+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
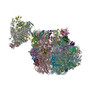
| Title | 30S-TEC (TEC in expressome position) Inactive state 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Transcription / translation / coupling / RIBOSOME | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of cytoplasmic translation / transcription elongation-coupled chromatin remodeling / RNA polymerase complex / submerged biofilm formation / cellular response to cell envelope stress / regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation / bacterial-type flagellum assembly / transcription antitermination factor activity, RNA binding / ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor activity / bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding ...positive regulation of cytoplasmic translation / transcription elongation-coupled chromatin remodeling / RNA polymerase complex / submerged biofilm formation / cellular response to cell envelope stress / regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation / bacterial-type flagellum assembly / transcription antitermination factor activity, RNA binding / ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor activity / bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding / cytosolic DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / misfolded RNA binding / Group I intron splicing / RNA folding / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / nitrate assimilation / negative regulation of cytoplasmic translation / four-way junction DNA binding / regulation of mRNA stability / positive regulation of RNA splicing / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / transcription elongation factor complex / transcription antitermination / DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / DNA endonuclease activity / cell motility / DNA-templated transcription initiation / DNA-templated transcription termination / maintenance of translational fidelity / mRNA 5'-UTR binding / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / regulation of translation / ribosome biogenesis / response to heat / ribosomal small subunit biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit assembly / protein-containing complex assembly / small ribosomal subunit / small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / cytoplasmic translation / tRNA binding / protein dimerization activity / negative regulation of translation / rRNA binding / single-stranded RNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / hydrolase activity / response to antibiotic / mRNA binding / DNA-templated transcription / magnesium ion binding / DNA binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Rahil H / Weixlbaumer A / Webster MW | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support | European Union,  France, France,  United States, United States,  United Kingdom, 6 items United Kingdom, 6 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2024 Journal: Science / Year: 2024Title: Molecular basis of mRNA delivery to the bacterial ribosome. Authors: Michael W Webster / Adrien Chauvier / Huma Rahil / Andrea Graziadei / Kristine Charles / Nataliya Miropolskaya / Maria Takacs / Charlotte Saint-André / Juri Rappsilber / Nils G Walter / Albert Weixlbaumer /     Abstract: Protein synthesis begins with the formation of a ribosome-messenger RNA (mRNA) complex. In bacteria, the small ribosomal subunit (30) is recruited to many mRNAs through base pairing with the Shine- ...Protein synthesis begins with the formation of a ribosome-messenger RNA (mRNA) complex. In bacteria, the small ribosomal subunit (30) is recruited to many mRNAs through base pairing with the Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence and RNA binding by ribosomal protein bS1. Translation can initiate on nascent mRNAs, and RNA polymerase (RNAP) can promote the recruitment of the pioneering 30. Here, we examined 30 recruitment to nascent mRNAs using cryo-electron microscopy, single-molecule fluorescence colocalization, and in-cell cross-linking mass spectrometry. We show that bS1 delivers the mRNA to the ribosome for SD duplex formation and 30 activation. Additionally, bS1 and RNAP stimulate translation initiation. Our work provides a mechanistic framework for how the SD duplex, ribosomal proteins, and RNAP cooperate in 30 recruitment to mRNAs and establish transcription-translation coupling. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_51622.map.gz emd_51622.map.gz | 740.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-51622-v30.xml emd-51622-v30.xml emd-51622.xml emd-51622.xml | 52.5 KB 52.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_51622.png emd_51622.png | 90.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-51622.cif.gz emd-51622.cif.gz | 14.7 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-51622 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-51622 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-51622 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-51622 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9guwMC  9gr1C  9gupC  9guqC  9gurC  9gusC  9gutC  9guuC  9guvC  9guxC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_51622.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 824 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_51622.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 824 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.84 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : 30S ribosomal subunit bound to TEC
+Supramolecule #1: 30S ribosomal subunit bound to TEC
+Supramolecule #2: TEC
+Macromolecule #1: 16S ribosomal RNA
+Macromolecule #22: mRNA
+Macromolecule #2: 30S ribosomal protein S1
+Macromolecule #3: 30S ribosomal protein S2
+Macromolecule #4: Small ribosomal subunit protein uS3
+Macromolecule #5: Small ribosomal subunit protein uS4
+Macromolecule #6: 30S ribosomal protein S5
+Macromolecule #7: Small ribosomal subunit protein bS6
+Macromolecule #8: 30S ribosomal protein S7
+Macromolecule #9: 30S ribosomal protein S8
+Macromolecule #10: 30S ribosomal protein S9
+Macromolecule #11: 30S ribosomal protein S10
+Macromolecule #12: 30S ribosomal protein S11
+Macromolecule #13: 30S ribosomal protein S12
+Macromolecule #14: 30S ribosomal protein S13
+Macromolecule #15: 30S ribosomal protein S14
+Macromolecule #16: Small ribosomal subunit protein uS15
+Macromolecule #17: 30S ribosomal protein S16
+Macromolecule #18: 30S ribosomal protein S17
+Macromolecule #19: 30S ribosomal protein S18
+Macromolecule #20: 30S ribosomal protein S19
+Macromolecule #21: 30S ribosomal protein S20
+Macromolecule #23: Transcription termination/antitermination protein NusG
+Macromolecule #24: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit alpha
+Macromolecule #25: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta
+Macromolecule #26: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta'
+Macromolecule #27: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit omega
+Macromolecule #28: Non-Template DNA strand
+Macromolecule #29: Template DNA strand
+Macromolecule #30: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #31: ZINC ION
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 49.95 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





















































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)