+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 3lue | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Model of alpha-actinin CH1 bound to F-actin | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / calponin homology domains / Acetylation / ATP-binding / Cytoplasm / Cytoskeleton / Methylation / Nucleotide-binding / Phosphoprotein / Actin-binding / Calcium / Polymorphism / Deafness / Disease mutation / Dystonia | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of glucose catabolic process to lactate via pyruvate / negative regulation of relaxation of muscle / skeletal muscle atrophy / regulation of the force of skeletal muscle contraction / positive regulation of skeletal muscle fiber development / positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue growth / response to denervation involved in regulation of muscle adaptation / positive regulation of fast-twitch skeletal muscle fiber contraction / positive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / positive regulation of bone mineralization involved in bone maturation ...positive regulation of glucose catabolic process to lactate via pyruvate / negative regulation of relaxation of muscle / skeletal muscle atrophy / regulation of the force of skeletal muscle contraction / positive regulation of skeletal muscle fiber development / positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue growth / response to denervation involved in regulation of muscle adaptation / positive regulation of fast-twitch skeletal muscle fiber contraction / positive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / positive regulation of bone mineralization involved in bone maturation / bBAF complex / cellular response to cytochalasin B / npBAF complex / nBAF complex / brahma complex / regulation of transepithelial transport / morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium / Formation of annular gap junctions / Formation of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC) / structural constituent of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / GBAF complex / Gap junction degradation / Folding of actin by CCT/TriC / focal adhesion assembly / regulation of G0 to G1 transition / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / protein localization to adherens junction / transition between fast and slow fiber / dense body / Tat protein binding / muscle cell development / negative regulation of oxidative phosphorylation / postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / Prefoldin mediated transfer of substrate to CCT/TriC / RSC-type complex / Striated Muscle Contraction / bone morphogenesis / regulation of double-strand break repair / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / negative regulation of glycolytic process / Adherens junctions interactions / Nephrin family interactions / RHOF GTPase cycle / adherens junction assembly / negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / apical protein localization / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / negative regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade / tight junction / SWI/SNF complex / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / structural constituent of muscle / regulation of aerobic respiration / positive regulation of T cell differentiation / apical junction complex / cortical actin cytoskeleton / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / nitric-oxide synthase binding / transporter regulator activity / cortical cytoskeleton / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / pseudopodium / Recycling pathway of L1 / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in pigmentation / brush border / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells / negative regulation of cell differentiation / kinesin binding / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / positive regulation of myoblast differentiation / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / cytoskeleton organization / substantia nigra development / axonogenesis / calyx of Held / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / adherens junction / FCGR3A-mediated phagocytosis / actin filament / cell projection / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / positive regulation of cell differentiation / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / cell motility / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / Signaling by high-kinase activity BRAF mutants / MAP2K and MAPK activation / Regulation of actin dynamics for phagocytic cup formation / kinetochore Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 15 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Galkin, V.E. / Orlova, A. / Salmazo, A. / Djinovic-Carugo, K. / Egelman, E.H. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2010 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2010Title: Opening of tandem calponin homology domains regulates their affinity for F-actin. Authors: Vitold E Galkin / Albina Orlova / Anita Salmazo / Kristina Djinovic-Carugo / Edward H Egelman /  Abstract: Many actin-binding proteins contain calponin homology (CH) domains, but the manner in which these domains interact with F-actin has been controversial. Crystal structures have shown the tandem CH ...Many actin-binding proteins contain calponin homology (CH) domains, but the manner in which these domains interact with F-actin has been controversial. Crystal structures have shown the tandem CH domains of alpha-actinin to be in a compact, closed conformation, but the interpretations of complexes of such tandem CH domains with F-actin have been ambiguous. We show that the tandem CH domains of alpha-actinin bind F-actin in an open conformation, explaining mutations that cause human diseases and suggesting that the opening of these domains may be one of the main regulatory mechanisms for proteins with tandem CH domains. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  3lue.cif.gz 3lue.cif.gz | 824.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb3lue.ent.gz pdb3lue.ent.gz | 640.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  3lue.json.gz 3lue.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lu/3lue https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lu/3lue ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lu/3lue ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lu/3lue | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 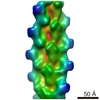 5170MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
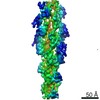
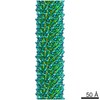
| Details | Authors state that the model is from a continuous helix where the rotation per subunit is -167.2 degrees and the rise per subunit is 26.6 Angstroms. |
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 41651.465 Da / Num. of mol.: 10 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ACTB / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ACTB / Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 12471.712 Da / Num. of mol.: 10 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ACTN3 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ACTN3 / Production host:  |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F20 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 50000 X / Camera length: 0 mm |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN / Specimen holder type: gatan 626 / Tilt angle max: 0 ° / Tilt angle min: 0 ° |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM |
| Image scans | Sampling size: 12.7 µm / Scanner model: NIKON COOLSCAN |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: Weiner filter | ||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: 166.8 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 27.7 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | ||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Method: back projection / Resolution: 15 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Nominal pixel size: 2.38 Å / Actual pixel size: 2.38 Å Details: AUTHORS STATE THAT THE STRANGE C-N BONDS WERE THE RESULT OF BREAKING THE CHAINS AT THESE POINTS TO DO RIGID BODY FITTING OF THE SUBDOMAINS. Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL Details: METHOD--both manually and with Chimera DETAILS--AUTHORS STATE THAT THE STRANGE C-N BONDS WERE THE RESULT OF BREAKING THE CHAINS AT THESE POINTS TO DO RIGID BODY FITTING OF THE SUBDOMAINS. | ||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj

















