+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | MUC5AC mucin amino acids 28 to 1483 | |||||||||
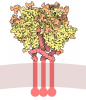
 Map data Map data | map resulting from local refinement around one bead of the MUC5AC two-start helix | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | mucin / lung / filament / polymer / disulfide / PROTEIN FIBRIL | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmucus layer / Defective GALNT3 causes HFTC / Defective C1GALT1C1 causes TNPS / Defective GALNT12 causes CRCS1 / Termination of O-glycan biosynthesis / O-linked glycosylation of mucins / extracellular matrix structural constituent / Dectin-2 family / extracellular matrix / Golgi lumen ...mucus layer / Defective GALNT3 causes HFTC / Defective C1GALT1C1 causes TNPS / Defective GALNT12 causes CRCS1 / Termination of O-glycan biosynthesis / O-linked glycosylation of mucins / extracellular matrix structural constituent / Dectin-2 family / extracellular matrix / Golgi lumen / extracellular space / extracellular exosome / metal ion binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.91 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Haberman M / Kamyshinsky R / Fass D | |||||||||
| Funding support | European Union,  Israel, 2 items Israel, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025Title: MUC5AC filaments illuminate the structural diversification of respiratory and intestinal mucins. Authors: Meital Haberman / Roman Kamyshinsky / Nava Reznik / Noa Yeshaya / Lev Khmelnitsky / Elizabeth G Plender / Evan E Eichler / Deborah Fass /   Abstract: Secreted mucins are multimegadalton glycoprotein polymers that share the function of protecting mucosal tissues but diversified for activities in different organs of the body. Structural studies of ...Secreted mucins are multimegadalton glycoprotein polymers that share the function of protecting mucosal tissues but diversified for activities in different organs of the body. Structural studies of secreted mucins are complicated by the enormous sizes, flexibility, and complex supramolecular assembly modes of these glycoproteins. The two major respiratory mucins are MUC5AC and MUC5B. Here, we present structures of a large amino-terminal segment of MUC5AC in the form of helical filaments. These filaments differ from filamentous and tubular structures observed previously for the intestinal mucin MUC2 and the partial mucin homolog VWF. Nevertheless, the MUC5AC helical filaments support the proposed mechanism, based on MUC2 and VWF, for how noncovalent interactions between mucin monomers guide disulfide crosslinking to form polymers. The high-resolution MUC5AC structures show how local and limited changes in amino acid sequence can profoundly affect higher-order assembly while preserving the overall folds and polymerization activity of mucin glycoproteins. Differences in supramolecular assembly are likely to be functionally significant considering the divergence of mechanical properties and physiological requirements between respiratory and intestinal mucins. Determining the high-resolution structures of respiratory mucins provides a foundation for understanding the mechanisms by which they clean and protect the lungs. Moreover, the MUC5AC structure enables visualization of the sites of human amino acid sequence variation and disease-associated mutations. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_51636.map.gz emd_51636.map.gz | 326.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-51636-v30.xml emd-51636-v30.xml emd-51636.xml emd-51636.xml | 19.8 KB 19.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_51636_fsc.xml emd_51636_fsc.xml | 18.3 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_51636.png emd_51636.png | 124.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-51636.cif.gz emd-51636.cif.gz | 7.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_51636_half_map_1.map.gz emd_51636_half_map_1.map.gz emd_51636_half_map_2.map.gz emd_51636_half_map_2.map.gz | 589.6 MB 589.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-51636 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-51636 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-51636 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-51636 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_51636_validation.pdf.gz emd_51636_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_51636_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_51636_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_51636_validation.xml.gz emd_51636_validation.xml.gz | 28.