[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-48504: Cryo-EM structure of VCP bound to p47 UBX domain and VCPIP1 VCPID... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
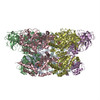
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of VCP bound to p47 UBX domain and VCPIP1 VCPIDs (with stalk region) | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | double-ring hexameric complex / valosin containing protein / ATPase / VCP / mammalian / DUB / deubiquitinase / deubiquitinating enzyme / VCIP135 / p97 / VCPIP1 / hydrolase / VCPID / p47 / adapter / SHP / UBX / TRANSLOCASE | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of protein localization to centrosome / positive regulation of mitotic centrosome separation / protein K11-linked deubiquitination / endoplasmic reticulum membrane fusion / Golgi reassembly / nuclear membrane reassembly / protein K48-linked deubiquitination / cytoplasmic ubiquitin ligase complex / flavin adenine dinucleotide catabolic process / VCP-NSFL1C complex ...negative regulation of protein localization to centrosome / positive regulation of mitotic centrosome separation / protein K11-linked deubiquitination / endoplasmic reticulum membrane fusion / Golgi reassembly / nuclear membrane reassembly / protein K48-linked deubiquitination / cytoplasmic ubiquitin ligase complex / flavin adenine dinucleotide catabolic process / VCP-NSFL1C complex / endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced pre-emptive quality control / endosome to lysosome transport via multivesicular body sorting pathway / BAT3 complex binding / cellular response to arsenite ion / protein-DNA covalent cross-linking repair / Derlin-1 retrotranslocation complex / positive regulation of protein K63-linked deubiquitination / cytoplasm protein quality control / positive regulation of oxidative phosphorylation / Golgi stack / aggresome assembly / deubiquitinase activator activity / ubiquitin-modified protein reader activity / regulation of protein localization to chromatin / mitotic spindle disassembly / cellular response to misfolded protein / VCP-NPL4-UFD1 AAA ATPase complex / ciliary transition zone / positive regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential / vesicle-fusing ATPase / K48-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / regulation of aerobic respiration / retrograde protein transport, ER to cytosol / stress granule disassembly / NAD+ metabolic process / ATPase complex / regulation of synapse organization / ubiquitin-specific protease binding / ciliary tip / Golgi organization / positive regulation of ATP biosynthetic process / MHC class I protein binding / ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / RHOH GTPase cycle / polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / protein deubiquitination / autophagosome maturation / autophagosome assembly / endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport / negative regulation of hippo signaling / HSF1 activation / interstrand cross-link repair / ATP metabolic process / translesion synthesis / endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response / proteasomal protein catabolic process / negative regulation of protein localization to chromatin / Attachment and Entry / Protein methylation / ERAD pathway / lipid droplet / proteasome complex / viral genome replication / ubiquitin binding / Josephin domain DUBs / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / macroautophagy / negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway / establishment of protein localization / Hh