+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-6937 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
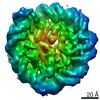
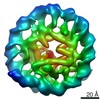
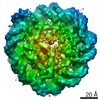
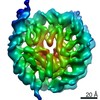
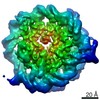
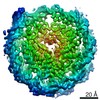
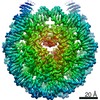
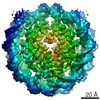
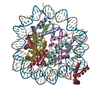
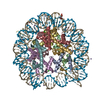
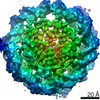
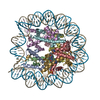
| Title | 112-bp octasome/Mid-pAID complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.7 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Mayanagi K / Saikusa K / Miyazaki N / Akashi S / Iwasaki K / Nishimura Y / Morikawa K / Tsunaka Y | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 10 items Japan, 10 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Genes Dev / Year: 2016 Journal: Genes Dev / Year: 2016Title: Integrated molecular mechanism directing nucleosome reorganization by human FACT. Authors: Yasuo Tsunaka / Yoshie Fujiwara / Takuji Oyama / Susumu Hirose / Kosuke Morikawa /  Abstract: Facilitates chromatin transcription (FACT) plays essential roles in chromatin remodeling during DNA transcription, replication, and repair. Our structural and biochemical studies of human FACT- ...Facilitates chromatin transcription (FACT) plays essential roles in chromatin remodeling during DNA transcription, replication, and repair. Our structural and biochemical studies of human FACT-histone interactions present precise views of nucleosome reorganization, conducted by the FACT-SPT16 (suppressor of Ty 16) Mid domain and its adjacent acidic AID segment. AID accesses the H2B N-terminal basic region exposed by partial unwrapping of the nucleosomal DNA, thereby triggering the invasion of FACT into the nucleosome. The crystal structure of the Mid domain complexed with an H3-H4 tetramer exhibits two separate contact sites; the Mid domain forms a novel intermolecular β structure with H4. At the other site, the Mid-H2A steric collision on the H2A-docking surface of the H3-H4 tetramer within the nucleosome induces H2A-H2B displacement. This integrated mechanism results in disrupting the H3 αN helix, which is essential for retaining the nucleosomal DNA ends, and hence facilitates DNA stripping from histone. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_6937.map.gz emd_6937.map.gz | 14.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-6937-v30.xml emd-6937-v30.xml emd-6937.xml emd-6937.xml | 15.8 KB 15.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_6937_1.png emd_6937_1.png emd_6937_2.png emd_6937_2.png | 157.9 KB 196.3 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6937 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6937 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6937 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6937 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_6937_validation.pdf.gz emd_6937_validation.pdf.gz | 78.4 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_6937_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_6937_full_validation.pdf.gz | 77.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_6937_validation.xml.gz emd_6937_validation.xml.gz | 494 B | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-6937 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-6937 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-6937 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-6937 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_6937.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 15.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_6937.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 15.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : 112-bp octasome/Mid-pAID
| Entire | Name: 112-bp octasome/Mid-pAID |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: 112-bp octasome/Mid-pAID
| Supramolecule | Name: 112-bp octasome/Mid-pAID / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 200 KDa |
-Supramolecule #2: Histone H2A
| Supramolecule | Name: Histone H2A / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: Histone H2B
| Supramolecule | Name: Histone H2B / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #4: Histone H3.1
| Supramolecule | Name: Histone H3.1 / type: complex / ID: 4 / Parent: 1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #5: Histone H4
| Supramolecule | Name: Histone H4 / type: complex / ID: 5 / Parent: 1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #6: Mid-pAID
| Supramolecule | Name: Mid-pAID / type: complex / ID: 6 / Parent: 1 / Details: humanFACT Spt16 Mid domain-AID |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #7: 112bp 601 DNA
| Supramolecule | Name: 112bp 601 DNA / type: complex / ID: 7 / Parent: 1 Details: 112 bp fragment of Widom-601 strong nucleosome positioning DNA sequence |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2.0 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Details: The grid was coated with gold prior to use. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 99 % / Chamber temperature: 20 K / Instrument: LEICA EM GP |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Phase plate: VOLTA PHASE PLATE / Spherical aberration corrector: Cs corrector used |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 36.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 5.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: RELION / Number images used: 30733 |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: COMMON LINE |
| Final angle assignment | Type: OTHER / Software - Name: RELION |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller