+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-8291 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | EM map of the Elp123 subcomplex of yeast Elongator | |||||||||
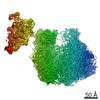
 Map data Map data | Elp123 subcomplex of yeast Elongator | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / negative staining / Resolution: 24.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Setiaputra D / Cheng DTH / Hansen JM / Yip CK | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO Rep / Year: 2017 Journal: EMBO Rep / Year: 2017Title: Molecular architecture of the yeast Elongator complex reveals an unexpected asymmetric subunit arrangement. Authors: Dheva T Setiaputra / Derrick Th Cheng / Shan Lu / Jesse M Hansen / Udit Dalwadi / Cindy Hy Lam / Jeffrey L To / Meng-Qiu Dong / Calvin K Yip /   Abstract: Elongator is a ~850 kDa protein complex involved in multiple processes from transcription to tRNA modification. Conserved from yeast to humans, Elongator is assembled from two copies of six unique ...Elongator is a ~850 kDa protein complex involved in multiple processes from transcription to tRNA modification. Conserved from yeast to humans, Elongator is assembled from two copies of six unique subunits (Elp1 to Elp6). Despite the wealth of structural data on the individual subunits, the overall architecture and subunit organization of the full Elongator and the molecular mechanisms of how it exerts its multiple activities remain unclear. Using single-particle electron microscopy (EM), we revealed that yeast Elongator adopts a bilobal architecture and an unexpected asymmetric subunit arrangement resulting from the hexameric Elp456 subassembly anchored to one of the two Elp123 lobes that form the structural scaffold. By integrating the EM data with available subunit crystal structures and restraints generated from cross-linking coupled to mass spectrometry, we constructed a multiscale molecular model that showed the two Elp3, the main catalytic subunit, are located in two distinct environments. This work provides the first structural insights into Elongator and a framework to understand the molecular basis of its multifunctionality. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_8291.map.gz emd_8291.map.gz | 350.1 KB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-8291-v30.xml emd-8291-v30.xml emd-8291.xml emd-8291.xml | 14.9 KB 14.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_8291_fsc.xml emd_8291_fsc.xml | 3.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_8291.png emd_8291.png | 36.3 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8291 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8291 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8291 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8291 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_8291.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 3.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_8291.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 3.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Elp123 subcomplex of yeast Elongator | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 7 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Elp123 subcomplex of yeast Elongator
| Entire | Name: Elp123 subcomplex of yeast Elongator |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Elp123 subcomplex of yeast Elongator
| Supramolecule | Name: Elp123 subcomplex of yeast Elongator / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Details: Endogenously purified yeast Elp123 complex |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 850 KDa |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
Details: The final purification buffer was used for size exclusion chromatography of the complex. | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Material: Uranyl formate Details: Sample was applied to a glow-discharged copper grid overlaid with carbon (carbon evaporator and amyl acetate) and stained with uranyl formate. | |||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Ted Pella Gilder Grids / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 400 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Pretreatment - Pressure: 0.039 kPa |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI SPIRIT |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI EAGLE (4k x 4k) / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 4096 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4096 pixel / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 106 / Average exposure time: 1.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 25.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 120 kV / Electron source: LAB6 |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 49000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: SIDE ENTRY, EUCENTRIC |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Spirit / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera





 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)






















