+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| タイトル | Cryo-EM structure of the rice isoamylase ISA1-ISA2 heterocomplex incubated with Amylopectin | |||||||||
 マップデータ マップデータ | ||||||||||
 試料 試料 |
| |||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | isoamylase ISA1-ISA2 / HYDROLASE | |||||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報chloroplast isoamylase complex / isoamylase / isoamylase complex / isoamylase activity / amylopectin biosynthetic process / starch biosynthetic process / starch catabolic process / chloroplast 類似検索 - 分子機能 | |||||||||
| 生物種 |  | |||||||||
| 手法 | 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 2.7 Å | |||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Guan ZY / Yan JJ | |||||||||
| 資金援助 |  中国, 1件 中国, 1件
| |||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Nat Commun / 年: 2025 ジャーナル: Nat Commun / 年: 2025タイトル: Amylopectin branch trimming and biosynthesis elucidated by the rice isoamylase ISA1-ISA2 heterocomplex. 著者: Rong Fan / Zeyuan Guan / Guanghong Zhou / Xi Yang / Fei Zhang / Menglong Wu / Xuecui Wang / Jian Liu / Pei Chen / Yanjun Liu / Delin Zhang / Ping Yin / Junjie Yan /  要旨: Amylopectin, the primary form of starch in plant leaves, seeds and tubers, features a tree-like architecture with branched glucose chains. Excess branches result in the formation of soluble ...Amylopectin, the primary form of starch in plant leaves, seeds and tubers, features a tree-like architecture with branched glucose chains. Excess branches result in the formation of soluble phytoglycogen instead of starch granules. In higher plants and green algae, the debranching enzyme isoamylase ISA1 forms either homomultimer or hetero-multimer with ISA2 to facilitate branch trimming and starch granule formation, but the molecular basis remains largely unknown. In this study, we reconstitute the rice OsISA1-ISA2 complex in vitro and determine the cryo-EM structures of the OsISA1 homodimer, as well as the malto-oligosaccharide (MOS)-free and MOS-bound OsISA1-ISA2 heterocomplex. The OsISA1 dimer shows a tail-to-tail rod-like architecture, whereas the OsISA1-ISA2 complex mainly exhibits as a trimer, with OsISA2 flanking on the N-terminal segments of the dimeric OsISA1. Combined with comprehensive biochemical analyses, these structural data elucidate the organization of the ISA1-ISA2 heterocomplex in higher plants and demonstrate how ISA1 and ISA2 cooperate during amylopectin biosynthesis. | |||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| 添付画像 |
|---|
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
-EMDBアーカイブ
| マップデータ |  emd_63051.map.gz emd_63051.map.gz | 230.2 MB |  EMDBマップデータ形式 EMDBマップデータ形式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ヘッダ (付随情報) |  emd-63051-v30.xml emd-63051-v30.xml emd-63051.xml emd-63051.xml | 18.9 KB 18.9 KB | 表示 表示 |  EMDBヘッダ EMDBヘッダ |
| 画像 |  emd_63051.png emd_63051.png | 70.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-63051.cif.gz emd-63051.cif.gz | 7 KB | ||
| その他 |  emd_63051_half_map_1.map.gz emd_63051_half_map_1.map.gz emd_63051_half_map_2.map.gz emd_63051_half_map_2.map.gz | 226.3 MB 226.3 MB | ||
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-63051 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-63051 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-63051 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-63051 | HTTPS FTP |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  emd_63051_validation.pdf.gz emd_63051_validation.pdf.gz | 1011.2 KB | 表示 |  EMDB検証レポート EMDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  emd_63051_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_63051_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1010.8 KB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  emd_63051_validation.xml.gz emd_63051_validation.xml.gz | 15.8 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  emd_63051_validation.cif.gz emd_63051_validation.cif.gz | 18.7 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-63051 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-63051 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-63051 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-63051 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
- リンク
リンク
| EMDBのページ |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| 「今月の分子」の関連する項目 |
- マップ
マップ
| ファイル |  ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_63051.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 244.1 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_63051.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 244.1 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 投影像・断面図 | 画像のコントロール