mutants are degraded by ERAD / positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / Hedgehog ligand biogenesis / Defective CFTR causes cystic fibrosis / positive regulation of non-canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / Translesion Synthesis by POLH / ADP binding / autophagy / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / cytoplasmic stress granule / Aggrephagy / azurophil granule lumen / positive regulation of protein catabolic process / Ovarian tumor domain proteases / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / double-strand break repair / positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / cellular response to heat / site of double-strand break / chromosome / Neddylation / secretory granule lumen / regulation of apoptotic process / protein phosphatase binding / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / ficolin-1-rich granule lumen / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / membrane fusion Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.63 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Shah B / Hunkeler M / Buhrlage SJ / Fischer EF | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025Title: Structural basis of VCP-VCPIP1-p47 ternary complex in Golgi maintenance. Authors: Binita Shah / Moritz Hunkeler / Ariana Bratt / Hong Yue / Isabella Jaen Maisonet / Eric S Fischer / Sara J Buhrlage /  Abstract: VCP/p97 regulates a wide range of cellular processes, including post-mitotic Golgi reassembly. In this context, VCP is assisted by p47, an adapter protein, and VCPIP1, a deubiquitylase (DUB). ...VCP/p97 regulates a wide range of cellular processes, including post-mitotic Golgi reassembly. In this context, VCP is assisted by p47, an adapter protein, and VCPIP1, a deubiquitylase (DUB). However, how they organize into a functional ternary complex to promote Golgi assembly remains unknown. Here, we use cryo-EM to characterize both VCP-VCPIP1 and VCP-VCPIP1-p47 complexes. We show that VCPIP1 engages VCP through two interfaces: one involving the N-domain of VCP and the UBX domain of VCPIP1, and the other involving the VCP D2 domains and a region of VCPIP1 we refer to as VCPID. The p47 UBX domain competitively binds to the VCP N-domain, while not affecting VCPID binding. We show that VCPID is critical for VCP-mediated enhancement of DUB activity and proper Golgi assembly. The ternary structure along with biochemical and cellular data provides new insights into the complex interplay of VCP with its co-factors. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_48504.map.gz emd_48504.map.gz | 63.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-48504-v30.xml emd-48504-v30.xml emd-48504.xml emd-48504.xml | 29.2 KB 29.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_48504_fsc.xml emd_48504_fsc.xml | 10.5 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_48504.png emd_48504.png | 92.5 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_48504_msk_1.map emd_48504_msk_1.map | 125 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-48504.cif.gz emd-48504.cif.gz | 7.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_48504_additional_1.map.gz emd_48504_additional_1.map.gz emd_48504_additional_2.map.gz emd_48504_additional_2.map.gz emd_48504_half_map_1.map.gz emd_48504_half_map_1.map.gz emd_48504_half_map_2.map.gz emd_48504_half_map_2.map.gz | 118 MB 116.4 MB 115.9 MB 115.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-48504 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-48504 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-48504 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-48504 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9mpqC  9mprC  9mpsC  9mptC  9mpuC  9mpvC C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_48504.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_48504.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_48504_msk_1.map emd_48504_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: #1
