[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-49300: Human polymerase epsilon bound to PCNA and DNA with an in-situ-ge... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human polymerase epsilon bound to PCNA and DNA with an in-situ-generated mismatch in the Pol-backtracking state | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Final sharpened EM map by cryosparc | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA polymerase / exo / holoenzyme / DNA / REPLICATION | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationDNA replication initiation / epsilon DNA polymerase complex / positive regulation of deoxyribonuclease activity / dinucleotide insertion or deletion binding / PCNA-p21 complex / mitotic telomere maintenance via semi-conservative replication / purine-specific mismatch base pair DNA N-glycosylase activity / nucleotide-excision repair, DNA gap filling / nuclear lamina / positive regulation of DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity ...DNA replication initiation / epsilon DNA polymerase complex / positive regulation of deoxyribonuclease activity / dinucleotide insertion or deletion binding / PCNA-p21 complex / mitotic telomere maintenance via semi-conservative replication / purine-specific mismatch base pair DNA N-glycosylase activity / nucleotide-excision repair, DNA gap filling / nuclear lamina / positive regulation of DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / Polymerase switching / MutLalpha complex binding / DNA replication proofreading / Processive synthesis on the lagging strand / PCNA complex / single-stranded DNA 3'-5' DNA exonuclease activity / Telomere C-strand (Lagging Strand) Synthesis / Removal of the Flap Intermediate / Mismatch repair (MMR) directed by MSH2:MSH3 (MutSbeta) / Mismatch repair (MMR) directed by MSH2:MSH6 (MutSalpha) / Transcription of E2F targets under negative control by DREAM complex / Polymerase switching on the C-strand of the telomere / replisome / Processive synthesis on the C-strand of the telomere / response to L-glutamate / Removal of the Flap Intermediate from the C-strand / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds; Exodeoxyribonucleases producing 5'-phosphomonoesters / response to dexamethasone / DNA synthesis involved in DNA repair / histone acetyltransferase binding / DNA polymerase processivity factor activity / G1/S-Specific Transcription / leading strand elongation / nuclear replication fork / replication fork processing / SUMOylation of DNA replication proteins / PCNA-Dependent Long Patch Base Excision Repair / Activation of the pre-replicative complex / embryonic organ development / response to cadmium ion / translesion synthesis / estrous cycle / mismatch repair / cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex / base-excision repair, gap-filling / DNA polymerase binding / epithelial cell differentiation / liver regeneration / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in G2 Cell Cycle Arrest / positive regulation of DNA repair / positive regulation of DNA replication / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / nuclear estrogen receptor binding / Translesion synthesis by POLK / replication fork / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / male germ cell nucleus / Termination of translesion DNA synthesis / G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / Translesion Synthesis by POLH / receptor tyrosine kinase binding / DNA-templated DNA replication / HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) / Dual Incision in GG-NER / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / cellular response to hydrogen peroxide / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / cellular response to UV / response to estradiol / mitotic cell cycle / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / heart development / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / chromatin organization / DNA-directed DNA polymerase / damaged DNA binding / DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / DNA replication / chromosome, telomeric region / nuclear body / nucleotide binding / chromatin binding / centrosome / chromatin / protein-containing complex binding / enzyme binding / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / DNA binding / extracellular exosome / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / nucleus / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.53 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang F / He Q / Li H | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025Title: The proofreading mechanism of the human leading-strand DNA polymerase ε holoenzyme. Authors: Feng Wang / Qing He / Michael E O'Donnell / Huilin Li /  Abstract: The eukaryotic leading-strand DNA polymerase ε (Polε) is a dual-function enzyme with a proofreading 3'-5' exonuclease () site located 40 Å from the DNA synthesizing site. Errors in Polε ...The eukaryotic leading-strand DNA polymerase ε (Polε) is a dual-function enzyme with a proofreading 3'-5' exonuclease () site located 40 Å from the DNA synthesizing site. Errors in Polε proofreading can cause various mutations, including C-to-G transversions, the most prevalent mutation in cancers and genetic diseases. Polε interacts with all three subunits of the PCNA ring to assemble a functional holoenzyme. Despite previous studies on proofreading of several Pol's, how Polε-or any Pol complexed with its sliding clamp-proofreads a mismatch generated in situ has been unknown. We show here by cryo-EM that a template/primer DNA substrate with a preexisting mismatch cannot enter the site of Polε-PCNA holoenzyme, but a mismatch generated in situ in the site yields three bona fide proofreading intermediates of Polε-PCNA holoenzyme. These intermediates reveal how the mismatch is dislodged from the site, how the DNA unwinds six base pairs, and how the unpaired primer 3'-end is inserted into the site for cleavage. These results unexpectedly demonstrate that PCNA imposes strong steric constraints that extend unwinding and direct the trajectory of mismatched DNA and that this trajectory is dramatically different than for Polε in the absence of PCNA. These findings suggest a physiologically relevant proofreading mechanism for the human Polε holoenzyme. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_49300.map.gz emd_49300.map.gz | 117.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-49300-v30.xml emd-49300-v30.xml emd-49300.xml emd-49300.xml | 21.9 KB 21.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_49300_fsc.xml emd_49300_fsc.xml | 10.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_49300.png emd_49300.png | 141.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-49300.cif.gz emd-49300.cif.gz | 7.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_49300_additional_1.map.gz emd_49300_additional_1.map.gz emd_49300_half_map_1.map.gz emd_49300_half_map_1.map.gz emd_49300_half_map_2.map.gz emd_49300_half_map_2.map.gz | 62.3 MB 116.1 MB 116.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-49300 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-49300 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-49300 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-49300 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9ne7MC  9ne6C  9ne8C  9ne9C  9neaC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_49300.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_49300.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Final sharpened EM map by cryosparc | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.828 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Unsharpened EM map
| File | emd_49300_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unsharpened EM map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
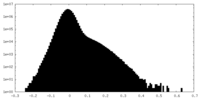
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map A
| File | emd_49300_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map B
| File | emd_49300_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Ternary complex of human DNA polymerase epsilon with PCNA and the...
| Entire | Name: Ternary complex of human DNA polymerase epsilon with PCNA and the mismatched DNA |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Ternary complex of human DNA polymerase epsilon with PCNA and the...
