+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-7130 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
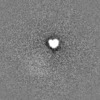
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of ENaC | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Unsharpened map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | sodium channel / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsensory perception of salty taste / Sensory perception of salty taste / neutrophil-mediated killing of bacterium / aldosterone metabolic process / leukocyte activation involved in inflammatory response / cellular response to vasopressin / sensory perception of sour taste / sperm principal piece / cellular response to aldosterone / sodium channel complex ...sensory perception of salty taste / Sensory perception of salty taste / neutrophil-mediated killing of bacterium / aldosterone metabolic process / leukocyte activation involved in inflammatory response / cellular response to vasopressin / sensory perception of sour taste / sperm principal piece / cellular response to aldosterone / sodium channel complex / epithelial fluid transport / mucus secretion / sodium ion homeostasis / renal system process / neutrophil activation involved in immune response / artery smooth muscle contraction / multicellular organismal-level water homeostasis / potassium ion homeostasis / intracellular sodium ion homeostasis / cellular response to acidic pH / sodium ion import across plasma membrane / motile cilium / ligand-gated sodium channel activity / response to food / ciliary membrane / WW domain binding / erythrocyte homeostasis / monoatomic ion channel activity / acrosomal vesicle / sodium ion transmembrane transport / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / regulation of blood pressure / Stimuli-sensing channels / multicellular organism growth / gene expression / apical plasma membrane / response to xenobiotic stimulus / external side of plasma membrane / extracellular exosome / nucleoplasm / plasma membrane / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Noreng S / Bharadwaj A | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2018 Journal: Elife / Year: 2018Title: Structure of the human epithelial sodium channel by cryo-electron microscopy. Authors: Sigrid Noreng / Arpita Bharadwaj / Richard Posert / Craig Yoshioka / Isabelle Baconguis /  Abstract: The epithelial sodium channel (ENaC), a member of the ENaC/DEG superfamily, regulates Na and water homeostasis. ENaCs assemble as heterotrimeric channels that harbor protease-sensitive domains ...The epithelial sodium channel (ENaC), a member of the ENaC/DEG superfamily, regulates Na and water homeostasis. ENaCs assemble as heterotrimeric channels that harbor protease-sensitive domains critical for gating the channel. Here, we present the structure of human ENaC in the uncleaved state determined by single-particle cryo-electron microscopy. The ion channel is composed of a large extracellular domain and a narrow transmembrane domain. The structure reveals that ENaC assembles with a 1:1:1 stoichiometry of α:β:γ subunits arranged in a counter-clockwise manner. The shape of each subunit is reminiscent of a hand with key gating domains of a 'finger' and a 'thumb.' Wedged between these domains is the elusive protease-sensitive inhibitory domain poised to regulate conformational changes of the 'finger' and 'thumb'; thus, the structure provides the first view of the architecture of inhibition of ENaC. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_7130.map.gz emd_7130.map.gz | 200.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-7130-v30.xml emd-7130-v30.xml emd-7130.xml emd-7130.xml | 30 KB 30 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_7130.png emd_7130.png | 107.7 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_7130_msk_1.map emd_7130_msk_1.map | 216 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-7130.cif.gz emd-7130.cif.gz | 7.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_7130_additional.map.gz emd_7130_additional.map.gz emd_7130_half_map_1.map.gz emd_7130_half_map_1.map.gz emd_7130_half_map_2.map.gz emd_7130_half_map_2.map.gz | 200.5 MB 16.5 MB 16.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7130 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7130 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7130 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7130 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6bqnMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_7130.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_7130.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unsharpened map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.33 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
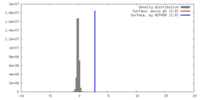
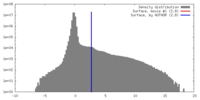
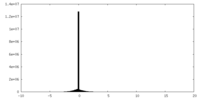
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_7130_msk_1.map emd_7130_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
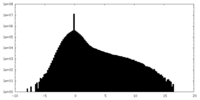
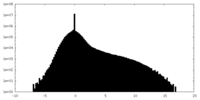
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Sharpened map
| File | emd_7130_additional.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Sharpened map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map 1
| File | emd_7130_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map 1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map 2
| File | emd_7130_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Membrane protein complex
| Entire | Name: Membrane protein complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Membrane protein complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Membrane protein complex / type: cell / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: SCNN1A