| File | emd_48504_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Low pass filtered map
| File | emd_48504_additional_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Low pass filtered map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half-map B
| File | emd_48504_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half-map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half-map A
| File | emd_48504_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half-map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of valosin containing protein (VCP)/p97 bound to valosin ...
| Entire | Name: Complex of valosin containing protein (VCP)/p97 bound to valosin containing protein interacting protein 1 (VCPIP1) and p47 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of valosin containing protein (VCP)/p97 bound to valosin ...
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of valosin containing protein (VCP)/p97 bound to valosin containing protein interacting protein 1 (VCPIP1) and p47 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: Full length valosin containing protein (VCP)/p97 with full length valosin containing protein interacting protein 1 (VCPIP1) and p47 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: Valosin containing protein (VCP)
| Supramolecule | Name: Valosin containing protein (VCP) / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #3: Valosin containing protein interacting protein 1 (VCPIP1)
| Supramolecule | Name: Valosin containing protein interacting protein 1 (VCPIP1) type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #4: p47
| Supramolecule | Name: p47 / type: complex / ID: 4 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #3 / Details: Adapter of valosin containing protein (VCP)/p97 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Transitional endoplasmic reticulum ATPase
| Macromolecule | Name: Transitional endoplasmic reticulum ATPase / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Details: N-term FLAG-tagged VCP / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: vesicle-fusing ATPase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MGDYKDDDDK GGGSGGLEVL FQGPGSMASG ADSKGDDLST AILKQKNRPN RLIVDEAINE DNSVVSLSQP KMDELQLFRG DTVLLKGKKR REAVCIVLSD DTCSDEKIRM NRVVRNNLRV RLGDVISIQP CPDVKYGKRI HVLPIDDTVE GITGNLFEVY LKPYFLEAYR ...String: MGDYKDDDDK GGGSGGLEVL FQGPGSMASG ADSKGDDLST AILKQKNRPN RLIVDEAINE DNSVVSLSQP KMDELQLFRG DTVLLKGKKR REAVCIVLSD DTCSDEKIRM NRVVRNNLRV RLGDVISIQP CPDVKYGKRI HVLPIDDTVE GITGNLFEVY LKPYFLEAYR PIRKGDIFLV RGGMRAVEFK VVETDPSPYC IVAPDTVIHC EGEPIKREDE EESLNEVGYD DIGGCRKQLA QIKEMVELPL RHPALFKAIG VKPPRGILLY GPPGTGKTLI ARAVANETGA FFFLINGPEI MSKLAGESES NLRKAFEEAE KNAPAIIFID ELDAIAPKRE KTHGEVERRI VSQLLTLMDG LKQRAHVIVM AATNRPNSID PALRRFGRFD REVDIGIPDA TGRLEILQIH TKNMKLADDV DLEQVANETH GHVGADLAAL CSEAALQAIR KKMDLIDLED ETIDAEVMNS LAVTMDDFRW ALSQSNPSAL RETVVEVPQV TWEDIGGLED VKRELQELVQ YPVEHPDKFL KFGMTPSKGV LFYGPPGCGK TLLAKAIANE CQANFISIKG PELLTMWFGE SEANVREIFD KARQAAPCVL FFDELDSIAK ARGGNIGDGG GAADRVINQI LTEMDGMSTK KNVFIIGATN RPDIIDPAIL RPGRLDQLIY IPLPDEKSRV AILKANLRKS PVAKDVDLEF LAKMTNGFSG ADLTEICQRA CKLAIRESIE SEIRRERERQ TNPSAMEVEE DDPVPEIRRD HFEEAMRFAR RSVSDNDIRK YEMFAQTLQQ SRGFGSFRFP SGNQGGAGPS QGSGGGTGGS VYTEDNDDDL YG UniProtKB: Transitional endoplasmic reticulum ATPase |
