[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-6152: Structures of Protective Antibodies Reveal Sites of Vulnerability... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-6152 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
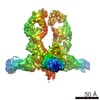
| Title | Structures of Protective Antibodies Reveal Sites of Vulnerability on Ebola Virus | |||||||||
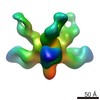
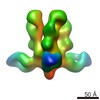
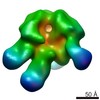
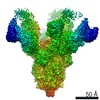
 Map data Map data | Reconstruction of Ebola virus glycoprotein bound to Fab fragments of c13C6 and c4G7 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Ebola / Antibody cocktails / mAbs / ZMAb / ZMapp / MB-003 | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Ebola virus sp. / Ebola virus sp. /  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / negative staining / Resolution: 24.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Murin CD / Fusco ML / Bornholdt ZA / Qiu X / Olinger GG / Zeitlin L / Kobinger GP / Ward AB / Saphire EO | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2014 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2014Title: Structures of protective antibodies reveal sites of vulnerability on Ebola virus. Authors: Charles D Murin / Marnie L Fusco / Zachary A Bornholdt / Xiangguo Qiu / Gene G Olinger / Larry Zeitlin / Gary P Kobinger / Andrew B Ward / Erica Ollmann Saphire /   Abstract: Ebola virus (EBOV) and related filoviruses cause severe hemorrhagic fever, with up to 90% lethality, and no treatments are approved for human use. Multiple recent outbreaks of EBOV and the likelihood ...Ebola virus (EBOV) and related filoviruses cause severe hemorrhagic fever, with up to 90% lethality, and no treatments are approved for human use. Multiple recent outbreaks of EBOV and the likelihood of future human exposure highlight the need for pre- and postexposure treatments. Monoclonal antibody (mAb) cocktails are particularly attractive candidates due to their proven postexposure efficacy in nonhuman primate models of EBOV infection. Two candidate cocktails, MB-003 and ZMAb, have been extensively evaluated in both in vitro and in vivo studies. Recently, these two therapeutics have been combined into a new cocktail named ZMapp, which showed increased efficacy and has been given compassionately to some human patients. Epitope information and mechanism of action are currently unknown for most of the component mAbs. Here we provide single-particle EM reconstructions of every mAb in the ZMapp cocktail, as well as additional antibodies from MB-003 and ZMAb. Our results illuminate key and recurring sites of vulnerability on the EBOV glycoprotein and provide a structural rationale for the efficacy of ZMapp. Interestingly, two of its components recognize overlapping epitopes and compete with each other for binding. Going forward, this work now provides a basis for strategic selection of next-generation antibody cocktails against Ebola and related viruses and a model for predicting the impact of ZMapp on potential escape mutations in ongoing or future Ebola outbreaks. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_6152.map.gz emd_6152.map.gz | 1.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-6152-v30.xml emd-6152-v30.xml emd-6152.xml emd-6152.xml | 11.1 KB 11.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_6152.jpg emd_6152.jpg | 143.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6152 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6152 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6152 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6152 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_6152.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 1.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_6152.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 1.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Reconstruction of Ebola virus glycoprotein bound to Fab fragments of c13C6 and c4G7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 4.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Fab fragment of c13C6 and c4G7 chimerized human monoclonal IgG1 a...
| Entire | Name: Fab fragment of c13C6 and c4G7 chimerized human monoclonal IgG1 antibody bound to Ebola virus glycoprotein |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Fab fragment of c13C6 and c4G7 chimerized human monoclonal IgG1 a...
| Supramolecule | Name: Fab fragment of c13C6 and c4G7 chimerized human monoclonal IgG1 antibody bound to Ebola virus glycoprotein type: sample / ID: 1000 Oligomeric state: Six Fab fragments bound to a single, trimeric GP (two Fabs per protomer) Number unique components: 3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 750 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Ebola virus glycoprotein
| Macromolecule | Name: Ebola virus glycoprotein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: EBOV GP / Number of copies: 1 / Oligomeric state: trimer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Ebola virus sp. Ebola virus sp. |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 450 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #2: chimerized human IgG1 antigen binding fragment c13C6
| Macromolecule | Name: chimerized human IgG1 antigen binding fragment c13C6 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Name.synonym: c13C6 Fab / Number of copies: 3 / Oligomeric state: monomer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: human Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: human |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #3: chimerized human IgG1 antigen binding fragment c4G7
| Macromolecule | Name: chimerized human IgG1 antigen binding fragment c4G7 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Name.synonym: c4G7 Fab / Number of copies: 3 / Oligomeric state: monomer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: human Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: human |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.03 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 / Details: 20 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl |
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE Details: To prepare negative stain grids, a 4 uL aliquot of each complex, which had been diluted to a concentration of ~0.03 ug/mL with TBS buffer, was placed for 15 seconds onto carbon-coated 400 Cu ...Details: To prepare negative stain grids, a 4 uL aliquot of each complex, which had been diluted to a concentration of ~0.03 ug/mL with TBS buffer, was placed for 15 seconds onto carbon-coated 400 Cu mesh grids that had been plasma cleaned for 20 s (Gatan), blotted off on the edge of the grid, then immediately stained for 30 s with 4 uL of 2% uranyl formate. The stain was blotted off on the edge of the grid and the grid was allowed to dry. |
| Grid | Details: 400 Cu mesh |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: NONE / Instrument: OTHER |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| Date | Feb 5, 2014 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: OTHER / Number real images: 65 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 120 kV / Electron source: TUNGSTEN HAIRPIN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 52000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: OTHER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 24.0 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: EMAN2, XMipp, IMAGIC / Number images used: 10210 |
|---|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera


 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















