[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
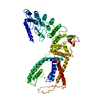
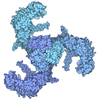
Yorodumi- EMDB-49845: Structure of Nanchung-Inactive-Calmodulin in complex with Nicotinamide -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of Nanchung-Inactive-Calmodulin in complex with Nicotinamide | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Structure of Nanchung-Inactive-Calmodulin in complex with Nicotinamide | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Membrane protein / membrane channel / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcation channel complex / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / Calmodulin induced events / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase ...cation channel complex / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / Calmodulin induced events / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / PKA activation / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / autophagosome membrane docking / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / presynaptic endocytosis / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / calcineurin-mediated signaling / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / calcium ion import across plasma membrane / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / Long-term potentiation / protein phosphatase activator activity / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / DARPP-32 events / Smooth Muscle Contraction / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / catalytic complex / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / calcium channel inhibitor activity / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / presynaptic cytosol / cellular response to interferon-beta / Protein methylation / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / titin binding / Ion homeostasis / eNOS activation / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / FCERI mediated Ca+2 mobilization / calcium channel complex / substantia nigra development / regulation of heart rate / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor / FCGR3A-mediated IL10 synthesis / Antigen activates B Cell Receptor (BCR) leading to generation of second messengers / calyx of Held / adenylate cyclase activator activity / sarcomere / VEGFR2 mediated cell proliferation / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / regulation of cytokinesis / spindle microtubule / positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / calcium channel regulator activity / RAF activation / Transcriptional activation of mitochondrial biogenesis / response to calcium ion / cellular response to type II interferon / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / Stimuli-sensing channels / calcium channel activity / spindle pole / calcium-dependent protein binding / Signaling by RAF1 mutants / RAS processing / Signaling by moderate kinase activity BRAF mutants / Paradoxical activation of RAF signaling by kinase inactive BRAF / Signaling downstream of RAS mutants / Signaling by BRAF and RAF1 fusions / long-term synaptic potentiation / Platelet degranulation / sperm midpiece / myelin sheath / synaptic vesicle membrane / Inactivation, recovery and regulation of the phototransduction cascade / RAF/MAP kinase cascade / Ca2+ pathway / High laminar flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and PECAM1:CDH5:KDR in endothelial cells / vesicle Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  Halyomorpha halys (brown marmorated stink bug) Halyomorpha halys (brown marmorated stink bug) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.49 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Fedor JG / Lee S-Y | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025Title: Visualizing insecticide control of insect TRP channel function and assembly. Authors: Justin G Fedor / Ramani Kandasamy / Cheon-Gyu Park / Yang Suo / Martin Weisel / Nancy B Rankl / Alexandre Nesterov / Seok-Yong Lee /   Abstract: Insecticides are vital to combating world food shortages and transmission of vector-borne human diseases. Increasing insecticide resistance necessitates discovery of novel compounds against ...Insecticides are vital to combating world food shortages and transmission of vector-borne human diseases. Increasing insecticide resistance necessitates discovery of novel compounds against underutilized targets. Nanchung (Nan) and Inactive (Iav), the transient receptor potential vanilloid-type (TRPV) channels in insects, likely form a heteromeric channel (Nan-Iav) and are localized in mechanosensory chordotonal organs which confer gravitaxis, hearing and proprioception. Several insecticides, such as afidopyropen (AP), target Nan-Iav through unknown mechanisms. Effective against piercing-sucking (hemipteran) insects, AP disrupts chordotonal functions preventing feeding. AP can bind to Nan alone, but only Nan-Iav exhibits channel activity with agonists including endogenous nicotinamide (NAM). Despite its importance as an insecticide target, much is unknown about Nan-Iav, such as channel assembly, modulator binding sites, and Ca-dependent regulation, hampering further insecticide development. Here we present the cryo-electron microscopy structures of hemipteran Nan-Iav with calmodulin bound in the apo state and with AP and NAM bound to cytosolic ankyrin repeat domain (ARD) interfaces. Unexpectedly, we found that Nan alone can form a pentamer, stabilized through AP-mediated ARD interactions. Our study provides molecular insights into insecticide and agonist interactions with Nan-Iav, highlighting the importance of the ARD on channel function and assembly, while also probing regulation by Ca. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_49845.map.gz emd_49845.map.gz | 43.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-49845-v30.xml emd-49845-v30.xml emd-49845.xml emd-49845.xml | 26.8 KB 26.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_49845.png emd_49845.png | 92.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-49845.cif.gz emd-49845.cif.gz | 8.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_49845_half_map_1.map.gz emd_49845_half_map_1.map.gz emd_49845_half_map_2.map.gz emd_49845_half_map_2.map.gz | 77.4 MB 77.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-49845 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-49845 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-49845 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-49845 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9nvoMC  9nvnC  9nvpC  9nvqC  9nvrC  9nvsC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_49845.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_49845.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Structure of Nanchung-Inactive-Calmodulin in complex with Nicotinamide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: half map 1
| File | emd_49845_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half map 1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: half map 2
| File | emd_49845_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half map 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Nanchung-Inactive-Calmodulin
| Entire | Name: Nanchung-Inactive-Calmodulin |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Nanchung-Inactive-Calmodulin
| Supramolecule | Name: Nanchung-Inactive-Calmodulin / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 700 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Inactive
| Macromolecule | Name: Inactive / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: The 30-N-terminal residues are MGIIWGSGASSVNAGTVLDRVISQASNKDE. The authors were not able to assign the register of the residues in this region Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Halyomorpha halys (brown marmorated stink bug) Halyomorpha halys (brown marmorated stink bug) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 109.381992 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)CLLYKLANY K KGGELIDA YNAGGQSEVE ...String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)CLLYKLANY K KGGELIDA YNAGGQSEVE KLIREQFGQL MYNEGKGALI NRAEYLRWKF RDMQQVQIPI EASLSSQDPL SKWEDHQACW QM QYRGSLG ETLLHVLIIC DTKIHTRLAR TLLKCFPNLA IDVVEGEEYL GASALHLAIA YFNNELVQDL VEAGANVEQR AIG SFFLPR DQQGQRPSKH TDYEGLAYLG EYPLAWAACC ANESIYNLLL DNGANPDQRD TFGNMILHMV VVCDKLDMFG YALR HPKMP ASNGIANVAG LTPLTLACKL GRAKVFREML ELSAREFWRY SNITCSAYPL NALDTLLPDG RTNWNSALFI ILNGT KEEH LDMLDGGIIQ RLLEEKWKTF ARRQFLKRLV ILMLHLICLS GAVYLRPTDR TKPLLGGDDW KSIARQGFEV ATVLGV LSY VLVQQGGEIR NQGFISFIKQ LDPAKAIFLV SNILILVCIP FRLIDDKRTE EAILVFAVPG SWFLLMFFAG AVRLTGP FV TMVYSMIVGD MFTFGIIYSI VLFGFSQSFY FLYKGFPGVK NTLYSSYHST WMALFQITLG DYNYAELSHT SYPTLSKT V FAIFMVLVPI LLLNMLIAMM GNTYAHVIEQ SEKEWMKQWA KIVVSLERAV NQEDCKQYLQ EYSIKLGPGD DPSTEQRGV MVIKSKSKTR AKQRKGAVAN WKRVGKVTIN ELRKRGMNGE QLRRIMWDRA SISTPVKVPQ NPVVDVLMEN TAEQQAQQTP GSFGGALTA ALDVMAFTHD LDLSASGITS SGLNAKELIV SDPFRDLVLS SEIDVGEEEL ATLAEAAVLS VMSGQSDESE K LKIAKFNK QISFEQNAVL EVSDSDGFLD GQPLGQGSRA RKVKSAQERQ RAERTWGGTS ISSIEEPPPY LPLPPPPPLH SH QRPRPKT AKPNRVVPEA VVAKRPQSSA LGDRVKSPPE LLEPWSTRGI ATINTILAWQ PSDQDSM UniProtKB: Uncharacterized protein, Ion transport domain-containing protein |