-Macromolecule #2: Deubiquitinating protein VCPIP1
| Macromolecule | Name: Deubiquitinating protein VCPIP1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Details: N-term Strep-tagged VCPIP1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: ubiquitinyl hydrolase 1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MGDWSHPQFE KSGGGSGGLE VLFQGPGSMS QPPPPPPPLP PPPPPPEAPQ TPSSLASAAA SGGLLKRRDR RILSGSCPDP KCQARLFFPA SGSVSIECTE CGQRHEQQQL LGVEEVTDPD VVLHNLLRNA LLGVTGAPKK NTELVKVMGL SNYHCKLLSP ILARYGMDKQ ...String: MGDWSHPQFE KSGGGSGGLE VLFQGPGSMS QPPPPPPPLP PPPPPPEAPQ TPSSLASAAA SGGLLKRRDR RILSGSCPDP KCQARLFFPA SGSVSIECTE CGQRHEQQQL LGVEEVTDPD VVLHNLLRNA LLGVTGAPKK NTELVKVMGL SNYHCKLLSP ILARYGMDKQ TGRAKLLRDM NQGELFDCAL LGDRAFLIEP EHVNTVGYGK DRSGSLLYLH DTLEDIKRAN KSQECLIPVH VDGDGHCLVH AVSRALVGRE LFWHALRENL KQHFQQHLAR YQALFHDFID AAEWEDIINE CDPLFVPPEG VPLGLRNIHI FGLANVLHRP IILLDSLSGM RSSGDYSATF LPGLIPAEKC TGKDGHLNKP ICIAWSSSGR NHYIPLVGIK GAALPKLPMN LLPKAWGVPQ DLIKKYIKLE EDGGCVIGGD RSLQDKYLLR LVAAMEEVFM DKHGIHPSLV ADVHQYFYRR TGVIGVQPEE VTAAAKKAVM DNRLHKCLLC GALSELHVPP EWLAPGGKLY NLAKSTHGQL RTDKNYSFPL NNLVCSYDSV KDVLVPDYGM SNLTACNWCH GTSVRKVRGD GSIVYLDGDR TNSRSTGGKC GCGFKHFWDG KEYDNLPEAF PITLEWGGRV VRETVYWFQY ESDSSLNSNV YDVAMKLVTK HFPGEFGSEI LVQKVVHTIL HQTAKKNPDD YTPVNIDGAH AQRVGDVQGQ ESESQLPTKI ILTGQKTKTL HKEELNMSKT ERTIQQNITE QASVMQKRKT EKLKQEQKGQ PRTVSPSTIR DGPSSAPATP TKAPYSPTTS KEKKIRITTN DGRQSMVTLK SSTTFFELQE SIAREFNIPP YLQCIRYGFP PKELMPPQAG MEKEPVPLQH GDRITIEILK SKAEGGQSAA AHSAHTVKQE DIAVTGKLSS KELQEQAEKE MYSLCLLATL MGEDVWSYAK GLPHMFQQGG VFYSIMKKTM GMADGKHCTF PHLPGKTFVY NASEDRLELC VDAAGHFPIG PDVEDLVKEA VSQVRAEATT RSRESSPSHG LLKLGSGGVV KKKSEQLHNV TAFQGKGHSL GTASGNPHLD PRARETSVVR KHNTGTDFSN SSTKTEPSVF TASSSNSELI RIAPGVVTMR DGRQLDPDLV EAQRKKLQEM VSSIQASMDR HLRDQSTEQS PSDLPQRKTE VVSSSAKSGS LQTGLPESFP LTGGTENLNT ETTDGCVADA LGAAFATRSK AQRGNSVEEL EEMDSQDAEM TNTTEPMDHS UniProtKB: Deubiquitinating protein VCPIP1 |
-Macromolecule #3: NSFL1 cofactor p47
| Macromolecule | Name: NSFL1 cofactor p47 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MHHHHHHHHH HDLGTENLYF QSMMAAERQE ALREFVAVTG AEEDRARFFL ESAGWDLQIA LASFYEDGGD EDIVTISQAT PSSVSRGTAP SDNRVTSFRD LIHDQDEDEE EEEGQRFYAG GSERSGQQIV GPPRKKSPNE LVDDLFKGAK EHGAVAVERV TKSPGETSKP ...String: MHHHHHHHHH HDLGTENLYF QSMMAAERQE ALREFVAVTG AEEDRARFFL ESAGWDLQIA LASFYEDGGD EDIVTISQAT PSSVSRGTAP SDNRVTSFRD LIHDQDEDEE EEEGQRFYAG GSERSGQQIV GPPRKKSPNE LVDDLFKGAK EHGAVAVERV TKSPGETSKP RPFAGGGYRL GAAPEEESAY VAGEKRQHSS QDVHVVLKLW KSGFSLDNGE LRSYQDPSNA QFLESIRRGE VPAELRRLAH GGQVNLDMED HRDEDFVKPK GAFKAFTGEG QKLGSTAPQV LSTSSPAQQA ENEAKASSSI LIDESEPTTN IQIRLADGGR LVQKFNHSHR ISDIRLFIVD ARPAMAATSF ILMTTFPNKE LADESQTLKE ANLLNAVIVQ RLT UniProtKB: NSFL1 cofactor p47 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
| ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Pretreatment - Pressure: 0.039 kPa | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 283.15 K / Instrument: LEICA EM GP | ||||||||||||
| Details | Final concentration of 0.2 mM CHAPSO |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Slit width: 10 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 12261 / Average exposure time: 2.87 sec. / Average electron dose: 49.22 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm / Nominal magnification: 165000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - Source name: PDB / Chain - Initial model type: experimental model |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)