| Macromolecule | Name: SCNN1A / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: Transmembrane helices have been built with poly UNK since the density for the transmembrane domain is not good enough to accurately build a model. Residues that have not been built is due to ...Details: Transmembrane helices have been built with poly UNK since the density for the transmembrane domain is not good enough to accurately build a model. Residues that have not been built is due to flexible areas of the protein where density is missing. The full sequence is described in sequence details. Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 54.038953 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) SYPVSLNINL NSDKL VFPA VTICTLNPYR ...String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) SYPVSLNINL NSDKL VFPA VTICTLNPYR YPEIKEELEE LDRITEQTLF DLYKYSSFTT LVAGSRSRAD LRGTLPHPLQ ALAVPPPPHG AAAAAS VAS SLRDNNPQVD WKDWKIGFQL CNQNKSDCFY QTYSSGVDAV AEWYAFHYIN ILSRLPETLP SLEEDTLGNF IFACRFN QV SCNQANYSHF HHPMYGNCYT FNDKNNSNLW MSSMPGINNG LSLMLRAEQN DFIPLLSTVT GARVMVHGQD EPAFMDDG G FNLRPGVETS ISMRKETLDR LGGDYGDCTK NGSDVPVENL YPSKYTQQVC IHSCFQESMI KECGCAYIFY PRPQNVEYC DYRKHSSWGY CYYKLQVDFS SDHLGCFTKC RKPCSVTSYQ LSAGYSRWPS VTSQEWVFQM LSRQNNYTVN NKRNGVAKVN IFFKELNYK TNSESPSVT(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) |
-Macromolecule #2: SCNN1B
| Macromolecule | Name: SCNN1B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 Details: Transmembrane helices have been built with poly UNK since the density for the transmembrane domain is not good enough to accurately build a model. Residues that have not been built is due to ...Details: Transmembrane helices have been built with poly UNK since the density for the transmembrane domain is not good enough to accurately build a model. Residues that have not been built is due to flexible areas of the protein where density is missing. The full sequence is described in sequence details. Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 55.038633 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)TYLS WEVSVSLSVG FKTMDFPAVT ICNASPFKYS K IKHLLKDL DELMEAVLER ...String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)TYLS WEVSVSLSVG FKTMDFPAVT ICNASPFKYS K IKHLLKDL DELMEAVLER ILAPELSHAN ATRNLNFSIW NHTPLVLIDE RNPHHPMVLD LFGDNHNGLT SSSASEKICN AH GCKMAMR LCSLNRTQCT FRNFTSATQA LTEWYILQAT NIFAQVPQQE LVEMSYPGEQ MILACLFGAE PCNYRNFTSI FYP HYGNCY IFNWGMTEKA LPSANPGTEF GLKLILDIGQ EDYVPFLAST AGVRLMLHEQ RSYPFIRDEG IYAMSGTETS IGVL VDKLQ RMGEPYSPCT VNGSEVPVQN FYSDYNTTYS IQACLRSCFQ DHMIRNCNCG HYLYPLPRGE KYCNNRDFPD WAHCY SDLQ MSVAQRETCI GMCKESCNDT QYKMTISMAD WPSEASEDWI FHVLSQERDQ STNITLSRKG IVKLNIYFQE FNYRTI EES AANNI(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) |
-Macromolecule #3: EGFP-SCNN1G chimera
| Macromolecule | Name: EGFP-SCNN1G chimera / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 Details: The protein is EGFP-SCNN1G chimera. Transmembrane helices have been built with poly UNK since the density for the transmembrane domain is not good enough to accurately build a model. ...Details: The protein is EGFP-SCNN1G chimera. Transmembrane helices have been built with poly UNK since the density for the transmembrane domain is not good enough to accurately build a model. Residues that have not been built is due to flexible areas of the protein where density is missing. The first 260 residues is a His8 tag and a strep-tag followed by EGFP (UniProt accession code: C5MKY7). The full sequence is described in sequence details. Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 55.834457 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) FYTVSVSIKV HFRKL DFPA VTICNINPYK ...String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) FYTVSVSIKV HFRKL DFPA VTICNINPYK YSTVRHLLAD LEQETREALK SLYGFPESAA AAEAESWNSV SEGKQPRFSH RIPLLIFDQD EKGKAR DFF TGQQQQVGGS IIHKASNVMH IESKQVVGFQ LCSNDTSDCA TYTFSSGINA IQEWYKLHYM NIMAQVPLEK KINMSYS AE ELLVTCFFDG VSCDARNFTL FHHPMHGNCY TFNNRENETI LSTSMGGSEY GLQVILYINE EEYNPFLVSS TGAKVIIH R QDEYPFVEDV GTEIETAMVT SIGMHLTESF KLSEPYSQCT EDGSDVPIRN IYNAAYSLQI CLHSCFQTKM VEKCGCAQY SQPLPPAANY CNYQQHPNWM YCYYQLHRAF VQEELGCQSV CKEACSFKEW TLTTSLAQWP SVVSEKWLLP VLTWDQGRQV NKKLNKTDL AKLLIFYKDL NQRSIMESPA NSI(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) |
-Macromolecule #4: 7B1 fab
| Macromolecule | Name: 7B1 fab / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Details: Sequence unknown, built with poly UNK. / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 9.039134 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) ...String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) |
-Macromolecule #5: 7B1 fab
| Macromolecule | Name: 7B1 fab / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Details: Sequence unknown, built with poly UNK. / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 10.315707 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) ...String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) |
-Macromolecule #6: 10D4 fab
| Macromolecule | Name: 10D4 fab / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Details: Sequence unknown, built with poly UNK. / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 9.805078 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) ...String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK) |
-Macromolecule #7: 10D4 fab
| Macromolecule | Name: 10D4 fab / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 7 / Details: Sequence unknown, built with poly UNK. / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 9.549763 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) ...String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: OTHER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




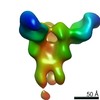
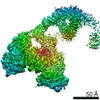
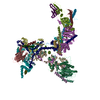



 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)