B. / Ouyang, Q. / Finley, D. / Kirschner, M.W. / Mao, Y. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2017 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2017Title: Conformational Landscape of the p28-Bound Human Proteasome Regulatory Particle. Authors: Ying Lu / Jiayi Wu / Yuanchen Dong / Shuobing Chen / Shuangwu Sun / Yong-Bei Ma / Qi Ouyang / Daniel Finley / Marc W Kirschner / Youdong Mao /   Abstract: The proteasome holoenzyme is activated by its regulatory particle (RP) consisting of two subcomplexes, the lid and the base. A key event in base assembly is the formation of a heterohexameric ring of ...The proteasome holoenzyme is activated by its regulatory particle (RP) consisting of two subcomplexes, the lid and the base. A key event in base assembly is the formation of a heterohexameric ring of AAA-ATPases, which is guided by at least four RP assembly chaperones in mammals: PAAF1, p28/gankyrin, p27/PSMD9, and S5b. Using cryogenic electron microscopy, we analyzed the non-AAA structure of the p28-bound human RP at 4.5 Å resolution and determined seven distinct conformations of the Rpn1-p28-AAA subcomplex within the p28-bound RP at subnanometer resolutions. Remarkably, the p28-bound AAA ring does not form a channel in the free RP and spontaneously samples multiple "open" and "closed" topologies at the Rpt2-Rpt6 and Rpt3-Rpt4 interfaces. Our analysis suggests that p28 assists the proteolytic core particle to select a specific conformation of the ATPase ring for RP engagement and is released in a shoehorn-like fashion in the last step of the chaperone-mediated proteasome assembly. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5vho.cif.gz 5vho.cif.gz | 527.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5vho.ent.gz pdb5vho.ent.gz | 409.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5vho.json.gz 5vho.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  5vho_validation.pdf.gz 5vho_validation.pdf.gz | 928 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  5vho_full_validation.pdf.gz 5vho_full_validation.pdf.gz | 956.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  5vho_validation.xml.gz 5vho_validation.xml.gz | 63.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  5vho_validation.cif.gz 5vho_validation.cif.gz | 94 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vh/5vho https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vh/5vho ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vh/5vho ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vh/5vho | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8680MC  8672C  8674C  8675C  8676C  8677C  8678C  8679C  8681C  8682C  8683C  8684C  5vgzC  5vhfC  5vhhC  5vhiC  5vhjC  5vhmC  5vhnC  5vhpC  5vhqC  5vhrC  5vhsC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10091 (Title: Conformational Landscape of the p28-Bound Human Proteasome Regulatory Particle EMPIAR-10091 (Title: Conformational Landscape of the p28-Bound Human Proteasome Regulatory ParticleData size: 70.0 Data #1: Classified single-particle datasets for multiple conformations of p28-bound human regulatory complex [picked particles - multiframe - processed]) |
| Experimental dataset #1 | Data reference:  10.6019/EMPIAR-10091 / Data set type: EMPIAR / Metadata reference: 10.6019/EMPIAR-10091 10.6019/EMPIAR-10091 / Data set type: EMPIAR / Metadata reference: 10.6019/EMPIAR-10091 |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit ... , 2 types, 2 molecules Gf
| #1: Protein | Mass: 24142.490 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PSMD10 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PSMD10 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O75832 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O75832 |
|---|---|
| #8: Protein | Mass: 93790.188 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PSMD2, TRAP2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PSMD2, TRAP2 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q13200 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q13200 |
-26S proteasome regulatory subunit ... , 6 types, 6 molecules ABDEFC
| #2: Protein | Mass: 29861.551 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PSMC2, MSS1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PSMC2, MSS1 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P35998 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P35998 |
|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 29958.395 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PSMC1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PSMC1 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P62191 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P62191 |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 29497.975 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PSMC4, MIP224, TBP7 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PSMC4, MIP224, TBP7 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P43686 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P43686 |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 29434.889 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PSMC6, SUG2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PSMC6, SUG2 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P62333 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P62333 |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 29773.246 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PSMC3, TBP1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PSMC3, TBP1 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P17980 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P17980 |
| #7: Protein | Mass: 29501.363 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PSMC5, SUG1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PSMC5, SUG1 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P62195 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P62195 |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Proteasome regulatory particle / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.11.1_2575: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 8.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 9004 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj