[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-50860: Cryo EM map of the type 2A polymorph of alpha-synuclein at pH 7.0. -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo EM map of the type 2A polymorph of alpha-synuclein at pH 7.0. | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | amyloid / polymorphism / PROTEIN FIBRIL | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
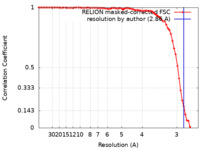
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.86 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Frey L / Qureshi BM / Kwiatkowski W / Rhyner D / Greenwald J / Riek R | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Switzerland, 2 items Switzerland, 2 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2024 Journal: Elife / Year: 2024Title: On the pH-dependence of α-synuclein amyloid polymorphism and the role of secondary nucleation in seed-based amyloid propagation. Authors: Lukas Frey / Dhiman Ghosh / Bilal M Qureshi / David Rhyner / Ricardo Guerrero-Ferreira / Aditya Pokharna / Witek Kwiatkowski / Tetiana Serdiuk / Paola Picotti / Roland Riek / Jason Greenwald /   Abstract: The aggregation of the protein α-synuclein is closely associated with several neurodegenerative disorders and as such the structures of the amyloid fibril aggregates have high scientific and medical ...The aggregation of the protein α-synuclein is closely associated with several neurodegenerative disorders and as such the structures of the amyloid fibril aggregates have high scientific and medical significance. However, there are dozens of unique atomic-resolution structures of these aggregates, and such a highly polymorphic nature of the α-synuclein fibrils hampers efforts in disease-relevant in vitro studies on α-synuclein amyloid aggregation. In order to better understand the factors that affect polymorph selection, we studied the structures of α-synuclein fibrils in vitro as a function of pH and buffer using cryo-EM helical reconstruction. We find that in the physiological range of pH 5.8-7.4, a pH-dependent selection between Type 1, 2, and 3 polymorphs occurs. Our results indicate that even in the presence of seeds, the polymorph selection during aggregation is highly dependent on the buffer conditions, attributed to the non-polymorph-specific nature of secondary nucleation. We also uncovered two new polymorphs that occur at pH 7.0 in phosphate-buffered saline. The first is a monofilament Type 1 fibril that highly resembles the structure of the juvenile-onset synucleinopathy polymorph found in patient-derived material. The second is a new Type 5 polymorph that resembles a polymorph that has been recently reported in a study that used diseased tissues to seed aggregation. Taken together, our results highlight the shallow amyloid energy hypersurface that can be altered by subtle changes in the environment, including the pH which is shown to play a major role in polymorph selection and in many cases appears to be the determining factor in seeded aggregation. The results also suggest the possibility of producing disease-relevant structure in vitro. #1:  Journal: Elife / Year: 2024 Journal: Elife / Year: 2024Title: On the pH-dependence of alpha-synuclein amyloid polymorphism and the role of secondary nucleation in seed-based amyloid propagation Authors: Frey L / Ghosh D / Qureshi BM / Rhyner D / Guerrero-Ferreira R / Pokharna A / Kwiatkowski W / Serdiuk T / Picotti P / Riek R / Greenwald J | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_50860.map.gz emd_50860.map.gz | 4.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-50860-v30.xml emd-50860-v30.xml emd-50860.xml emd-50860.xml | 16.7 KB 16.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_50860_fsc.xml emd_50860_fsc.xml | 7.1 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_50860.png emd_50860.png | 53.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-50860.cif.gz emd-50860.cif.gz | 5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_50860_half_map_1.map.gz emd_50860_half_map_1.map.gz emd_50860_half_map_2.map.gz emd_50860_half_map_2.map.gz | 22.3 MB 25.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50860 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50860 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50860 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50860 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_50860.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_50860.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
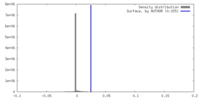
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_50860_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : alpha-synuclein amyloid fibril
| Entire | Name: alpha-synuclein amyloid fibril |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: alpha-synuclein amyloid fibril
| Supramolecule | Name: alpha-synuclein amyloid fibril / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: alpha-synuclein
| Macromolecule | Name: alpha-synuclein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MDVFMKGLSK AKEGVVAAA E KTKQGVAE AA GKTKEGV LYV GSKTKE GVVH GVATV AEKTK EQVT NVGGAV VTG VTAVAQK TV EGAGSIAA A TGFVKKDQL GKNEEGAPQE GILEDMPVD P DNEAYEMP SE EGYQDYE PEA |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7 Component:
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Number real images: 1339 / Average exposure time: 1.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 58.5 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm / Nominal magnification: 130000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL |
|---|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller













 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)