[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-7010: Cryo-EM structure of human immunoproteasome with a novel noncompe... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-7010 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
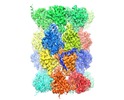
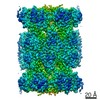
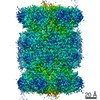
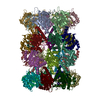
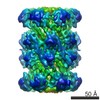
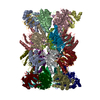
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of human immunoproteasome with a novel noncompetitive inhibitor that selectively inhibits activated lymphocytes | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | human immunoproteasome with a novel noncompetitive inhibitor | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | inhibitor / complex / immunoproteasome / HYDROLASE-HYDROLASE INHIBITOR complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationspermatoproteasome complex / purine ribonucleoside triphosphate binding / Antigen processing: Ub, ATP-independent proteasomal degradation / Regulation of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) / Proteasome assembly / Cross-presentation of soluble exogenous antigens (endosomes) / proteasome core complex / Somitogenesis / antigen processing and presentation / myofibril ...spermatoproteasome complex / purine ribonucleoside triphosphate binding / Antigen processing: Ub, ATP-independent proteasomal degradation / Regulation of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) / Proteasome assembly / Cross-presentation of soluble exogenous antigens (endosomes) / proteasome core complex / Somitogenesis / antigen processing and presentation / myofibril / humoral immune response / immune system process / NF-kappaB binding / proteasome endopeptidase complex / proteasome core complex, beta-subunit complex / threonine-type endopeptidase activity / T cell proliferation / proteasome core complex, alpha-subunit complex / fat cell differentiation / proteasome complex / : / Degradation of CDH1 / sarcomere / Degradation of CRY and PER proteins / Regulation of activated PAK-2p34 by proteasome mediated degradation / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / Asymmetric localization of PCP proteins / Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Cyclin D / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / NIK-->noncanonical NF-kB signaling / TNFR2 non-canonical NF-kB pathway / AUF1 (hnRNP D0) binds and destabilizes mRNA / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / negative regulation of inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus / Vpu mediated degradation of CD4 / P-body / Degradation of DVL / Cdc20:Phospho-APC/C mediated degradation of Cyclin A / Dectin-1 mediated noncanonical NF-kB signaling / Degradation of AXIN / lipopolysaccharide binding / Hh mutants are degraded by ERAD / Activation of NF-kappaB in B cells / G2/M Checkpoints / Degradation of GLI1 by the proteasome / Hedgehog ligand biogenesis / Defective CFTR causes cystic fibrosis / Autodegradation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 / Regulation of RUNX3 expression and activity / GSK3B and BTRC:CUL1-mediated-degradation of NFE2L2 / Negative regulation of NOTCH4 signaling / Ubiquitin-Mediated Degradation of Phosphorylated Cdc25A / Hedgehog 'on' state / Vif-mediated degradation of APOBEC3G / APC/C:Cdh1 mediated degradation of Cdc20 and other APC/C:Cdh1 targeted proteins in late mitosis/early G1 / FBXL7 down-regulates AURKA during mitotic entry and in early mitosis / Degradation of GLI2 by the proteasome / GLI3 is processed to GLI3R by the proteasome / MAPK6/MAPK4 signaling / Degradation of beta-catenin by the destruction complex / Oxygen-dependent proline hydroxylation of Hypoxia-inducible Factor Alpha / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) signaling / response to virus / SCF(Skp2)-mediated degradation of p27/p21 / FCERI mediated NF-kB activation / nuclear matrix / Regulation of expression of SLITs and ROBOs / cell morphogenesis / Regulation of PTEN stability and activity / Interleukin-1 signaling / Orc1 removal from chromatin / Regulation of RAS by GAPs / Regulation of RUNX2 expression and activity / The role of GTSE1 in G2/M progression after G2 checkpoint / Interferon alpha/beta signaling / Separation of Sister Chromatids / UCH proteinases / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway / Downstream TCR signaling / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / Neddylation / ER-Phagosome pathway / regulation of inflammatory response / secretory granule lumen / endopeptidase activity / ficolin-1-rich granule lumen / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / Ub-specific processing proteases / cilium / ciliary basal body / ribosome / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / Neutrophil degranulation / centrosome Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Li H / Santos R | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2017 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2017Title: Structure of human immunoproteasome with a reversible and noncompetitive inhibitor that selectively inhibits activated lymphocytes. Authors: Ruda de Luna Almeida Santos / Lin Bai / Pradeep K Singh / Naoka Murakami / Hao Fan / Wenhu Zhan / Yingrong Zhu / Xiuju Jiang / Kaiming Zhang / Jean Pierre Assker / Carl F Nathan / Huilin Li ...Authors: Ruda de Luna Almeida Santos / Lin Bai / Pradeep K Singh / Naoka Murakami / Hao Fan / Wenhu Zhan / Yingrong Zhu / Xiuju Jiang / Kaiming Zhang / Jean Pierre Assker / Carl F Nathan / Huilin Li / Jamil Azzi / Gang Lin /  Abstract: Proteasome inhibitors benefit patients with multiple myeloma and B cell-dependent autoimmune disorders but exert toxicity from inhibition of proteasomes in other cells. Toxicity should be minimized ...Proteasome inhibitors benefit patients with multiple myeloma and B cell-dependent autoimmune disorders but exert toxicity from inhibition of proteasomes in other cells. Toxicity should be minimized by reversible inhibition of the immunoproteasome β5i subunit while sparing the constitutive β5c subunit. Here we report β5i-selective inhibition by asparagine-ethylenediamine (AsnEDA)-based compounds and present the high-resolution cryo-EM structural analysis of the human immunoproteasome. Despite inhibiting noncompetitively, an AsnEDA inhibitor binds the active site. Hydrophobic interactions are accompanied by hydrogen bonding with β5i and β6 subunits. The inhibitors are far more cytotoxic for myeloma and lymphoma cell lines than for hepatocarcinoma or non-activated lymphocytes. They block human B-cell proliferation and promote apoptotic cell death selectively in antibody-secreting B cells, and to a lesser extent in activated human T cells. Reversible, β5i-selective inhibitors may be useful for treatment of diseases involving activated or neoplastic B cells or activated T cells. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_7010.map.gz emd_7010.map.gz | 5.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-7010-v30.xml emd-7010-v30.xml emd-7010.xml emd-7010.xml | 27.8 KB 27.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_7010.png emd_7010.png | 201.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-7010.cif.gz emd-7010.cif.gz | 7.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7010 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7010 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7010 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7010 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6avoMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_7010.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_7010.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | human immunoproteasome with a novel noncompetitive inhibitor | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
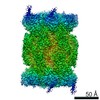
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.2 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : human immunoproteasome with a novel noncompetitive inhibitor that...
+Supramolecule #1: human immunoproteasome with a novel noncompetitive inhibitor that...
+Macromolecule #1: Proteasome subunit beta type-9
+Macromolecule #2: Proteasome subunit beta type-10
+Macromolecule #3: Proteasome subunit beta type-8
+Macromolecule #4: Proteasome subunit alpha type-1
+Macromolecule #5: Proteasome subunit alpha type-5
+Macromolecule #6: Proteasome subunit alpha type-7
+Macromolecule #7: Proteasome subunit alpha type-3
+Macromolecule #8: Proteasome subunit alpha type-6
+Macromolecule #9: Proteasome subunit alpha type-4
+Macromolecule #10: Proteasome subunit alpha type-2
+Macromolecule #11: Proteasome subunit beta type-1
+Macromolecule #12: Proteasome subunit beta type-2
+Macromolecule #13: Proteasome subunit beta type-3
+Macromolecule #14: Proteasome subunit beta type-4
+Macromolecule #15: N~1~-{2-[([1,1'-biphenyl]-3-carbonyl)amino]ethyl}-N~4~-tert-butyl...
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | JEOL 3200FS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



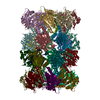
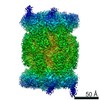
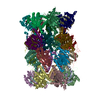






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)