+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 4blr | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
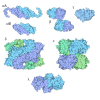
| Title | P4 PROTEIN FROM BACTERIOPHAGE PHI12 IN COMPLEX WITH UTP | ||||||
 Components Components | NTPASE P4 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / PACKAGING / CYSTOVIRIDAE | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||
| Biological species |  PSEUDOMONAS PHAGE PHI12 (virus) PSEUDOMONAS PHAGE PHI12 (virus) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.9 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.9 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | El Omari, K. / Meier, C. / Kainov, D. / Sutton, G. / Grimes, J.M. / Poranen, M.M. / Bamford, D.H. / Tuma, R. / Stuart, D.I. / Mancini, E.J. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2013 Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2013Title: Tracking in atomic detail the functional specializations in viral RecA helicases that occur during evolution. Authors: Kamel El Omari / Christoph Meier / Denis Kainov / Geoff Sutton / Jonathan M Grimes / Minna M Poranen / Dennis H Bamford / Roman Tuma / David I Stuart / Erika J Mancini /  Abstract: Many complex viruses package their genomes into empty protein shells and bacteriophages of the Cystoviridae family provide some of the simplest models for this. The cystoviral hexameric NTPase, P4, ...Many complex viruses package their genomes into empty protein shells and bacteriophages of the Cystoviridae family provide some of the simplest models for this. The cystoviral hexameric NTPase, P4, uses chemical energy to translocate single-stranded RNA genomic precursors into the procapsid. We previously dissected the mechanism of RNA translocation for one such phage, 12, and have now investigated three further highly divergent, cystoviral P4 NTPases (from 6, 8 and 13). High-resolution crystal structures of the set of P4s allow a structure-based phylogenetic analysis, which reveals that these proteins form a distinct subfamily of the RecA-type ATPases. Although the proteins share a common catalytic core, they have different specificities and control mechanisms, which we map onto divergent N- and C-terminal domains. Thus, the RNA loading and tight coupling of NTPase activity with RNA translocation in 8 P4 is due to a remarkable C-terminal structure, which wraps right around the outside of the molecule to insert into the central hole where RNA binds to coupled L1 and L2 loops, whereas in 12 P4, a C-terminal residue, serine 282, forms a specific hydrogen bond to the N7 of purines ring to confer purine specificity for the 12 enzyme. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  4blr.cif.gz 4blr.cif.gz | 355.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb4blr.ent.gz pdb4blr.ent.gz | 289.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  4blr.json.gz 4blr.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bl/4blr https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bl/4blr ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bl/4blr ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bl/4blr | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  4bloC 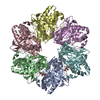 4blpC  4blqC  4blsC  4bltC  4bwyC  1w44S C: citing same article ( S: Starting model for refinement |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unit cell |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Components on special symmetry positions |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Noncrystallographic symmetry (NCS) | NCS domain:
NCS domain segments: Component-ID: _ / Beg auth comp-ID: MET / Beg label comp-ID: MET / End auth comp-ID: LEU / End label comp-ID: LEU / Refine code: _ / Auth seq-ID: 1 - 328 / Label seq-ID: 1 - 328
NCS ensembles :
|
- Components
Components
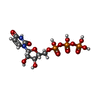
| #1: Protein | Mass: 35150.430 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  PSEUDOMONAS PHAGE PHI12 (virus) / Production host: PSEUDOMONAS PHAGE PHI12 (virus) / Production host:  #2: Chemical | #3: Chemical | ChemComp-DTT / | #4: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.6 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 53 % / Description: NONE |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | pH: 4.8 Details: 10% PEG 1500 IN 100 MM SODIUM ACETATE PH 4.8, AND 5MM AMCPP |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  SRS SRS  / Beamline: PX14.2 / Wavelength: 0.975 / Beamline: PX14.2 / Wavelength: 0.975 |
| Detector | Type: ADSC QUANTUM 4 / Detector: CCD |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.975 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.9→20 Å / Num. obs: 85262 / % possible obs: 100 % / Observed criterion σ(I): 4.9 / Redundancy: 7.2 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.07 / Net I/σ(I): 29.4 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 1.9→1.97 Å / Redundancy: 5.8 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.38 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 4.9 / % possible all: 99.8 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: PDB ENTRY 1W44 Resolution: 1.9→19.96 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.948 / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc free: 0.943 / SU B: 4.887 / SU ML: 0.077 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / ESU R: 0.143 / ESU R Free: 0.12 / Stereochemistry target values: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Details: HYDROGENS HAVE BEEN ADDED IN THE RIDING POSITIONS.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Ion probe radii: 0.8 Å / Shrinkage radii: 0.8 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.2 Å / Solvent model: MASK | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 26.097 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 1.9→19.96 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj