[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-50819: Cryo-EM structure of E. coli transcription factor NrdR in complex... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
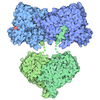
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of E. coli transcription factor NrdR in complex with DNA | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Sharpened map from non-uniform refinement in cryoSPARC | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | transcription factor / ribonucleotide reductase / repressor / ATP-cone / Zn-ribbon / DNA BINDING PROTEIN | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationdouble-stranded DNA binding / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / zinc ion binding / ATP binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.1 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Banerjee I / Bimai O / Martinez-Carranza M / Stenmark P / Sjoberg BM / Rozman Grinberg I / Logan DT | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Sweden, Sweden,  United States, 6 items United States, 6 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: FEBS J / Year: 2025 Journal: FEBS J / Year: 2025Title: Bacterial transcriptional repressor NrdR - a flexible multifactorial nucleotide sensor. Authors: Inna Rozman Grinberg / Ornella Bimaï / Saher Shahid / Lena Philipp / Markel Martínez-Carranza / Ipsita Banerjee / Daniel Lundin / Pål Stenmark / Britt-Marie Sjöberg / Derek T Logan /  Abstract: NrdR is a bacterial transcriptional repressor consisting of a zinc (Zn)-ribbon domain followed by an ATP-cone domain. Understanding its mechanism of action could aid the design of novel ...NrdR is a bacterial transcriptional repressor consisting of a zinc (Zn)-ribbon domain followed by an ATP-cone domain. Understanding its mechanism of action could aid the design of novel antibacterials. NrdR binds specifically to two "NrdR boxes" upstream of ribonucleotide reductase operons, of which Escherichia coli has three: nrdHIEF, nrdDG and nrdAB, in the last of which we identified a new box. We show that E. coli NrdR (EcoNrdR) has similar binding strength to all three sites when loaded with ATP plus deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP) or equivalent diphosphate combinations. No other combination of adenine nucleotides promotes binding to DNA. We present crystal structures of EcoNrdR-ATP-dATP and EcoNrdR-ADP-dATP, which are the first high-resolution crystal structures of an NrdR. We have also determined cryo-electron microscopy structures of DNA-bound EcoNrdR-ATP-dATP and novel filaments of EcoNrdR-ATP. Tetrameric forms of EcoNrdR involve alternating interactions between pairs of Zn-ribbon domains and ATP-cones. The structures reveal considerable flexibility in relative orientation of ATP-cones vs Zn-ribbon domains. The structure of DNA-bound EcoNrdR-ATP-dATP shows that significant conformational rearrangements between ATP-cones and Zn-ribbons accompany DNA binding while the ATP-cones retain the same relative orientation. In contrast, ATP-loaded EcoNrdR filaments show rearrangements of the ATP-cone pairs and sequester the DNA-binding residues of NrdR such that they are unable to bind to DNA. Our results, in combination with a previous structural and biochemical study, point to highly flexible EcoNrdR structures that, when loaded with the correct nucleotides, adapt to an optimal promoter-binding conformation. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_50819.map.gz emd_50819.map.gz | 59.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-50819-v30.xml emd-50819-v30.xml emd-50819.xml emd-50819.xml | 22.7 KB 22.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_50819_fsc.xml emd_50819_fsc.xml | 8.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_50819.png emd_50819.png | 93.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-50819.cif.gz emd-50819.cif.gz | 5.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_50819_additional_1.map.gz emd_50819_additional_1.map.gz emd_50819_half_map_1.map.gz emd_50819_half_map_1.map.gz emd_50819_half_map_2.map.gz emd_50819_half_map_2.map.gz | 57.4 MB 59.3 MB 59.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50819 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50819 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50819 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50819 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9fvrC  9fxkC  9fzfC C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_50819.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_50819.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Sharpened map from non-uniform refinement in cryoSPARC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.26 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Locally sharpened map from DeepEMhancer
| File | emd_50819_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Locally sharpened map from DeepEMhancer | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half-map B
| File | emd_50819_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half-map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half-map A
| File | emd_50819_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half-map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : E. coli NrdR/ATP/dATP/DNA
| Entire | Name: E. coli NrdR/ATP/dATP/DNA |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: E. coli NrdR/ATP/dATP/DNA
| Supramolecule | Name: E. coli NrdR/ATP/dATP/DNA / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: Tetrameric transcription factor NrdR from E. coli in complex with ATP, dATP and a DNA 57-mer containing two NrdR boxes. |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 128 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: E. coli NrdR
| Macromolecule | Name: E. coli NrdR / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MHCPFCFAVD TKVIDSRLVG EGSSVRRRRQ CLVCNERFTT FEVAELVMPR VVKSNDVREP FNEEKLRSGM LRALEKRPV SSDDVEMAIN HIKSQLRATG EREVPSKMIG NLVMEQLKKL DKVAYIRFAS VYRSFEDIKD F GEEIARLE DKLAAALEHH HHHH UniProtKB: Transcriptional repressor NrdR |
-Macromolecule #2: DNA 57-mer from E. coli with two NrdR boxes
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA 57-mer from E. coli with two NrdR boxes / type: dna / ID: 2 / Details: DNA 57-mer from E. coli with two NrdR boxes / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GCACTATTTG CTATATATTG TGTGGTTGAA TCTTTTTTCA ACTACATCTA GTATCTC |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.31 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8.5 Component:
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: GRAPHENE OXIDE / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 4 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | 16 uM monomeric protein, 6 uM oligonucleotide |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-40 / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 14789 / Average electron dose: 58.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.4 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Details | Three models were used to fit the best cryo-EM volume: DNA from the S. coelicor NrdR-dATP-ATP-DNA complex, and pairs of ATP-cones and Zn-ribbons from the EcNrdR-ATP-dAMPPNP complex. These were fitted to the volume using Molrep in the order DNA:ATP-cones:Zn ribbons. Domain-wise rigid body real space refinement was then carried out using phenix.refine. | ||||||
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)