+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | MicroED structure of proteinase K without energy filtering | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | serine protease / hydrolase | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpeptidase K / serine-type endopeptidase activity / proteolysis / extracellular region / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Parengyodontium album (fungus) Parengyodontium album (fungus) | ||||||||||||
| Method | electron crystallography / cryo EM / Resolution: 1.3 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Clabbers MTB / Gonen T / Martynoqycz MW | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Struct Dyn / Year: 2025 Journal: Struct Dyn / Year: 2025Title: Recovering high-resolution information using energy filtering in MicroED. Authors: Max T B Clabbers / Tamir Gonen Abstract: Inelastic scattering poses a significant challenge in electron crystallography by elevating background noise and broadening Bragg peaks, thereby reducing the overall signal-to-noise ratio. This is ...Inelastic scattering poses a significant challenge in electron crystallography by elevating background noise and broadening Bragg peaks, thereby reducing the overall signal-to-noise ratio. This is particularly detrimental to data quality in structural biology, as the diffraction signal is relatively weak. These effects are aggravated even further by the decay of the diffracted intensities as a result of accumulated radiation damage, and rapidly fading high-resolution information can disappear beneath the noise. Loss of high-resolution reflections can partly be mitigated using energy filtering, which removes inelastically scattered electrons and improves data quality and resolution. Here, we systematically compared unfiltered and energy-filtered microcrystal electron diffraction data from proteinase K crystals, first collecting an unfiltered dataset followed directly by a second sweep using the same settings but with the energy filter inserted. Our results show that energy filtering consistently reduces noise, sharpens Bragg peaks, and extends high-resolution information, even though the absorbed dose was doubled for the second pass. Importantly, our results demonstrate that high-resolution information can be recovered by inserting the energy filter slit. Energy-filtered datasets showed improved intensity statistics and better internal consistency, highlighting the effectiveness of energy filtering for improving data quality. These findings underscore its potential to overcome limitations in macromolecular electron crystallography, enabling higher-resolution structures with greater reliability. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_70378.map.gz emd_70378.map.gz | 23.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-70378-v30.xml emd-70378-v30.xml emd-70378.xml emd-70378.xml | 15.9 KB 15.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_70378.png emd_70378.png | 83.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-70378.cif.gz emd-70378.cif.gz | 6.2 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-70378 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-70378 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-70378 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-70378 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_70378_validation.pdf.gz emd_70378_validation.pdf.gz | 670.9 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_70378_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_70378_full_validation.pdf.gz | 670.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_70378_validation.xml.gz emd_70378_validation.xml.gz | 4.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_70378_validation.cif.gz emd_70378_validation.cif.gz | 4.9 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-70378 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-70378 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-70378 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-70378 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9odvMC  9odwC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_70378.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 25.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_70378.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 25.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.3131 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Proteinase K
| Entire | Name: Proteinase K |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Proteinase K
| Supramolecule | Name: Proteinase K / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 / Details: Serine protease |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Parengyodontium album (fungus) Parengyodontium album (fungus) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 28.9 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Proteinase K
| Macromolecule | Name: Proteinase K / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: peptidase K |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Parengyodontium album (fungus) Parengyodontium album (fungus) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 28.958791 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Parengyodontium album (fungus) Parengyodontium album (fungus) |
| Sequence | String: AAQTNAPWGL ARISSTSPGT STYYYDESAG QGSCVYVIDT GIEASHPEFE GRAQMVKTYY YSSRDGNGHG THCAGTVGSR TYGVAKKTQ LFGVKVLDDN GSGQYSTIIA GMDFVASDKN NRNCPKGVVA SLSLGGGYSS SVNSAAARLQ SSGVMVAVAA G NNNADARN ...String: AAQTNAPWGL ARISSTSPGT STYYYDESAG QGSCVYVIDT GIEASHPEFE GRAQMVKTYY YSSRDGNGHG THCAGTVGSR TYGVAKKTQ LFGVKVLDDN GSGQYSTIIA GMDFVASDKN NRNCPKGVVA SLSLGGGYSS SVNSAAARLQ SSGVMVAVAA G NNNADARN YSPASEPSVC TVGASDRYDR RSSFSNYGSV LDIFGPGTDI LSTWIGGSTR SISGTSMATP HVAGLAAYLM TL GKTTAAS ACRYIADTAN KGDLSNIPFG TVNLLAYNNY QA UniProtKB: Proteinase K |
-Macromolecule #2: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #3: NITRATE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: NITRATE ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: NO3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 62.005 Da |
| Chemical component information | 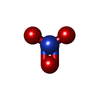 ChemComp-NO3: |
-Macromolecule #4: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 375 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | electron crystallography |
| Aggregation state | 3D array |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 40 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 6.5 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/2 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Support film - Film thickness: 10 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. / Details: Negative 15 mA |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: LEICA PLUNGER |
| Details | Microcrystals |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Min: 77.0 K / Max: 90.0 K |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 4096 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4096 pixel / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 1 / Number diffraction images: 420 / Average exposure time: 1.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 0.002 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: DIFFRACTION / Nominal defocus max: 0.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.0 µm / Camera length: 1402 mm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - Source name: PDB / Chain - Initial model type: experimental model / Details: Molecular replacement |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: RECIPROCAL / Protocol: OTHER / Overall B value: 11.57 / Target criteria: Maximum likelihood |
| Output model |  PDB-9odv: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)