+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | E. coli MaeB acetyl-CoA bound form | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | oxidoreductase / cryo-EM / allostery / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmalolactic enzyme activity / malate dehydrogenase (oxaloacetate-decarboxylating) (NADP+) / malate dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) (NADP+) activity / oxaloacetate decarboxylase activity / malate metabolic process / acyltransferase activity / NAD binding / manganese ion binding / identical protein binding / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.03 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Sassa M / Yamato H / Tanino H / Fukuda Y / Inoue T | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 2 items Japan, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2025 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2025Title: Divergent acetyl-CoA binding modes mediate allosteric inhibition of bacterial hybrid-type malic enzymes. Authors: Munetoshi Sassa / Haruka Yamato / Hiroki Tanino / Yohta Fukuda / Tsuyoshi Inoue /  Abstract: Malic enzymes (MEs) function as the bypass enzyme in the Krebs cycle and have attracted attention in a wide range of scientific and industrial fields. In contrast to eukaryotic MEs, there is ...Malic enzymes (MEs) function as the bypass enzyme in the Krebs cycle and have attracted attention in a wide range of scientific and industrial fields. In contrast to eukaryotic MEs, there is currently a lack of understanding of the structure-function relationships of prokaryotic MEs. Especially, little is known about an allosteric inhibition mechanism by an effector ligand in multi-domain MEs called hybrid-type MEs. Many bacterial hybrid-type MEs are inhibited by acetyl-CoA; however, the proposed acetyl-CoA binding site is not conserved. Here, we determined crystal and cryo-EM structures of hybrid-type MEs from Escherichia coli (EcMaeB) and Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus including complexes with acetyl-CoA. They reveal that these MaeBs have totally different acetyl-CoA binding sites and show different overall structural changes. However, the binding acetyl-CoA molecules induce identical movements of several α helices near the ligand both in EcMaeB and BbMaeB. Enzymatic assays proved that residues at the acetyl-CoA binding site are needed for inhibition. Phylogenetic analysis uncovered that EcMaeB and BbMaeB are classified into different clades of hybrid-type MEs and that the amino acid residues at the acetyl-CoA binding sites in different clades have evolved exclusively from each other. These results not only provide insights into bacterial MEs but also expand our knowledge about allosteric regulation in enzymes. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_62816.map.gz emd_62816.map.gz | 483.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-62816-v30.xml emd-62816-v30.xml emd-62816.xml emd-62816.xml | 20 KB 20 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_62816_fsc.xml emd_62816_fsc.xml | 16.7 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_62816.png emd_62816.png | 206 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_62816_msk_1.map emd_62816_msk_1.map emd_62816_msk_2.map emd_62816_msk_2.map emd_62816_msk_3.map emd_62816_msk_3.map | 512 MB 512 MB 512 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-62816.cif.gz emd-62816.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_62816_half_map_1.map.gz emd_62816_half_map_1.map.gz emd_62816_half_map_2.map.gz emd_62816_half_map_2.map.gz | 474.6 MB 474.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-62816 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-62816 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-62816 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-62816 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9l4nMC  9krtC  9kruC  9krvC  9krwC  9m2iC  9m35C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_62816.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_62816.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.87 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_62816_msk_1.map emd_62816_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Mask #2
| File |  emd_62816_msk_2.map emd_62816_msk_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Mask #3
| File |  emd_62816_msk_3.map emd_62816_msk_3.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_62816_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_62816_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Malic enzyme B from Escherichia coli acetyl-CoA bound form
| Entire | Name: Malic enzyme B from Escherichia coli acetyl-CoA bound form |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Malic enzyme B from Escherichia coli acetyl-CoA bound form
| Supramolecule | Name: Malic enzyme B from Escherichia coli acetyl-CoA bound form type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: NADP-dependent malic enzyme
| Macromolecule | Name: NADP-dependent malic enzyme / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number: malate dehydrogenase (oxaloacetate-decarboxylating) (NADP+) |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 82.507266 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MDDQLKQSAL DFHEFPVPGK IQVSPTKPLA TQRDLALAYS PGVAAPCLEI EKDPLKAYKY TARGNLVAVI SNGTAVLGLG NIGALAGKP VMEGKGVLFK KFAGIDVFDI EVDELDPDKF IEVVAALEPT FGGINLEDIK APECFYIEQK LRERMNIPVF H DDQHGTAI ...String: MDDQLKQSAL DFHEFPVPGK IQVSPTKPLA TQRDLALAYS PGVAAPCLEI EKDPLKAYKY TARGNLVAVI SNGTAVLGLG NIGALAGKP VMEGKGVLFK KFAGIDVFDI EVDELDPDKF IEVVAALEPT FGGINLEDIK APECFYIEQK LRERMNIPVF H DDQHGTAI ISTAAILNGL RVVEKNISDV RMVVSGAGAA AIACMNLLVA LGLQKHNIVV CDSKGVIYQG REPNMAETKA AY AVVDDGK RTLDDVIEGA DIFLGCSGPK VLTQEMVKKM ARAPMILALA NPEPEILPPL AKEVRPDAII CTGRSDYPNQ VNN VLCFPF IFRGALDVGA TAINEEMKLA AVRAIAELAH AEQSEVVASA YGDQDLSFGP EYIIPKPFDP RLIVKIAPAV AKAA MESGV ATRPIADFDV YIDKLTEFVY KTNLFMKPIF SQARKAPKRV VLPEGEEARV LHATQELVTL GLAKPILIGR PNVIE MRIQ KLGLQIKAGV DFEIVNNESD PRFKEYWTEY FQIMKRRGVT QEQAQRALIS NPTVIGAIMV QRGEADAMIC GTVGDY HEH FSVVKNVFGY RDGVHTAGAM NALLLPSGNT FIADTYVNDE PDAEELAEIT LMAAETVRRF GIEPRVALLS HSNFGSS DC PSSSKMRQAL ELVRERAPEL MIDGEMHGDA ALVEAIRNDR MPDSSLKGSA NILVMPNMEA ARISYNLLRV SSSEGVTV G PVLMGVAKPV HVLTPIASVR RIVNMVALAV VEAQTQPL UniProtKB: NADP-dependent malic enzyme |
-Macromolecule #2: NADP NICOTINAMIDE-ADENINE-DINUCLEOTIDE PHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: NADP NICOTINAMIDE-ADENINE-DINUCLEOTIDE PHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: NAP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 743.405 Da |
| Chemical component information | 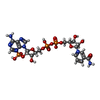 ChemComp-NAP: |
-Macromolecule #3: ACETYL COENZYME *A
| Macromolecule | Name: ACETYL COENZYME *A / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ACO |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 809.571 Da |
| Chemical component information | 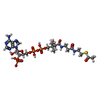 ChemComp-ACO: |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
| |||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 20 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Pretreatment - Pressure: 0.007 kPa / Details: 20 mA current | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 281 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV Details: 3 microliters droplet, 3 seconds delay before blotting, 3 seconds blot, 0 second delay before plunging.. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | JEOL CRYO ARM 300 |
|---|---|
| Software | Name: SerialEM |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 10332 / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.7000000000000001 µm |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Software | Name:  UCSF Chimera UCSF Chimera |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-9l4n: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





























