| Supramolecule | Name: Ternary complex of human DNA polymerase epsilon with PCNA and the mismatched DNA type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#4 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 220 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: DNA polymerase epsilon catalytic subunit A
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA polymerase epsilon catalytic subunit A / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: DNA-directed DNA polymerase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 138.137562 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism: Insect cell expression vector pTIE1 (others) |
| Sequence | String: MSLRSGGRRR ADPGADGEAS RDDGATSSVS ALKRLERSQW TDKMDLRFGF ERLKEPGEKT GWLINMHPTE ILDEDKRLGS AVDYYFIQD DGSRFKVALP YKPYFYIATR KGCEREVSSF LSKKFQGKIA KVETVPKEDL DLPNHLVGLK RNYIRLSFHT V EDLVKVRK ...String: MSLRSGGRRR ADPGADGEAS RDDGATSSVS ALKRLERSQW TDKMDLRFGF ERLKEPGEKT GWLINMHPTE ILDEDKRLGS AVDYYFIQD DGSRFKVALP YKPYFYIATR KGCEREVSSF LSKKFQGKIA KVETVPKEDL DLPNHLVGLK RNYIRLSFHT V EDLVKVRK EISPAVKKNR EQDHASDAYT ALLSSVLQRG GVITDEEETS KKIADQLDNI VDMREYDVPY HIRLSIDLKI HV AHWYNVR YRGNAFPVEI TRRDDLVERP DPVVLAFAIA TTKLPLKFPD AETDQIMMIS YMIDGQGYLI TNREIVSEDI EDF EFTPKP EYEGPFCVFN EPDEAHLIQR WFEHVQETKP TIMVTYNGDF FDWPFVEARA AVHGLSMQQE IGFQKDSQGE YKAP QCIHM DCLRWVKRDS YLPVGSHNLK AAAKAKLGYD PVELDPEDMC RMATEQPQTL ATYSVSDAVA TYYLYMKYVH PFIFA LCTI IPMEPDEVLR KGSGTLCEAL LMVQAFHANI IFPNKQEQEF NKLTDDGHVL DSETYVGGHV EALESGVFRS DIPCRF RMN PAAFDFLLQR VEKTLRHALE EEEKVPVEQV TNFEEVCDEI KSKLASLKDV PSRIECPLIY HLDVGAMYPN IILTNRL QP SAMVDEATCA ACDFNKPGAN CQRKMAWQWR GEFMPASRSE YHRIQHQLES EKFPPLFPEG PARAFHELSR EEQAKYEK R RLADYCRKAY KKIHITKVEE RLTTICQREN SFYVDTVRAF RDRRYEFKGL HKVWKKKLSA AVEVGDAAEV KRCKNMEVL YDSLQLAHKC ILNSFYGYVM RKGARWYSME MAGIVCFTGA NIITQARELI EQIGRPLELD TDGIWCVLPN SFPENFVFKT TNVKKPKVT ISYPGAMLNI MVKEGFTNDQ YQELAEPSSL TYVTRSENSI FFEVDGPYLA MILPASKEEG KKLKKRYAVF N EDGSLAEL KGFEVKRRGE LQLIKIFQSS VFEAFLKGST LEEVYGSVAK VADYWLDVLY SKAANMPDSE LFELISENRS MS RKLEDYG EQKSTSISTA KRLAEFLGDQ MVKDAGLSCR YIISRKPEGS PVTERAIPLA IFQAEPTVRK HFLRKWLKSS SLQ DFDIRA ILDWDYYIER LGSAIQKIIT IPAALQQVKN PVPRVKHPDW LHKKLLEKND VYKQKKISEL FTLEGRRQVT MAEA UniProtKB: DNA polymerase epsilon catalytic subunit A |
-Macromolecule #2: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen
| Macromolecule | Name: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 28.795752 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MFEARLVQGS ILKKVLEALK DLINEACWDI SSSGVNLQSM DSSHVSLVQL TLRSEGFDTY RCDRNLAMGV NLTSMSKILK CAGNEDIIT LRAEDNADTL ALVFEAPNQE KVSDYEMKLM DLDVEQLGIP EQEYSCVVKM PSGEFARICR DLSHIGDAVV I SCAKDGVK ...String: MFEARLVQGS ILKKVLEALK DLINEACWDI SSSGVNLQSM DSSHVSLVQL TLRSEGFDTY RCDRNLAMGV NLTSMSKILK CAGNEDIIT LRAEDNADTL ALVFEAPNQE KVSDYEMKLM DLDVEQLGIP EQEYSCVVKM PSGEFARICR DLSHIGDAVV I SCAKDGVK FSASGELGNG NIKLSQTSNV DKEEEAVTIE MNEPVQLTFA LRYLNFFTKA TPLSSTVTLS MSADVPLVVE YK IADMGHL KYYLAPKIED EEGS UniProtKB: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen |
-Macromolecule #3: DNA (33-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (33-MER) / type: dna / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 10.236587 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DT)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DG) (DC)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DG) (DC)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DT)(DT) |
-Macromolecule #4: DNA (47-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (47-MER) / type: dna / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.419317 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DG)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DA) (DA)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DA) (DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DA) (DT)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DT) (DG) (DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DA) |
-Macromolecule #5: IRON/SULFUR CLUSTER
| Macromolecule | Name: IRON/SULFUR CLUSTER / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: SF4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 351.64 Da |
| Chemical component information | 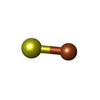 ChemComp-FS1: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.6 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)