[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-63925: Cryo-EM structure of the V1 domain of V/A-ATPase in liposomes und... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
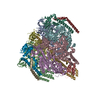
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the V1 domain of V/A-ATPase in liposomes under pmf condition, state3W | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ATP synthase / V ATPase / V1 ATPase / MOTOR PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ATP binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Nakano A / Kishikawa J / Nishida Y / Shigematsu H / Gerle C / Mitsuoka M / Yokoyama K | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 3 items Japan, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2025 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2025Title: Structures of rotary ATP synthase from during proton powered ATP synthesis. Authors: Atsuki Nakano / Jun-Ichi Kishikawa / Nishida Yui / Kyosuke Sugawara / Yuto Kan / Christoph Gerle / Hideki Shigematsu / Kaoru Mitsuoka / Ken Yokoyama /  Abstract: ATP synthases are rotary molecular machines that use the proton motive force to rotate the central rotor complex relative to the surrounding stator apparatus, thereby coupling the ATP synthesis. We ...ATP synthases are rotary molecular machines that use the proton motive force to rotate the central rotor complex relative to the surrounding stator apparatus, thereby coupling the ATP synthesis. We reconstituted the V/A-ATPase into liposomes and performed structural analysis using cryo-EM under conditions where the proton motive force was applied in the presence of ADP and Pi. ATP molecules were bound at two of the three catalytic sites of V/A-ATPase, confirming that the structure represents a state adopted during ATP synthesis. In this structure, the catalytic site closes upon binding of ADP and Pi through an induced fit mechanism. Multiple structures were obtained where the membrane-embedded rotor ring was in a different position relative to the stator. By comparing these structures, we found that torsion occurs in both the central rotor and the peripheral stator during 31° rotation of rotor ring. These structural snapshots of V/A-ATPase provide crucial insights into the mechanism of rotary catalysis of ATP synthesis. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_63925.map.gz emd_63925.map.gz | 62.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-63925-v30.xml emd-63925-v30.xml emd-63925.xml emd-63925.xml | 27.4 KB 27.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_63925_fsc.xml emd_63925_fsc.xml | 10.5 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_63925.png emd_63925.png | 74.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-63925.cif.gz emd-63925.cif.gz | 7.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_63925_additional_1.map.gz emd_63925_additional_1.map.gz emd_63925_additional_2.map.gz emd_63925_additional_2.map.gz emd_63925_half_map_1.map.gz emd_63925_half_map_1.map.gz emd_63925_half_map_2.map.gz emd_63925_half_map_2.map.gz | 118 MB 376.9 KB 116 MB 116 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-63925 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-63925 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-63925 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-63925 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9u6wMC  9u6fC  9u6gC  9u6hC  9u6iC  9u6jC  9u6kC  9u6lC  9u6mC  9u6nC  9u6oC  9u6pC  9u6qC  9u6tC  9u6uC  9u6vC  9u6xC  9u6yC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_63925.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_63925.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.05 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: #1
| File | emd_63925_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: #2
| File | emd_63925_additional_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_63925_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_63925_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Vo domain of V/A-ATPase from Thermus thermophilus
| Entire | Name: Vo domain of V/A-ATPase from Thermus thermophilus |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Vo domain of V/A-ATPase from Thermus thermophilus
| Supramolecule | Name: Vo domain of V/A-ATPase from Thermus thermophilus / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#4 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 660 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: V-type ATP synthase alpha chain
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type ATP synthase alpha chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: H+-transporting two-sector ATPase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 63.69998 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) |
| Sequence | String: MIQGVIQKIA GPAVIAKGML GARMYDICKV GEEGLVGEII RLDGDTAFVQ VYEDTSGLKV GEPVVSTGLP LAVELGPGML NGIYDGIQR PLERIREKTG IYITRGVVVH ALDREKKWAW TPMVKPGDEV RGGMVLGTVP EFGFTHKILV PPDVRGRVKE V KPAGEYTV ...String: MIQGVIQKIA GPAVIAKGML GARMYDICKV GEEGLVGEII RLDGDTAFVQ VYEDTSGLKV GEPVVSTGLP LAVELGPGML NGIYDGIQR PLERIREKTG IYITRGVVVH ALDREKKWAW TPMVKPGDEV RGGMVLGTVP EFGFTHKILV PPDVRGRVKE V KPAGEYTV EEPVVVLEDG TELKMYHTWP VRRARPVQRK LDPNTPFLTG MRILDVLFPV AMGGTAAIPG PFGSGKTVTQ QS LAKWSNA DVVVYVGCGE RGNEMTDVLV EFPELTDPKT GGPLMHRTVL IANTSNMPVA AREASIYVGV TIAEYFRDQG FSV ALMADS TSRWAEALRE ISSRLEEMPA EEGYPPYLAA RLAAFYERAG KVITLGGEEG AVTIVGAVSP PGGDMSEPVT QSTL RIVGA FWRLDASLAF RRHFPAINWN GSYSLFTSAL DPWYRENVAE DYPELRDAIS ELLQREAGLQ EIVQLVGPDA LQDAE RLVI EVGRIIREDF LQQNAYHEVD AYCSMKKAYG IMKMILAFYK EAEAAIKRGV SIDEILQLPV LERIGRARYV SEEEFP AYF EEAMKEIQGA FKALA UniProtKB: V-type ATP synthase alpha chain |
-Macromolecule #2: V-type ATP synthase beta chain
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type ATP synthase beta chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 52.660852 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) |
| Sequence | String: DLLKKEYTGI TYISGPLLFV ENAKDLAYGA IVDIKDGTGR VRGGQVIEVS EEYAVIQVFE ETTGLDLATT SVSLVEDVAR LGVSKEMLG RRFNGIGKPI DGLPPITPEK RLPITGLPLN PVARRKPEQF IQTGISTIDV MNTLVRGQKL PIFSGSGLPA N EIAAQIAR ...String: DLLKKEYTGI TYISGPLLFV ENAKDLAYGA IVDIKDGTGR VRGGQVIEVS EEYAVIQVFE ETTGLDLATT SVSLVEDVAR LGVSKEMLG RRFNGIGKPI DGLPPITPEK RLPITGLPLN PVARRKPEQF IQTGISTIDV MNTLVRGQKL PIFSGSGLPA N EIAAQIAR QATVRPDLSG EGEKEEPFAV VFAAMGITQR ELSYFIQEFE RTGALSRSVL FLNKADDPTI ERILTPRMAL TV AEYLAFE HDYHVLVILT DMTNYCEALR EIGAAREEIP GRRGYPGYMY TDLATIYERA GVVEGKKGSV TQIPILSMPD DDR THPIPD LTGYITEGQI QLSRELHRKG IYPPIDPLPS LSRLMNNGVG KGKTREDHKQ VSDQLYSAYA NGVDIRKLVA IIGE DALTE NDRRYLQFAD AFERFFINQG QQNRSIEESL QIAWALLSML PQGELKRISK DHIGKYYGQK LEEIWGAP UniProtKB: V-type ATP synthase beta chain |
-Macromolecule #3: V-type ATP synthase subunit D
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type ATP synthase subunit D / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 23.021662 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) |
| Sequence | String: VSPTRMNLLQ RRGQLRLAQK GVDLLKKKRD ALVAEFFGLV REAMEARKAL DQAAKEAYAA LLLAQAFDGP EVVAGAALGV PPLEGVEAE VENVWGSKVP RLKATFPDGA LLSPVGTPAY TLEASRAFRR YAEALIRVAN TETRLKKIGE EIKKTTRRVN A LEQVVIPG ...String: VSPTRMNLLQ RRGQLRLAQK GVDLLKKKRD ALVAEFFGLV REAMEARKAL DQAAKEAYAA LLLAQAFDGP EVVAGAALGV PPLEGVEAE VENVWGSKVP RLKATFPDGA LLSPVGTPAY TLEASRAFRR YAEALIRVAN TETRLKKIGE EIKKTTRRVN A LEQVVIPG IRAQIRFIQQ VLEQREREDT FRLKRIKGKI EAREAEEE UniProtKB: V-type ATP synthase subunit D |
-Macromolecule #4: V-type ATP synthase subunit F
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type ATP synthase subunit F / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.294904 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) |
| Sequence | String: MAVIADPETA QGFRLAGLEG YGASSAEEAQ SLLETLVERG GYALVAVDEA LLPDPERAVE RLMRGRDLPV LLPIAGLKEA FQGHDVEGY MRELVRKTIG FDIKL UniProtKB: V-type ATP synthase subunit F |
-Macromolecule #5: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #6: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Macromolecule #7: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Macromolecule #8: PHOSPHATE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHATE ION / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: PO4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 94.971 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PO4: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.6 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.4000000000000001 µm / Nominal magnification: 60000 |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)