[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-1z1d: Structural Model for the interaction between RPA32 C-terminal dom... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 1z1d | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
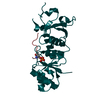
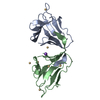
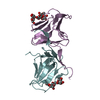
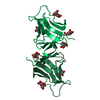
| Title | Structural Model for the interaction between RPA32 C-terminal domain and SV40 T antigen origin binding domain. | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | REPLICATION / Winged Helix-turn-Helix motif / Origin binding domain / Protein-Protein Complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationprotein localization to chromosome / DNA replication factor A complex / symbiont-mediated suppression of host JAK-STAT cascade via inhibition of JAK1 activity / Removal of the Flap Intermediate / regulation of DNA damage checkpoint / G-rich strand telomeric DNA binding / Mismatch repair (MMR) directed by MSH2:MSH3 (MutSbeta) / Mismatch repair (MMR) directed by MSH2:MSH6 (MutSalpha) / bidirectional double-stranded viral DNA replication / viral DNA genome replication ...protein localization to chromosome / DNA replication factor A complex / symbiont-mediated suppression of host JAK-STAT cascade via inhibition of JAK1 activity / Removal of the Flap Intermediate / regulation of DNA damage checkpoint / G-rich strand telomeric DNA binding / Mismatch repair (MMR) directed by MSH2:MSH3 (MutSbeta) / Mismatch repair (MMR) directed by MSH2:MSH6 (MutSalpha) / bidirectional double-stranded viral DNA replication / viral DNA genome replication / Removal of the Flap Intermediate from the C-strand / DNA 3'-5' helicase / HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) / regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / Impaired BRCA2 binding to RAD51 / telomeric DNA binding / symbiont-mediated perturbation of host cell cycle G1/S transition checkpoint / DNA replication origin binding / Presynaptic phase of homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange / PCNA-Dependent Long Patch Base Excision Repair / Activation of the pre-replicative complex / Regulation of HSF1-mediated heat shock response / HSF1 activation / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / mismatch repair / mitotic G1 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / telomere maintenance / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / Translesion synthesis by POLK / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / nucleotide-excision repair / Fanconi Anemia Pathway / Termination of translesion DNA synthesis / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / Translesion Synthesis by POLH / helicase activity / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / base-excision repair / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / PML body / HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) / Meiotic recombination / Dual Incision in GG-NER / Formation of Incision Complex in GG-NER / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / single-stranded DNA binding / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / double-stranded DNA binding / protein phosphatase binding / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Phosphorylation / symbiont-mediated perturbation of host ubiquitin-like protein modification / damaged DNA binding / DNA replication / chromosome, telomeric region / nuclear body / symbiont-mediated suppression of host innate immune response / symbiont-mediated suppression of host type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / chromatin / host cell nucleus / enzyme binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / identical protein binding / nucleus Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) Simian virus 40 Simian virus 40 | ||||||
| Method | SOLUTION NMR / Rigid body docking, Semi-flexible simulated annealing, Refinement using explicit water | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Arunkumar, A.I. / Klimovich, V. / Jiang, X. / Ott, R.D. / Mizoue, L. / Fanning, E. / Chazin, W.J. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol. / Year: 2005 Journal: Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol. / Year: 2005Title: Insights into hRPA32 C-terminal domain--mediated assembly of the simian virus 40 replisome. Authors: Arunkumar, A.I. / Klimovich, V. / Jiang, X. / Ott, R.D. / Mizoue, L. / Fanning, E. / Chazin, W.J. #1:  Journal: Cell(Cambridge,Mass.) / Year: 2000 Journal: Cell(Cambridge,Mass.) / Year: 2000Title: Structural basis for the recognition of DNA repair proteins UNG2, XPA, and RAD52 by replication factor A Authors: Mer, G. / Bochkarev, A. / Gupta, R. / Bochkareva, E. / Frappier, L. / Ingles, C.M. / Edwards, A.M. / Chazin, W.J. #2:  Journal: Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol. / Year: 1996 Journal: Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol. / Year: 1996Title: Solution structure of the origin DNA binding domain of SV40 T antigen Authors: Luo, X. / Sanford, D.G. / Bullock, P.A. / Bachovchin, W.W. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  1z1d.cif.gz 1z1d.cif.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb1z1d.ent.gz pdb1z1d.ent.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  1z1d.json.gz 1z1d.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z1/1z1d https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z1/1z1d ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z1/1z1d ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z1/1z1d | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| Other databases |
|
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 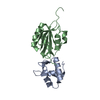
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| |||||||||
| NMR ensembles |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 10999.127 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: RPA32 C-terminal domain Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RPA2, REPA2, RPA32 / Species (production host): Escherichia coli / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RPA2, REPA2, RPA32 / Species (production host): Escherichia coli / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 15111.362 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: SV40 T antigen Origin binding domain Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Simian virus 40 / Genus: Polyomavirus / Species (production host): Escherichia coli / Production host: Simian virus 40 / Genus: Polyomavirus / Species (production host): Escherichia coli / Production host:  |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: SOLUTION NMR | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMR experiment |
| ||||||||||||
| NMR details | Text: This model structure was obtained using ambigous chemical shift pertubation constraints and validated using residual dipolar couplings and point mutations on the interface |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Details |
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample conditions | Ionic strength: 0.03 M / pH: 7 / Pressure: ambient / Temperature: 298 K |
-NMR measurement
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M |
|---|---|
| Radiation wavelength | Relative weight: 1 |
| NMR spectrometer | Type: Bruker AVANCE / Manufacturer: Bruker / Model: AVANCE / Field strength: 600 MHz |
- Processing
Processing
| NMR software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method: Rigid body docking, Semi-flexible simulated annealing, Refinement using explicit water Software ordinal: 1 Details: 1500 conformers were obtained in the rigid body docking and 200 best conformers were selected for semi-flexible simulated annealing followed by refinement. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| NMR representative | Selection criteria: lowest energy | ||||||||||||||||||||
| NMR ensemble | Conformer selection criteria: structures with acceptable covalent geometry,structures with favorable non-bond energy Conformers calculated total number: 200 / Conformers submitted total number: 20 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj











 HSQC
HSQC