画像は Spider により作成 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ボクセルのサイズ | X=Y=Z: 0.824 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 密度 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 空間群: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | EMDB XML:
|
-添付データ
-ハーフマップ: #2
| ファイル | emd_63051_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
-ハーフマップ: #1
| ファイル | emd_63051_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
- 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素
-全体 : SA1-ISA2-Amylopectin
| 全体 | 名称: SA1-ISA2-Amylopectin |
|---|---|
| 要素 |
|
-超分子 #1: SA1-ISA2-Amylopectin
| 超分子 | 名称: SA1-ISA2-Amylopectin / タイプ: complex / ID: 1 / 親要素: 0 / 含まれる分子: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  |
-分子 #1: Isoamylase 1, chloroplastic
| 分子 | 名称: Isoamylase 1, chloroplastic / タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / コピー数: 2 / 光学異性体: LEVO / EC番号: isoamylase |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 87.281594 KDa |
| 組換発現 | 生物種:  |
| 配列 | 文字列: MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH SDEVDAHMSV ASAVEVGVGE DEEEGVEEEE EEVEAVVMPE RYALGGACRV LAGMPAPLGA TALDGGVNF AVYSAGASAA SLCLFTPDDL EADEVTEEVP LDPLFNRTGN VWHVFIEGEL HNMLYGYRFD GMFAPHCGQY F DVSNVVVD ...文字列: MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH SDEVDAHMSV ASAVEVGVGE DEEEGVEEEE EEVEAVVMPE RYALGGACRV LAGMPAPLGA TALDGGVNF AVYSAGASAA SLCLFTPDDL EADEVTEEVP LDPLFNRTGN VWHVFIEGEL HNMLYGYRFD GMFAPHCGQY F DVSNVVVD PYAKAVISRG EYGVPGPGGD CWPQMAGMIP LPYSTFDWQG DLPLRYPQKD LVIYEMHLRG FTKHSSSNVE HP GTYIGAI SKLDYLKELG VNCVELMPCH EFNELEYFSC SSKMNFWGYS TINFFSPMIR YSSGGIRNCG RDAINEFKTF VRE AHKRGI EVIMDVVFNH TAEGNEKGPI LSFRGIDNST YYMLAPKGEF YNYSGCGNTF NCNHPVVREF IVDCLRYWVT EMHV DGFRF DLASIMTRGC SLWDPVNVYG SPVEGDMTTT GTPLATPPLI DMISNDPILG DVKLIAEAWD AGGLYQVGQF PHWKI WSEW NGKYRDIVRQ FIKGTDGFAG GFAECLCGSP HLYQAGGRKP WHSINFVCAH DGFTLADLVT YNKKYNSSNG EDNRDG ENH NLSWNCGEEG EFAGLSVKRL RKRQMRNFFV SLMVSQGVPM FYMGDEYGHT KGGNNNTYCH DHYVNYFRWD KKEESSD LQ RFCSLMTKFR KQCESLGLAD FPTAQRLHWH GHQPGKPDWS ETSRFVAFST KDETKGEIYV AFNASHLPAV VGLPERPG Y RWEPLVDTGK PAPYDFLTDD LPDRAHAVHL FSHFLNSNLY PMLSYSSIIL ELQPDD UniProtKB: Isoamylase 1, chloroplastic |
-分子 #2: Isoamylase 2, chloroplastic
| 分子 | 名称: Isoamylase 2, chloroplastic / タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / コピー数: 1 / 光学異性体: LEVO / EC番号: isoamylase |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 86.622008 KDa |
| 組換発現 | 生物種:  |
| 配列 | 文字列: MASLPAPPTP LGSCPRGRGG GRVVARPRRA GLACAARSCY RFRTDDDGVV DVAVSGEDGD GGGGGYAVSV EVPGTRGREG GLVLRASGS GEGVPLAPAA GGASLAAELS FDPTRAPFYL SFLLTDASGA EIRTHRKTSF RVPVGVGPGS PAPLGMSISG D GAVNFAVY ...文字列: MASLPAPPTP LGSCPRGRGG GRVVARPRRA GLACAARSCY RFRTDDDGVV DVAVSGEDGD GGGGGYAVSV EVPGTRGREG GLVLRASGS GEGVPLAPAA GGASLAAELS FDPTRAPFYL SFLLTDASGA EIRTHRKTSF RVPVGVGPGS PAPLGMSISG D GAVNFAVY SKNANAVSLY LYAAAVGGGG GDEPALEIDL DPYIHRTGNV WHVSLASVDG YVSYAFCCGG IRRPLLDPYA KV IGDFVSS NSVYDEGVTA PSMRCFASLA IAPSYNWGRD RHPRLPLEKL VVYRANVALF TKDRSSGLPD DAAGTFTGLS AKV EHFRSL GVNAILLEPV FPFHQVKGPY FPYHFFSPMN LYSSKGLSVS AIKSMKDMVR VMHRNGIEVL LEVVFTHTAE GESE CQTIS MRGIDNSSYY IANGIAGCKA SILNCNHPVT QKLILDSLRH WVLDFHVDGF CFINAPFLVR GPGGEYLSRP PLLEA ITFD PVLSMTKIIA DPWSPLDISN VQFPFPHWKR WAEVNTRFSI DVRKFLKREA LISDLATRLC GSGDLFSTRG PAFSFN HVS RNSGLSLVDL VSFSNDDLLS ESSWNCGEEG PSENSAVLQT RLRQIRNFLF ILFVSLGVPV LNMGDECGHS AAGSVSY KD RGPLNWRGMK TTFVKEVTGF ISFLTALRSR RGDIFQRREF LKLENIHWYG SDLCEPGWDD PTSNFLCMHI NAEVDEMA A DSVRGDLYIC FNANEESVSA ALPALAEGSV WLRLVDTSLA FPGFFATESN PKVQQVPGLS SYHVEAHTCV LFESKSALA UniProtKB: Isoamylase 2, chloroplastic |
-分子 #5: alpha-D-glucopyranose
| 分子 | 名称: alpha-D-glucopyranose / タイプ: ligand / ID: 5 / コピー数: 7 / 式: GLC |
|---|---|
| 分子量 | 理論値: 180.156 Da |
| Chemical component information | 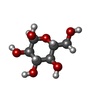 ChemComp-GLC: |
-実験情報
-構造解析
| 手法 | クライオ電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
 解析 解析 | 単粒子再構成法 |
| 試料の集合状態 | particle |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 緩衝液 | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| 凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE |
- 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法
| 顕微鏡 | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| 撮影 | フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) 平均電子線量: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| 電子線 | 加速電圧: 300 kV / 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| 電子光学系 | 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM / 撮影モード: BRIGHT FIELD / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 1.6 µm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 1.2 µm |
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)




