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_51636_validation.cif.gz emd_51636_validation.cif.gz | 36.9 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-51636 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-51636 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-51636 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-51636 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9gvjMC  9gvqC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_51636.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 634.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_51636.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 634.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | map resulting from local refinement around one bead of the MUC5AC two-start helix | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.8242 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_51636_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_51636_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : filament of the MUC5AC amino-terminal segment
| Entire | Name: filament of the MUC5AC amino-terminal segment |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: filament of the MUC5AC amino-terminal segment
| Supramolecule | Name: filament of the MUC5AC amino-terminal segment / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Tissue: lung / Location in cell: secreted Homo sapiens (human) / Tissue: lung / Location in cell: secreted |
-Macromolecule #1: Mucin-5AC
| Macromolecule | Name: Mucin-5AC / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 157.080688 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: QDGSSESSYK HHPALSPIAR GPSGVPLRGA TVFPSLRTIP VVRASNPAHN GRVCSTWGSF HYKTFDGDVF RFPGLCNYVF SEHCGAAYE DFNIQLRRSQ ESAAPTLSRV LMKVDGVVIQ LTKGSVLVNG HPVLLPFSQS GVLIQQSSSY TKVEARLGLV L MWNHDDSL ...String: QDGSSESSYK HHPALSPIAR GPSGVPLRGA TVFPSLRTIP VVRASNPAHN GRVCSTWGSF HYKTFDGDVF RFPGLCNYVF SEHCGAAYE DFNIQLRRSQ ESAAPTLSRV LMKVDGVVIQ LTKGSVLVNG HPVLLPFSQS GVLIQQSSSY TKVEARLGLV L MWNHDDSL LLELDTKYAN KTCGLCGDFN GMPVVSELLS HNTKLTPMEF GNLQKMDDPT DQCQDPVPEP PRNCSTGFGI CE ELLHGQL FSGCVALVDV GSYLEACRQD LCFCEDTDLL SCVCHTLAEY SRQCTHAGGL PQDWRGPDFC PQKCPNNMQY HEC RSPCAD TCSNQEHSRA CEDHCVAGCF CPEGTVLDDI GQTGCVPVSK CACVYNGAAY APGATYSTDC TNCTCSGGRW SCQE VPCPG TCSVLGGAHF STFDGKQYTV HGDCSYVLTK PCDSSAFTVL AELRRCGLTD SETCLKSVTL SLDGAQTVVV IKASG EVFL NQIYTQLPIS AANVTIFRPS TFFIIAQTSL GLQLNLQLVP TMQLFMQLAP KLRGQTCGLC GNFNSIQADD FRTLSG VVE ATAAAFFNTF KTQAACPNIR NSFEDPCSLS VENEKYAQHW CSQLTDADGP FGRCHAAVKP GTYYSNCMFD TCNCERS ED CLCAALSSYV HACAAKGVQL GGWRDGVCTK PMTTCPKSMT YHYHVSTCQP TCRSLSEGDI TCSVGFIPVD GCICPKGT F LDDTGKCVQA SNCPCYHRGS MIPNGESVHD SGAICTCTHG KLSCIGGQAP APVCAAPMVF FDCRNATPGD TGAGCQKSC HTLDMTCYSP QCVPGCVCPD GLVADGEGGC ITAEDCPCVH NEASYRAGQT IRVGCNTCTC DSRMWRCTDD PCLATCAVYG DGHYLTFDG QSYSFNGDCE YTLVQNHCGG KDSTQDSFRV VTENVPCGTT GTTCSKAIKI FLGGFELKLS HGKVEVIGTD E SQEVPYTI RQMGIYLVVD TDIGLVLLWD KKTSIFINLS PEFKGRVCGL CGNFDDIAVN DFATRSRSVV GDVLEFGNSW KL SPSCPDA LAPKDPCTAN PFRKSWAQKQ CSILHGPTFA ACHAHVEPAR YYEACVNDAC ACDSGGDCEC FCTAVAAYAQ ACH EVGLCV SWRTPSICPL FCDYYNPEGQ CEWHYQPCGV PCLRTCRNPR GDCLRDVRGL EGCYPKCPPE APIFDEDKMQ CVAT CPTPP LPPRCHVHGK SYRPGAVVPS DKNCQSCLCT ERGVECTYKA EACVCTYNGQ RFHPGDVIYH TTDGTGGCIS ARCGA NGTI ERRVYPCSPT TPVPPTTFSF STPPLVVSST HTPSNGPSSA HTGPPSSAWP TTAGTSPRTR LPTASASLPP VCGEKC LWS PWMDVSRPGR GTDSGDFDTL ENLRAHGYRV CESPRSVECR AEDAPGVPLR ALGQRVQCSP DVGLTCRNRE QASGLCY NY QIRVQCCTPL PCST UniProtKB: Mucin-5AC |
-Macromolecule #2: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #3: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: COPPER (II) ION
| Macromolecule | Name: COPPER (II) ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: CU |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 63.546 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-CU: |
-Macromolecule #5: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 177 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.45 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 5.2 Component:
| |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 45.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.6 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





































