+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
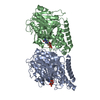
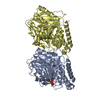
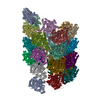
| Title | CryoEM structure of Asgard AtubA/B microtubule | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Asgard archaea / microtubule / cryoEM / cytomotive filaments / cytoskeleton / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Candidatus Lokiarchaeum ossiferum (archaea) Candidatus Lokiarchaeum ossiferum (archaea) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wollweber F / Xu J / Ponce-Toledo RI / Rodrigues-Oliveira T / Malit JJL / Kokhanovska A / Wieczorek M / Schleper C / Pilhofer M | |||||||||
| Funding support | European Union, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2025 Journal: Cell / Year: 2025Title: Microtubules in Asgard archaea. Authors: Florian Wollweber / Jingwei Xu / Rafael I Ponce-Toledo / Florina Marxer / Thiago Rodrigues-Oliveira / Anja Pössnecker / Zhen-Hao Luo / Jessie James Limlingan Malit / Anastasiia Kokhanovska ...Authors: Florian Wollweber / Jingwei Xu / Rafael I Ponce-Toledo / Florina Marxer / Thiago Rodrigues-Oliveira / Anja Pössnecker / Zhen-Hao Luo / Jessie James Limlingan Malit / Anastasiia Kokhanovska / Michal Wieczorek / Christa Schleper / Martin Pilhofer /   Abstract: Microtubules are a hallmark of eukaryotes. Archaeal and bacterial homologs of tubulins typically form homopolymers and non-tubular superstructures. The origin of heterodimeric tubulins assembling ...Microtubules are a hallmark of eukaryotes. Archaeal and bacterial homologs of tubulins typically form homopolymers and non-tubular superstructures. The origin of heterodimeric tubulins assembling into microtubules remains unclear. Here, we report the discovery of microtubule-forming tubulins in Asgard archaea, the closest known relatives of eukaryotes. These Asgard tubulins (AtubA/B) are closely related to eukaryotic α/β-tubulins and the enigmatic bacterial tubulins BtubA/B. Proteomics of Candidatus Lokiarchaeum ossiferum showed that AtubA/B were highly expressed. Cryoelectron microscopy structures demonstrate that AtubA/B form eukaryote-like heterodimers, which assembled into 5-protofilament bona fide microtubules in vitro. The additional paralog AtubB2 lacks a nucleotide-binding site and competitively displaced AtubB. These AtubA/B2 heterodimers polymerized into 7-protofilament non-canonical microtubules. In a sub-population of Ca. Lokiarchaeum ossiferum cells, cryo-tomography revealed tubular structures, while expansion microscopy identified AtubA/B cytoskeletal assemblies. Our findings suggest a pre-eukaryotic origin of microtubules and provide a framework for understanding the fundamental principles of microtubule assembly. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_52465.map.gz emd_52465.map.gz | 38.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-52465-v30.xml emd-52465-v30.xml emd-52465.xml emd-52465.xml | 14.9 KB 14.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_52465.png emd_52465.png | 44.5 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_52465_msk_1.map emd_52465_msk_1.map | 178 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-52465.cif.gz emd-52465.cif.gz | 5.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_52465_half_map_1.map.gz emd_52465_half_map_1.map.gz emd_52465_half_map_2.map.gz emd_52465_half_map_2.map.gz | 141.9 MB 141.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-52465 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-52465 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-52465 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-52465 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_52465.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_52465.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.065 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_52465_msk_1.map emd_52465_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_52465_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_52465_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : microtubule structure of Asgard tubulins AtubA/B
| Entire | Name: microtubule structure of Asgard tubulins AtubA/B |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: microtubule structure of Asgard tubulins AtubA/B
| Supramolecule | Name: microtubule structure of Asgard tubulins AtubA/B / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Candidatus Lokiarchaeum ossiferum (archaea) Candidatus Lokiarchaeum ossiferum (archaea) |
-Macromolecule #1: Asgard tubulin AtubA
| Macromolecule | Name: Asgard tubulin AtubA / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Candidatus Lokiarchaeum ossiferum (archaea) Candidatus Lokiarchaeum ossiferum (archaea) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAGEIVCIQV GQAGNQIAGA FWQKICAEHG IDPVNGKAID VVGDTDIFFN TIGDKYIPRA VVVDLEPAV VENIREKFGT LFDPKSIVSG ADGAGNNFAI GFNEHGAETL EKVMQVVEQR V SETESIGG FILTHSCGGG TGSGFGSKIL KTIRERYPKV PIFTFSIFPS ...String: MAGEIVCIQV GQAGNQIAGA FWQKICAEHG IDPVNGKAID VVGDTDIFFN TIGDKYIPRA VVVDLEPAV VENIREKFGT LFDPKSIVSG ADGAGNNFAI GFNEHGAETL EKVMQVVEQR V SETESIGG FILTHSCGGG TGSGFGSKIL KTIRERYPKV PIFTFSIFPS PKISETVVEP YN AIMTLSN LIKYASCSIV LDNEALFSIA EKKLEVENPS LEDLNLIIAQ VLTNVTASLR FSG TLNLDL GKLVTNLVPF SNLHFLMAST APLVLAGKES YEKMTAKELS AQVFGDEYIC AACK PTTGR YLAASVLFRG AVKTSDVNEA MATVKEQNSF VNWIPTGFKI SKSETSPKDS ALGVI MLGN NSEIVSVFER IGANFDRLWS RKAFAHWFTD SGFEEKDLDD ARALVQKVID DYRKLT EDA |
-Macromolecule #2: Asgard tubulin AtubB
| Macromolecule | Name: Asgard tubulin AtubB / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Candidatus Lokiarchaeum ossiferum (archaea) Candidatus Lokiarchaeum ossiferum (archaea) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGREVIMLHV GQAGIQVGAM YWKQICAEHN LDHNGAPIGG DIKGDPDCFF MKASGGKYVP RALLIDLEP KVVRQVGNEQ LPSFFDPKNL IHGLYGGANS FAKGYLGEGR DMIDNIMEQL K KEVAKCES LQGFIMTHAV GGGSGGGLGC LIMEKIKEEY PKKILWSYSI ...String: MGREVIMLHV GQAGIQVGAM YWKQICAEHN LDHNGAPIGG DIKGDPDCFF MKASGGKYVP RALLIDLEP KVVRQVGNEQ LPSFFDPKNL IHGLYGGANS FAKGYLGEGR DMIDNIMEQL K KEVAKCES LQGFIMTHAV GGGSGGGLGC LIMEKIKEEY PKKILWSYSI LPSPLLSDAV VE PYNAILS LDKMIQYTDE TVVIDNHALF QIVTKNMGID DPIYDDLNHV ISQALSDITA SLR FKGSLN TDMKEFLVNL VPYPRSHFLM ASFAPMATAE DRQYAKLTTS NLANALFEEN YMMA AVDVT KGTFLACSLL FRGENTAQDI TNALLDIKGR IKFSSFIPTG IKYGMTGTAP EGLER SGSA LINHTGVAEI FNRILAQFNL MFDKGAFLNW YEIEGMSKDD FAGARDNVQK LSDEYK RDE E |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 6.8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.4 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)












































