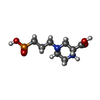
登録情報 データベース : EMDB / ID : EMD-61000タイトル Structure of the human GluN1-N2B NMDA receptors in the Mg2+ bound state 複合体 : Human GluN1-N2B receptors in the Mg2+-bond stateタンパク質・ペプチド : Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1タンパク質・ペプチド : Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2Bリガンド : GLYCINEリガンド : 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranoseリガンド : (2R)-4-(3-phosphonopropyl)piperazine-2-carboxylic acidリガンド : MAGNESIUM ION / 機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Homo sapiens (ヒト)手法 / / 解像度 : 3.27 Å Huang X / Sun X / Zhu S 資金援助 Organization Grant number 国 Ministry of Science and Technology (MoST, China) 2022ZD0212700 National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) 32221003 Chinese Academy of Sciences to S.Z.
ジャーナル : Neuron / 年 : 2025タイトル : Structural insights into the diverse actions of magnesium on NMDA receptors.著者 : Xuejing Huang / Xiaole Sun / Qinrui Wang / Jilin Zhang / Han Wen / Wan-Jin Chen / Shujia Zhu / 要旨 : Magnesium (Mg) is a key regulatory ion of N-methyl-ᴅ-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, including conferring them to function as coincidence detectors for excitatory synaptic transmission. However, the ... Magnesium (Mg) is a key regulatory ion of N-methyl-ᴅ-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, including conferring them to function as coincidence detectors for excitatory synaptic transmission. However, the structural basis underlying the Mg action on NMDA receptors remains unclear. Here, we report the cryo-EM structures of GluN1-N2B receptors and identify three distinct Mg-binding pockets. Specifically, site Ⅰ is located at the selectivity filter where an asparagine ring forms coordination bonds with Mg and is responsible for the voltage-dependent block. Sites Ⅱ and Ⅲ are located at the N-terminal domain (NTD) of the GluN2B subunit and involved in the allosteric potentiation and inhibition, respectively. Site Ⅱ consists of three acidic residues, and the combination of three mutations abolishes the GluN2B-specific Mg potentiation, while site Ⅲ overlaps with the Zn pocket, and mutations here significantly reduce the inhibition. Our study enhances the understanding of multifaceted roles of Mg in NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity. 履歴 登録 2024年7月31日 - ヘッダ(付随情報) 公開 2025年3月5日 - マップ公開 2025年3月5日 - 更新 2025年4月16日 - 現状 2025年4月16日 処理サイト : PDBc / 状態 : 公開
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報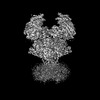
 マップデータ
マップデータ 試料
試料 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) データ登録者
データ登録者 中国, 3件
中国, 3件  引用
引用 ジャーナル: Neuron / 年: 2025
ジャーナル: Neuron / 年: 2025
 構造の表示
構造の表示 ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク emd_61000.map.gz
emd_61000.map.gz EMDBマップデータ形式
EMDBマップデータ形式 emd-61000-v30.xml
emd-61000-v30.xml emd-61000.xml
emd-61000.xml EMDBヘッダ
EMDBヘッダ emd_61000_fsc.xml
emd_61000_fsc.xml FSCデータファイル
FSCデータファイル emd_61000.png
emd_61000.png emd_61000_msk_1.map
emd_61000_msk_1.map マスクマップ
マスクマップ emd-61000.cif.gz
emd-61000.cif.gz emd_61000_half_map_1.map.gz
emd_61000_half_map_1.map.gz emd_61000_half_map_2.map.gz
emd_61000_half_map_2.map.gz http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-61000
http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-61000 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-61000
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-61000 emd_61000_validation.pdf.gz
emd_61000_validation.pdf.gz EMDB検証レポート
EMDB検証レポート emd_61000_full_validation.pdf.gz
emd_61000_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_61000_validation.xml.gz
emd_61000_validation.xml.gz emd_61000_validation.cif.gz
emd_61000_validation.cif.gz https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-61000
https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-61000 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-61000
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-61000

 F&H 検索
F&H 検索 リンク
リンク EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /
EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource
EMDataResource マップ
マップ ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_61000.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 163.6 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES)
ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_61000.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 163.6 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) emd_61000_msk_1.map
emd_61000_msk_1.map 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト)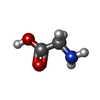

 解析
解析 試料調製
試料調製 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法 FIELD EMISSION GUN
FIELD EMISSION GUN
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー

















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)














































