[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
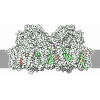
Yorodumi- EMDB-63167: Cryo-EM structure of Lhcb4.1-C2S2 PSII-LHCII supercomplex from Ar... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Lhcb4.1-C2S2 PSII-LHCII supercomplex from Arabidopsis thaliana | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Photosystem II / light harvesting / photoacclimation / stress-induced antennae / cryo-EM / PHOTOSYNTHESIS | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationphotoinhibition / photosynthesis, light harvesting in photosystem II / photosystem II antenna complex / PSII associated light-harvesting complex II / response to desiccation / response to red light / nonphotochemical quenching / chloroplast photosystem II / cellular response to abscisic acid stimulus / cellular response to water deprivation ...photoinhibition / photosynthesis, light harvesting in photosystem II / photosystem II antenna complex / PSII associated light-harvesting complex II / response to desiccation / response to red light / nonphotochemical quenching / chloroplast photosystem II / cellular response to abscisic acid stimulus / cellular response to water deprivation / chloroplast stromal thylakoid / response to low light intensity stimulus / thylakoid lumen / plastid thylakoid membrane / plastoglobule / regulation of stomatal closure / response to far red light / thylakoid membrane / response to high light intensity / chloroplast thylakoid / vacuolar transport / photosynthesis, light harvesting in photosystem I / thylakoid / apoplast / photosystem II oxygen evolving complex / response to fructose / photosystem II assembly / chloroplast thylakoid lumen / oxygen evolving activity / protein phosphatase regulator activity / photosystem II stabilization / photosystem II reaction center / photosystem II / chloroplast envelope / plant-type vacuole / oxidoreductase activity, acting on diphenols and related substances as donors, oxygen as acceptor / photosynthetic electron transport chain / photosystem I / response to herbicide / photosystem II / chloroplast stroma / poly(U) RNA binding / plastid / photosynthetic electron transport in photosystem II / chlorophyll binding / phosphate ion binding / photosynthesis, light reaction / chloroplast thylakoid membrane / positive regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / response to light stimulus / photosynthesis / response to cold / chloroplast / electron transfer activity / protein stabilization / iron ion binding / protein domain specific binding / mRNA binding / heme binding / mitochondrion / metal ion binding / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhou Q / Caferri R / Shan JY / Amelii A / Bassi R / Liu ZF | ||||||||||||
| Funding support | European Union,  China, 3 items China, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025Title: A stress-induced paralog of Lhcb4 controls the photosystem II functional architecture in Arabidopsis thaliana. Authors: Roberto Caferri / Qian Zhou / Luca Dall'Osto / Antonello Amelii / Jianyu Shan / Zhenfeng Liu / Roberto Bassi /   Abstract: Photosystem II (PSII) is the pigment-protein complex catalysing light-induced water oxidation. In Arabidopsis thaliana, it includes three Lhcb4-6 proteins linking the core complex to peripheral ...Photosystem II (PSII) is the pigment-protein complex catalysing light-induced water oxidation. In Arabidopsis thaliana, it includes three Lhcb4-6 proteins linking the core complex to peripheral trimeric antennae. While Lhcb5 and Lhcb6 are encoded by single genes, Lhcb4 is encoded by three isoforms: Lhcb4.1 and Lhcb4.2, constitutively expressed, and Lhcb4.3 (Lhcb8), which accumulates under prolonged abiotic stress. Lhcb8 substitutes for Lhcb4, preventing Lhcb6 accumulation and resulting in a smaller PSII with high quantum yield. Cryo-electron microscopy reveals that Lhcb8 has a shorter carboxy-terminal domain, lacks two chlorophylls, and interacts more tightly with the PSII core, inducing structural changes in the PSII antenna system, ultimately inhibiting the formation of PSII arrays and favouring plastoquinone diffusion. We suggest that dynamic Lhcb4 vs Lhcb8 expression allows for PSII acclimation to contrasting light conditions, offering the potential for engineering crops with improved light use efficiency. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_63167.map.gz emd_63167.map.gz | 220.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-63167-v30.xml emd-63167-v30.xml emd-63167.xml emd-63167.xml | 42.6 KB 42.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_63167.png emd_63167.png | 117.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-63167.cif.gz emd-63167.cif.gz | 10.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-63167 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-63167 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-63167 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-63167 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9lk4MC  9lk5C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_63167.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_63167.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Cryo-EM structure of the Lhcb8-C2S2 PSII-LHCII supercomplex from ...
+Supramolecule #1: Cryo-EM structure of the Lhcb8-C2S2 PSII-LHCII supercomplex from ...
+Macromolecule #1: Photosystem II protein D1
+Macromolecule #2: Photosystem II CP47 reaction center protein
+Macromolecule #3: Photosystem II CP43 reaction center protein
+Macromolecule #4: Photosystem II D2 protein
+Macromolecule #5: Cytochrome b559 subunit alpha
+Macromolecule #6: Cytochrome b559 subunit beta
+Macromolecule #7: Chlorophyll a-b binding protein 2, chloroplastic
+Macromolecule #8: Photosystem II reaction center protein H
+Macromolecule #9: Photosystem II reaction center protein I
+Macromolecule #10: Photosystem II reaction center protein J
+Macromolecule #11: Photosystem II reaction center protein K
+Macromolecule #12: Photosystem II reaction center protein L
+Macromolecule #13: Photosystem II reaction center protein M
+Macromolecule #14: Oxygen-evolving enhancer protein 1-1, chloroplastic
+Macromolecule #15: Chlorophyll a-b binding protein CP29.1, chloroplastic
+Macromolecule #16: Photosystem II reaction center protein T
+Macromolecule #17: Photosystem II 5 kDa protein, chloroplastic
+Macromolecule #18: Photosystem II reaction center W protein, chloroplastic
+Macromolecule #19: (thale cress) hypothetical protein
+Macromolecule #20: Chlorophyll a-b binding protein 2.2, chloroplastic
+Macromolecule #21: Photosystem II reaction center protein Z
+Macromolecule #22: Chlorophyll a-b binding protein CP26, chloroplastic
+Macromolecule #23: CHLOROPHYLL A
+Macromolecule #24: PHEOPHYTIN A
+Macromolecule #25: BETA-CAROTENE
+Macromolecule #26: 1,2-DI-O-ACYL-3-O-[6-DEOXY-6-SULFO-ALPHA-D-GLUCOPYRANOSYL]-SN-GLYCEROL
+Macromolecule #27: 1,2-DISTEAROYL-MONOGALACTOSYL-DIGLYCERIDE
+Macromolecule #28: DIGALACTOSYL DIACYL GLYCEROL (DGDG)
+Macromolecule #29: FE (II) ION
+Macromolecule #30: 1,2-DIPALMITOYL-PHOSPHATIDYL-GLYCEROLE
+Macromolecule #31: BICARBONATE ION
+Macromolecule #32: 2,3-DIMETHYL-5-(3,7,11,15,19,23,27,31,35-NONAMETHYL-2,6,10,14,18,...
+Macromolecule #33: PROTOPORPHYRIN IX CONTAINING FE
+Macromolecule #34: CHLOROPHYLL B
+Macromolecule #35: (3R,3'R,6S)-4,5-DIDEHYDRO-5,6-DIHYDRO-BETA,BETA-CAROTENE-3,3'-DIOL
+Macromolecule #36: (1R,3R)-6-{(3E,5E,7E,9E,11E,13E,15E,17E)-18-[(1S,4R,6R)-4-HYDROXY...
+Macromolecule #37: (3S,5R,6S,3'S,5'R,6'S)-5,6,5',6'-DIEPOXY-5,6,5',6'- TETRAHYDRO-BE...
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)