[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-8342: Structural basis for gating and activation of RyR1 (30 uM Ca2+ da... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-8342 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
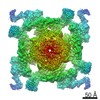
| Title | Structural basis for gating and activation of RyR1 (30 uM Ca2+ dataset, all particles) | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | RyR1-Cs2 complex | |||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RyR / Ca2+ / EC coupling / gating / TRANSPORT PROTEIN-ISOMERASE complex | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationATP-gated ion channel activity / : / negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / neuronal action potential propagation / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / terminal cisterna / ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / ryanodine receptor complex ...ATP-gated ion channel activity / : / negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / neuronal action potential propagation / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / terminal cisterna / ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / ryanodine receptor complex / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / response to redox state / ossification involved in bone maturation / negative regulation of heart rate / cellular response to caffeine / 'de novo' protein folding / skin development / FK506 binding / organelle membrane / intracellularly gated calcium channel activity / smooth endoplasmic reticulum / outflow tract morphogenesis / smooth muscle contraction / toxic substance binding / T cell proliferation / striated muscle contraction / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / calcium channel inhibitor activity / skeletal muscle fiber development / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / Ion homeostasis / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / calcium channel complex / sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane / cellular response to calcium ion / muscle contraction / sarcoplasmic reticulum / protein maturation / peptidylprolyl isomerase / calcium channel regulator activity / peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity / calcium-mediated signaling / sarcolemma / calcium ion transmembrane transport / Stimuli-sensing channels / calcium channel activity / Z disc / intracellular calcium ion homeostasis / disordered domain specific binding / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / protein refolding / protein homotetramerization / transmembrane transporter binding / calmodulin binding / signaling receptor binding / calcium ion binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding / membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Clarke OB / des Georges A | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4 items United States, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2016 Journal: Cell / Year: 2016Title: Structural Basis for Gating and Activation of RyR1. Authors: Amédée des Georges / Oliver B Clarke / Ran Zalk / Qi Yuan / Kendall J Condon / Robert