+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-8396 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
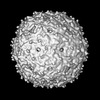
| Title | Asymmetric reconstruction of bacteriophage MS2 mutant NEO1 | |||||||||
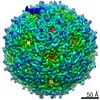
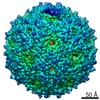
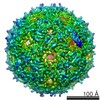
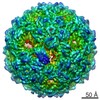
 Map data Map data | Cryo-EM reconstruction of mutant NE01 of bacteriophage MS2 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Biological species |  Enterobacterio phage MS2 (virus) Enterobacterio phage MS2 (virus) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 9.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Guerrero-Ferreira RC / Nazarov SY / Zhong Q / Kohn T / Leiman PG | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Environ Sci Technol / Year: 2016 Journal: Environ Sci Technol / Year: 2016Title: Genetic, Structural, and Phenotypic Properties of MS2 Coliphage with Resistance to ClO Disinfection. Authors: Qingxia Zhong / Anna Carratalà / Sergey Nazarov / Ricardo Cesar Guerrero-Ferreira / Laura Piccinini / Virginie Bachmann / Petr G Leiman / Tamar Kohn /  Abstract: Common water disinfectants like chlorine have been reported to select for resistant viruses, yet little attention has been devoted to characterizing disinfection resistance. Here, we investigated the ...Common water disinfectants like chlorine have been reported to select for resistant viruses, yet little attention has been devoted to characterizing disinfection resistance. Here, we investigated the resistance of MS2 coliphage to inactivation by chlorine dioxide (ClO). ClO inactivates MS2 by degrading its structural proteins, thereby disrupting the ability of MS2 to attach to and infect its host. ClO-resistant virus populations emerged not only after repeated cycles of ClO disinfection followed by regrowth but also after dilution-regrowth cycles in the absence of ClO. The resistant populations exhibited several fixed mutations which caused the substitution of ClO-labile by ClO-stable amino acids. On a phenotypic level, these mutations resulted in a more stable host binding during inactivation compared to the wild-type, thus resulting in a greater ability to maintain infectivity. This conclusion was supported by cryo-electron microscopy reconstruction of the virus particle, which demonstrated that most structural modification occurred in the putative A protein, an important binding factor. Resistance was specific to the inactivation mechanism of ClO and did not result in significant cross-resistance to genome-damaging disinfectants. Overall, our data indicate that resistant viruses may emerge even in the absence of ClO pressure but that they can be inactivated by other common disinfectants. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_8396.map.gz emd_8396.map.gz | 57.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-8396-v30.xml emd-8396-v30.xml emd-8396.xml emd-8396.xml | 10.9 KB 10.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_8396.png emd_8396.png | 86 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8396 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8396 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8396 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8396 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_8396.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_8396.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM reconstruction of mutant NE01 of bacteriophage MS2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.37 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Enterobacterio phage MS2
| Entire | Name:  Enterobacterio phage MS2 (virus) Enterobacterio phage MS2 (virus) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Enterobacterio phage MS2
| Supramolecule | Name: Enterobacterio phage MS2 / type: virus / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 Details: Wildtype MS2 populations were subjected to repeated propagation without ClO2 exposure. NE01 (non-exposed control 1) is the first of the five resulting populations. NCBI-ID: 12022 / Sci species name: Enterobacterio phage MS2 / Sci species strain: MS2-NE01 / Virus type: VIRION / Virus isolate: STRAIN / Virus enveloped: No / Virus empty: No |
|---|---|
| Host (natural) | Organism:  |
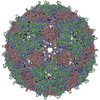
| Virus shell | Shell ID: 1 / T number (triangulation number): 3 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Details: Phosphate buffered saline: 5 mM Na2HPO4, 10 mM NaCl, pH 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY ARRAY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
| Details | Stock solution concentration: 10E12 pfu/ml. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI EAGLE (4k x 4k) / Number real images: 717 / Average exposure time: 1.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 25.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: GATAN 626 SINGLE TILT LIQUID NITROGEN CRYO TRANSFER HOLDER Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)