+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | 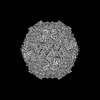 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
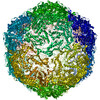
| Title | CryoEM structure of Encapsulin::tdNfsB with an open pore state | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Nanocompartment / BIOSYNTHETIC PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology | Type 1 encapsulin shell protein / Encapsulating protein for peroxidase / : / encapsulin nanocompartment / plasma membrane / Type 1 encapsulin shell protein Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.22 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Capper MJ / Kohhnke J | |||||||||
| Funding support | European Union, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: RSC Chem Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: RSC Chem Biol / Year: 2024Title: A nanoengineered tandem nitroreductase: designing a robust prodrug-activating nanoreactor. Authors: Mariia Zmyslia / Michael J Capper / Michael Grimmeisen / Kerstin Sartory / Benedikt Deuringer / Mohamed Abdelsalam / Kaiwei Shen / Manfred Jung / Wolfgang Sippl / Hans-Georg Koch / Laurine ...Authors: Mariia Zmyslia / Michael J Capper / Michael Grimmeisen / Kerstin Sartory / Benedikt Deuringer / Mohamed Abdelsalam / Kaiwei Shen / Manfred Jung / Wolfgang Sippl / Hans-Georg Koch / Laurine Kaul / Regine Süss / Jesko Köhnke / Claudia Jessen-Trefzer /    Abstract: Nitroreductases are important enzymes for a variety of applications, including cancer therapy and bioremediation. They often require encapsulation to improve stability and activity. We focus on ...Nitroreductases are important enzymes for a variety of applications, including cancer therapy and bioremediation. They often require encapsulation to improve stability and activity. We focus on genetically encoded encapsulation of nitroreductases within protein capsids, like encapsulins. Our study showcases the encapsulation of nitroreductase NfsB as functional dimers within encapsulins, which enhances protein activity and stability in diverse conditions. Mutations within the pore region are beneficial for activity of the encapsulated enzyme, potentially by increasing diffusion rates. Cryogenic electron microscopy reveals the overall architecture of the encapsulated dimeric NfsB within the nanoreactor environment and identifies multiple pore states in the shell. These findings highlight the potential of encapsulins as versatile tools for enhancing enzyme performance across various fields. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_50586.map.gz emd_50586.map.gz | 243.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-50586-v30.xml emd-50586-v30.xml emd-50586.xml emd-50586.xml | 16.9 KB 16.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_50586_fsc.xml emd_50586_fsc.xml | 16.8 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_50586.png emd_50586.png | 152 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_50586_msk_1.map emd_50586_msk_1.map | 512 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-50586.cif.gz emd-50586.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_50586_half_map_1.map.gz emd_50586_half_map_1.map.gz emd_50586_half_map_2.map.gz emd_50586_half_map_2.map.gz | 472.6 MB 472.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50586 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50586 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50586 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50586 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 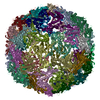 9fnaMC 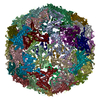 9fn9C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_50586.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_50586.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.7832 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_50586_msk_1.map emd_50586_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_50586_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_50586_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Cryo-EM structure of encapsulin shell containing engineered tande...
| Entire | Name: Cryo-EM structure of encapsulin shell containing engineered tandem dimer NfsB |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Cryo-EM structure of encapsulin shell containing engineered tande...
| Supramolecule | Name: Cryo-EM structure of encapsulin shell containing engineered tandem dimer NfsB type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: 29 kDa antigen Cfp29
| Macromolecule | Name: 29 kDa antigen Cfp29 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 60 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 30.045578 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MNNLYRDLAP ITESAWAEIE LEATRTFKRH IAGRRVVDVS GPNGPTTASV STGHLLDVSP PGDGVIAHLR DAKPLVRLRV PFTVARRDI DDVERGSQDS DWDPVKDAAK KLAFVEDRAI FEGYAAASIE GIRSSSSNPA LALPDDAREI PDVIAQALSE L RLAGVDGP ...String: MNNLYRDLAP ITESAWAEIE LEATRTFKRH IAGRRVVDVS GPNGPTTASV STGHLLDVSP PGDGVIAHLR DAKPLVRLRV PFTVARRDI DDVERGSQDS DWDPVKDAAK KLAFVEDRAI FEGYAAASIE GIRSSSSNPA LALPDDAREI PDVIAQALSE L RLAGVDGP YSVLLSAETY TKVSETTAHG YPIREHINRL VDGEIIWAPA IDGAFVLSTR GGDFDLQLGT DVSIGYLSHD AE VVHLYME ETMTFLCYTA EASVALTPEL WSHPQFEK UniProtKB: Type 1 encapsulin shell protein |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 20 mg/mL | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 / Component:
| ||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. | ||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 281 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | JEOL CRYO ARM 300 |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: In-column Omega Filter |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: DIRECT ELECTRON APOLLO (4k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Average exposure time: 1.5 sec. / Average electron dose: 60.2 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 80000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: JEOL / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)