A Grassucci / Wayne A Hendrickson / Andrew R Marks / Joachim Frank /  Abstract: The type-1 ryanodine receptor (RyR1) is an intracellular calcium (Ca(2+)) release channel required for skeletal muscle contraction. Here, we present cryo-EM reconstructions of RyR1 in multiple ...The type-1 ryanodine receptor (RyR1) is an intracellular calcium (Ca(2+)) release channel required for skeletal muscle contraction. Here, we present cryo-EM reconstructions of RyR1 in multiple functional states revealing the structural basis of channel gating and ligand-dependent activation. Binding sites for the channel activators Ca(2+), ATP, and caffeine were identified at interdomain interfaces of the C-terminal domain. Either ATP or Ca(2+) alone induces conformational changes in the cytoplasmic assembly ("priming"), without pore dilation. In contrast, in the presence of all three activating ligands, high-resolution reconstructions of open and closed states of RyR1 were obtained from the same sample, enabling analyses of conformational changes associated with gating. Gating involves global conformational changes in the cytosolic assembly accompanied by local changes in the transmembrane domain, which include bending of the S6 transmembrane segment and consequent pore dilation, displacement, and deformation of the S4-S5 linker and conformational changes in the pseudo-voltage-sensor domain. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_8342.map.gz emd_8342.map.gz | 228.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-8342-v30.xml emd-8342-v30.xml emd-8342.xml emd-8342.xml | 31.2 KB 31.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_8342_fsc.xml emd_8342_fsc.xml | 13.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_8342.png emd_8342.png | 102.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-8342.cif.gz emd-8342.cif.gz | 8.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_8342_half_map_1.map.gz emd_8342_half_map_1.map.gz emd_8342_half_map_2.map.gz emd_8342_half_map_2.map.gz | 188.2 MB 188.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8342 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8342 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8342 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8342 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5t15MC  8372C  8373C  8374C  8375C  8376C  8377C  8378C  8379C  8380C  8381C  8382C  8383C  8384C  8385C  8386C  8387C  8388C  8389C  8390C  8391C  8392C  8393C  8394C 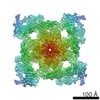 8395C  5t9mC  5t9nC  5t9rC  5t9sC  5t9vC  5ta3C  5talC  5tamC  5tanC  5tapC  5taqC  5tasC  5tatC  5tauC  5tavC  5tawC  5taxC  5tayC  5tazC  5tb0C  5tb1C  5tb2C  5tb3C  5tb4C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_8342.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_8342.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | RyR1-Cs2 complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.255 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
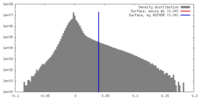
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Half map: RyR1-Cs2 complex, half map 1
