+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5a9q | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human nuclear pore complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnephron development / GATOR2 complex / Seh1-associated complex / nuclear pore inner ring / nuclear envelope organization / COPII-coated vesicle budding / protein exit from endoplasmic reticulum / transcription-dependent tethering of RNA polymerase II gene DNA at nuclear periphery / nuclear pore complex assembly / telomere tethering at nuclear periphery ...nephron development / GATOR2 complex / Seh1-associated complex / nuclear pore inner ring / nuclear envelope organization / COPII-coated vesicle budding / protein exit from endoplasmic reticulum / transcription-dependent tethering of RNA polymerase II gene DNA at nuclear periphery / nuclear pore complex assembly / telomere tethering at nuclear periphery / nuclear pore outer ring / protein localization to nuclear inner membrane / COPII-coated vesicle cargo loading / nuclear pore organization / somite development / atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / nuclear pore cytoplasmic filaments / COPII vesicle coat / paraxial mesoderm development / post-transcriptional tethering of RNA polymerase II gene DNA at nuclear periphery / Nuclear Pore Complex (NPC) Disassembly / nuclear inclusion body / Regulation of Glucokinase by Glucokinase Regulatory Protein / Defective TPR may confer susceptibility towards thyroid papillary carcinoma (TPC) / nuclear pore nuclear basket / Transport of Ribonucleoproteins into the Host Nucleus / miRNA processing / attachment of mitotic spindle microtubules to kinetochore / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / Transport of the SLBP independent Mature mRNA / Transport of the SLBP Dependant Mature mRNA / NS1 Mediated Effects on Host Pathways / SUMOylation of SUMOylation proteins / structural constituent of nuclear pore / positive regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome / Transport of Mature mRNA Derived from an Intronless Transcript / Rev-mediated nuclear export of HIV RNA / SUMOylation of RNA binding proteins / Nuclear import of Rev protein / NEP/NS2 Interacts with the Cellular Export Machinery / Transport of Mature mRNA derived from an Intron-Containing Transcript / RNA export from nucleus / tRNA processing in the nucleus / COPII-mediated vesicle transport / Postmitotic nuclear pore complex (NPC) reformation / neural tube development / protein-containing complex localization / lamellipodium assembly / nucleocytoplasmic transport / nuclear localization sequence binding / Viral Messenger RNA Synthesis / poly(A)+ mRNA export from nucleus / mitotic metaphase chromosome alignment / female gonad development / SUMOylation of ubiquitinylation proteins / Vpr-mediated nuclear import of PICs / macrophage chemotaxis / SUMOylation of DNA replication proteins / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Serine endopeptidases / Regulation of HSF1-mediated heat shock response / positive regulation of TOR signaling / mRNA transport / nuclear pore / mRNA export from nucleus / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins / negative regulation of TORC1 signaling / neurogenesis / cellular response to nutrient levels / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / positive regulation of TORC1 signaling / MHC class II antigen presentation / nuclear periphery / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / serine-type peptidase activity / cellular response to amino acid starvation / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / HCMV Late Events / Antigen Presentation: Folding, assembly and peptide loading of class I MHC / intracellular protein transport / chromosome segregation / promoter-specific chromatin binding / molecular condensate scaffold activity / ER to Golgi transport vesicle membrane / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / kinetochore / ISG15 antiviral mechanism / spindle / protein import into nucleus / HCMV Early Events / Separation of Sister Chromatids / nuclear envelope / actin cytoskeleton / protein transport / snRNP Assembly / nuclear membrane / transcription coactivator activity / nuclear speck Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  HOMO SAPIENS (human) HOMO SAPIENS (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / electron tomography / cryo EM / Resolution: 23 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | von Appen, A. / Kosinski, J. / Sparks, L. / Ori, A. / DiGuilio, A. / Vollmer, B. / Mackmull, M. / Banterle, N. / Parca, L. / Kastritis, P. ...von Appen, A. / Kosinski, J. / Sparks, L. / Ori, A. / DiGuilio, A. / Vollmer, B. / Mackmull, M. / Banterle, N. / Parca, L. / Kastritis, P. / Buczak, K. / Mosalaganti, S. / Hagen, W. / Andres-Pons, A. / Lemke, E.A. / Bork, P. / Antonin, W. / Glavy, J.S. / Bui, K.H. / Beck, M. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2015 Journal: Nature / Year: 2015Title: In situ structural analysis of the human nuclear pore complex. Authors: Alexander von Appen / Jan Kosinski / Lenore Sparks / Alessandro Ori / Amanda L DiGuilio / Benjamin Vollmer / Marie-Therese Mackmull / Niccolo Banterle / Luca Parca / Panagiotis Kastritis / ...Authors: Alexander von Appen / Jan Kosinski / Lenore Sparks / Alessandro Ori / Amanda L DiGuilio / Benjamin Vollmer / Marie-Therese Mackmull / Niccolo Banterle / Luca Parca / Panagiotis Kastritis / Katarzyna Buczak / Shyamal Mosalaganti / Wim Hagen / Amparo Andres-Pons / Edward A Lemke / Peer Bork / Wolfram Antonin / Joseph S Glavy / Khanh Huy Bui / Martin Beck /    Abstract: Nuclear pore complexes are fundamental components of all eukaryotic cells that mediate nucleocytoplasmic exchange. Determining their 110-megadalton structure imposes a formidable challenge and ...Nuclear pore complexes are fundamental components of