-Macromolecule #2: Nanchung
| Macromolecule | Name: Nanchung / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Halyomorpha halys (brown marmorated stink bug) Halyomorpha halys (brown marmorated stink bug) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 101.194867 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MGNTESNVTS GVKKQADTSS IKIYKLVDLK GGGLLVELMK RAAQTKQYAE LDHAIKTKVE PFLYNKGQGK MMPVSQLVLM RNKERPRHK MLPPLRNLEN PDDYDIESYV VPEPTEEDLK DPNKYREVCW DLKERGAVGE TILHLCLLNA TSLHADLAKR L LRFYPKLI ...String: MGNTESNVTS GVKKQADTSS IKIYKLVDLK GGGLLVELMK RAAQTKQYAE LDHAIKTKVE PFLYNKGQGK MMPVSQLVLM RNKERPRHK MLPPLRNLEN PDDYDIESYV VPEPTEEDLK DPNKYREVCW DLKERGAVGE TILHLCLLNA TSLHADLAKR L LRFYPKLI NDVYMSDEYY GESVLHIAIV NEDPAMVKFL LDSGVNVNER CFGNFMCPED QKASRTDSFD HEWVNLQSFT TY EGYVYWG EYPLSFAACL GQEECYRLML ARGANPDNQD TNGNTVLHML VIYSKIQTFD MAYEVGGDLS IRNVQYLTPL TLA AKLARI ELFFHILNIE REIYWQIGSI TCAAYPLSQI DTIDIVTGNI SKNSALNLVV FGEKDEHLEL MDGVLIDLLN AKWN AFVKF RFYRQFFLFL FYFLISLICF TLRPGPPPVK PISSINSTKP NGNNITADLS PENLTTLPKW IYKTEIKKYD PEDNT SQNS RLNVILREVI LTSLKVEDID KVVSFSNAET PDNSREDAEG LVCNGNSIHS CIGNGSDVIS VFGKGKSPKV PKPGAS ADD FDYDDTWWEE FGQCRLLQVT SYIEMTRLIS EVMLDIGALL YILAALREAR FLGWSMFVEN LMTAPSRVMF LFSCCLM LT MPFLRFTCNE EIEDMMAVII MLTTAPYFLF FCRGFKTVGP FVVMIYRMIM GDLLRFATIY LVFVMGFAQA YYIIFLSF D NPLTPEGVDD SVSNPIPNPM EAVMAMFFMS MTSFGDYYPA LERTAHEFCA KLCFVIYMAI VAILLVNMLI AMMGNTYQK IAETRNEWQR QWARIVLVVE RGVSPSERLT KLMWYSQPMS DGRRALVLRL NQSEEDKEEM KEILEMKRIH NRMVQKRKER EM |
-Macromolecule #3: Calmodulin-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Calmodulin-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 8.167979 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MADQLTEEQI AEFKEAFSLF DKDGDGTITT KELGTVMRSL GQNPTEAELQ DMINEVDADG NGTIDFPEFL TMMA UniProtKB: Calmodulin-1 |
-Macromolecule #4: [(2~{R})-1-[2-azanylethoxy(oxidanyl)phosphoryl]oxy-3-hexadecanoyl...
| Macromolecule | Name: [(2~{R})-1-[2-azanylethoxy(oxidanyl)phosphoryl]oxy-3-hexadecanoyloxy-propan-2-yl] (~{Z})-octadec-9-enoate type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 14 / Formula: 6OU |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 717.996 Da |
| Chemical component information | 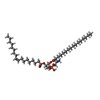 ChemComp-6OU: |
-Macromolecule #5: 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
| Macromolecule | Name: 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: LBN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 760.076 Da |
| Chemical component information | 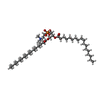 ChemComp-LBN: |
-Macromolecule #6: NICOTINAMIDE
| Macromolecule | Name: NICOTINAMIDE / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: NCA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 122.125 Da |
| Chemical component information | 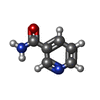 ChemComp-NCA: |
-Macromolecule #7: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #8: (2~{S})-2-azanyl-3-[[(2~{R})-3-hexadecanoyloxy-2-[(~{Z})-octadec-...
| Macromolecule | Name: (2~{S})-2-azanyl-3-[[(2~{R})-3-hexadecanoyloxy-2-[(~{Z})-octadec-9-enoyl]oxy-propoxy]-oxidanyl-phosphoryl]oxy-propanoic acid type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: D39 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 762.006 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-D39: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.9 mg/mL | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS / Support film - Film thickness: 2 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Pretreatment - Pressure: 0.00037 kPa | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 280 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV | ||||||||||||||||||
| Details | Monodisperse sample |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Max: 70.0 K |
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 5760 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4092 pixel / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 11850 / Average exposure time: 2.4 sec. / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 81000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)