| File | emd_8342_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | RyR1-Cs2 complex, half map 1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: RyR1-Cs2 complex, half map 2
| File | emd_8342_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | RyR1-Cs2 complex, half map 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : RyR1-Cs2 complex
| Entire | Name: RyR1-Cs2 complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: RyR1-Cs2 complex
| Supramolecule | Name: RyR1-Cs2 complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B
| Macromolecule | Name: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: peptidylprolyl isomerase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.798501 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGVEIETISP GDGRTFPKKG QTCVVHYTGM LQNGKKFDSS RDRNKPFKFR IGKQEVIKGF EEGAAQMSLG QRAKLTCTPD VAYGATGHP GVIPPNATLI FDVELLNLE UniProtKB: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B |
-Macromolecule #2: Ryanodine receptor 1,Ryanodine receptor 1,Ryanodine receptor 1,Ry...
| Macromolecule | Name: Ryanodine receptor 1,Ryanodine receptor 1,Ryanodine receptor 1,Ryanodine receptor 1,Ryanodine receptor 1,Ryanodine receptor 1,Ryanodine receptor 1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 501.17075 KDa |
| Sequence | String: QFLRTDDEVV LQCSATVLKE QLKLCLAAEG FGNRLCFLEP TSNAQNVPPD LAICCFTLEQ SLSVRALQEM LANTVEAGVE SSQGGGHRT LLYGHAILLR HAHSRMYLSC LTTSRSMTDK LAFDVGLQED ATGEACWWTM HPASKQRSEG EKVRVGDDLI L VSVSSERY ...String: QFLRTDDEVV LQCSATVLKE QLKLCLAAEG FGNRLCFLEP TSNAQNVPPD LAICCFTLEQ SLSVRALQEM LANTVEAGVE SSQGGGHRT LLYGHAILLR HAHSRMYLSC LTTSRSMTDK LAFDVGLQED ATGEACWWTM HPASKQRSEG EKVRVGDDLI L VSVSSERY LHLSTASGEL QVDASFMQTL WNMNPICSCC EEGYVTGGHV LRLFHGHMDE CLTISAADSD DQRRLVYYEG GA VCTHARS LWRLEPLRIS WSGSHLRWGQ PLRIRHVTTG RYLALTEDQG LVVVDACKAH TKATSFCFRV SKEKLDTAPK RDV EGMGPP EIKYGESLCF VQHVASGLWL TYAAPDPKAL RLGVLKKKAI LHQEGHMDDA LFLTRCQQEE SQAARMIHST AGLY NQFIK GLDSFSGKPR GSGPPAGPAL PIEAVILSLQ DLIGYFEPPS EELQHEEKQS KLRSLRNRQS LFQEEGMLSL VLNCI DRLN VYTTAAHFAE YAGEEAAESW KEIVNLLYEL LASLIRGNRA NCALFSTNLD WVVSKLDRLE ASSGILEVLY CVLIES PEV LNIIQENHIK SIISLLDKHG RNHKVLDVLC SLCVCNGVAV RSNQDLITEN LLPGRELLLQ TNLINYVTSI RPNIFVG RA EGSTQYGKWY FEVMVDEVVP FLTAQATHLR VGWALTEGYS PYPGGGEGWG GNGVGDDLYS YGFDGLHLWT GHVARPVT S PGQHLLAPED VVSCCLDLSV PSISFRINGC PVQGVFEAFN LDGLFFPVVS FSAGVKVRFL LGGRHGEFKF LPPPGYAPC HEAVLPRERL RLEPIKEYRR EGPRGPHLVG PSRCLSHTDF VPCPVDTVQI VLPPHLERIR EKLAENIHEL WALTRIEQGW TYGPVRDDN KRLHPCLVNF HSLPEPERNY NLQMSGETLK TLLALGCHVG MADEKAEDNL KKTKLPKTYM MSNGYKPAPL D LSHVRLTP AQTTLVDRLA ENGHNVWARD RVAQGWSYSA VQDIPARRNP RLVPYRLLDE ATKRSNRDSL CQAVRTLLGY GY NIEPPDQ EPSQVENQSR WDRVRIFRAE KSYTVQSGRW YFEFEAVTTG EMRVGWARPE LRPDVELGAD ELAYVFNGHR GQR WHLGSE PFGRPWQSGD VVGCMIDLTE NTIIFTLNGE VLMSDSGSET AFREIEIGDG FLPVCSLGPG QVGHLNLGQD VSSL RFFAI CGLQEGFEPF AINMQRPVTT WFSKSLPQFE PVPPEHPHYE VARMDGTVDT PPCLRLAHR(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)MPLS AAMFLSERKN PAPQCPPRLE VQMLMP VSW SRMPNHFLQV ETRRAGERLG WAVQCQDPLT MMALHIPEEN RCMDILELSE RLDLQRFHSH TLRLYRAVCA LGNNRVA HA LCSHVDQAQL LHALEDAHLP GPLRAGYYDL LISIHLESAC RSRRSMLSEY IVPLTPETRA ITLFPPGRKG GNARRHGL P GVGVTTSLRP PHHFSPPCFV AALPAAGVAE APARLSPAIP LEALRDKALR MLGEAVRDGG QHARDPVGGS VEFQFVPVL KLVSTLLVMG IFGDEDVKQI LKMIEPEVFT EEEEEEEEEE EEEEEEEEDE EEKEEDEEEE EKEDAEKEEE EAPEGEKEDL EEGLLQMKL PESVKLQMCN LLEYFCDQEL QHRVESLAAF AERYVDKLQA NQRSRYALLM RAFTMSAAET ARRTREFRSP P QEQINMLL HFKDEADEED CPLPEDIRQD LQDFHQDLLA HCGIQLEGEE EEPEEETSLS SRLRSLLETV RLVKKKEEKP EE ELPAEEK KPQSLQELVS HMVVRWAQED YVQSPELVRA MFSLLHRQYD GLGELLRALP RAYTISPSSV EDTMSLLECL GQI RSLLIV QMGPQEENLM IQSIGNIMNN KVFYQHPNLM RALGMHETVM EVMVNVLGGG ETKEIRFPKM VTSCCRFLCY FCRI SRQNQ RSMFDHLSYL LENSGIGLGM QGSTPLDVAA ASVIDNNELA LALQEQDLEK VVSYLAGCGL QSCPMLLAKG YPDIG WNPC GGERYLDFLR FAVFVNGESV EENANVVVRL LIRKPECFGP ALRGEGGSGL LAAIEEAIRI SEDPARDGPG VRRDRR REH FGEEPPEENR VHLGHAIMSF YAALIDLLGR CAPEMHLIQA GKGEALRIRA ILRSLVPLDD LVGIISLPLQ IPTL (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)NFDPR PVETLNVIIP EKLDSFINKF AEYTHEKWAF DKIQNNWSY GENVDEELKT HPMLRPYKTF SEKDKEIYRW PIKESLKAMI AWEWTIEKAR EGEEERTEKK KTRKISQTAQ T YDPREGYN PQPPDLSGVT LSRELQAMAE QLAENYHNTW GRKKKQELEA KGGGTHPLLV PYDTLTAKEK ARDREKAQEL LK FLQMNGY AVTR(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)TPLYNLP THRACNMFLE SYKAAWILTE DHSFEDRMID DLSKAGEQEE EEEEVEEKKP DPLHQLVLHF SRTALTEK S KLDEDYLYMA YADIMAKSCH LEEGGENGEA EEEEVEVSFE EKEMEKQRLL YQQSRLHTRG AAEMVLQMIS ACKGETGAM VSSTLKLGIS ILNGGNAEVQ QKMLDYLKDK KEVGFFQSIQ ALMQTCSVLD LNAFERQNKA EGLGMVNEDG TVINRQNGEK VMADDEFTQ DLFRFLQLLC EGHNNDFQNY LRTQTGNTTT INIIICTVDY LLRLQESISD FYWYYSGKDV IEEQGKRNFS K AMSVAKQV FNSLTEYIQG PCTGNQQSLA HSRLWDAVVG FLHVFAHMMM KLAQDSSQIE LLKELLDLQK DMVVMLLSLL EG NVVNGMI ARQMVDMLVE SSSNVEMILK FFDMFLKLKD IVGSEAFQDY VTDPRGLISK KDFQKAMDSQ KQFTGPEIQF LLS CSEADE NEMINFEEFA NRFQEPARDI GFNVAVLLTN LSEHVPHDPR LRNFLELAES ILEYFRPYLG RIEIMGASRR IERI YFEIS ETNRAQWEMP QVKESKRQFI FDVVNEGGEA EKMELFVSFC EDTIFEMQIA AQISEPEGEP EADEDEGMGE AAAEG AEEG AAGAEGAAGT VAAGATARLA AAAARALRGL SYRSLRRRVR RLRRLTAREA ATALAALLWA VVARAGAAGA GAAAGA LRL LWGSLFGGGL VEGAKKVTVT ELLAGMPDPT SDEVHGEQPA GPGGDADGAG EGEGEGDAAE GDGDEEVAGH EAGPGGA EG VVAVADGGPF RPEGAGGLGD MGDTTPAEPP TPEGSPILKR KLGVDGEEEE LVPEPEPEPE PEPEKADEEN GEKEEVPE A PPEPPKKAPP SPPAKKEEAG GAGMEFWGEL EVQRVKFLNY LSRNFYTLRF LALFLAFAIN FILLFYKVSD SPPGEDDME GSAAGDLAGA GSGGGSGWGS GAGEEAEGDE DENMVYYFLE ESTGYMEPAL WCLSLLHTLV AFLCIIGYNC LKVPLVIFKR EKELARKLE FDGLYITEQP GDDDVKGQWD RLVLNTPSFP SNYWDKFVKR KVLDKHGDIF GRERIAELLG MDLASLEITA H NERKPDPP PGLLTWLMSI DVKYQIWKFG VIFTDNSFLY LGWYMVMSLL GHYNNFFFAA HLLDIAMGVK TLRTILSSVT HN GKQLVMT VGLLAVVVYL YTVVAFNFFR KFYNKSEDED EPDMKCDDMM TCYLFHMYVG VRAGGGIGDE IEDPAGDEYE LYR VVFDIT FFFFVIVILL AIIQGLIIDA FGELRDQQEQ VKEDMETKCF ICGIGSDYFD TTPHGFETHT LEEHNLANYM FFLM YLINK DETEHTGQES YVWKMYQERC WDFFPAGDCF RKQYEDQLS UniProtKB: Ryanodine receptor 1, Ryanodine receptor 1, Ryanodine receptor 1, Ryanodine receptor 1 |
-Macromolecule #3: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 6.0 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 400 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV Details: Blotted for 3-4 seconds on both sides with Whatman ashless filter paper, blot force 3, wait time 30 seconds. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI POLARA 300 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)