all eukaryotic cells that mediate nucleocytoplasmic exchange. Determining their 110-megadalton structure imposes a formidable challenge and requires in situ structural biology approaches. Of approximately 30 nucleoporins (Nups), 15 are structured and form the Y and inner-ring complexes. These two major scaffolding modules assemble in multiple copies into an eight-fold rotationally symmetric structure that fuses the inner and outer nuclear membranes to form a central channel of ~60 nm in diameter. The scaffold is decorated with transport-channel Nups that often contain phenylalanine-repeat sequences and mediate the interaction with cargo complexes. Although the architectural arrangement of parts of the Y complex has been elucidated, it is unclear how exactly it oligomerizes in situ. Here we combine cryo-electron tomography with mass spectrometry, biochemical analysis, perturbation experiments and structural modelling to generate, to our knowledge, the most comprehensive architectural model of the human nuclear pore complex to date. Our data suggest previously unknown protein interfaces across Y complexes and to inner-ring complex members. We show that the transport-channel Nup358 (also known as Ranbp2) has a previously unanticipated role in Y-complex oligomerization. Our findings blur the established boundaries between scaffold and transport-channel Nups. We conclude that, similar to coated vesicles, several copies of the same structural building block--although compositionally identical--engage in different local sets of interactions and conformations. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5a9q.cif.gz 5a9q.cif.gz | 2.7 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5a9q.ent.gz pdb5a9q.ent.gz | 1.7 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5a9q.json.gz 5a9q.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a9/5a9q https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a9/5a9q ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a9/5a9q ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a9/5a9q | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3103MC 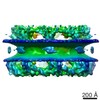 3104C  3105C  3106C  3107C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | x 8
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 4 types, 16 molecules 09IR2KTb6FOX7GPY
| #1: Protein | Mass: 42195.652 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: Q8NFH3 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: Q8NFH3#3: Protein | Mass: 36748.512 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: Q8NFH4 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: Q8NFH4#7: Protein | Mass: 35578.438 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: P55735 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: P55735#8: Protein | Mass: 39700.566 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: Q96EE3 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: Q96EE3 |
|---|
-NUCLEAR PORE COMPLEX PROTEIN ... , 6 types, 22 molecules 1JSa3CLU4DMV5ENW8HQZAB
| #2: Protein | Mass: 162280.203 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: Q12769 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: Q12769#4: Protein | Mass: 129108.461 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: Q8WUM0 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: Q8WUM0#5: Protein | Mass: 106504.969 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: P57740 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: P57740#6: Protein | Mass: 106039.656 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: P52948 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: P52948#9: Protein | Mass: 75105.266 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: Q9BW27 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: Q9BW27#10: Protein | Mass: 155357.281 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: O75694 HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: O75694 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: electron tomography |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: HUMAN NUCLEAR PORE COMPLEX / Type: ORGANELLE OR CELLULAR COMPONENT |
|---|---|
| Buffer solution | Name: 20MM TRIS, 0.2-0.4% TREHALOSE / pH: 7.5 / Details: 20MM TRIS, 0.2-0.4% TREHALOSE |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Details: CARBON |
| Vitrification | Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE Details: VITRIFICATION 1 -- CRYOGEN- ETHANE-PROPANE MIXTURE, INSTRUMENT- HOMEMADE PLUNGER, |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS / Date: Oct 17, 2014 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 42000 X / Calibrated magnification: 42000 X / Nominal defocus max: 4000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 2000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Tilt angle max: 60 ° / Tilt angle min: -45 ° |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 110 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: PHASE FLIPPING OF TILT SERIES | ||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C8 (8 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Method: SUBTOMOGRAM AVERAGING / Resolution: 23 Å Details: THIS PDB STRUCTURE INCLUDES UNAMBIGUOUS FITS ONLY. THE STRUCTURE WITH LESS CONFIDENT FITS CAN BE OBTAINED FROM AUTHORS. PROTEIN-PROTEIN INTERFACES SHALL NOT BE INTERPRETED AT RESIDUE-LEVEL ...Details: THIS PDB STRUCTURE INCLUDES UNAMBIGUOUS FITS ONLY. THE STRUCTURE WITH LESS CONFIDENT FITS CAN BE OBTAINED FROM AUTHORS. PROTEIN-PROTEIN INTERFACES SHALL NOT BE INTERPRETED AT RESIDUE-LEVEL RESOLUTION. SUBMISSION BASED ON EXPERIMENTAL DATA FROM EMDB EMD-3103. (DEPOSITION ID: 13616). Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 23 Å | ||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Highest resolution: 23 Å
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj