+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
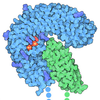
| Title | Tubulin cofactors D,E,G bound to tubulin dimer | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Tubulin / Tubulin cofactors / Tubulin biogenesis / Tubulin degradation / microtubules / CYTOSOLIC PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpost-chaperonin tubulin folding pathway / tubulin complex assembly / motile cilium / alpha-tubulin binding / beta-tubulin binding / GTPase activator activity / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / neuron migration / protein folding ...post-chaperonin tubulin folding pathway / tubulin complex assembly / motile cilium / alpha-tubulin binding / beta-tubulin binding / GTPase activator activity / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / neuron migration / protein folding / mitotic cell cycle / microtubule cytoskeleton / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / microtubule / hydrolase activity / GTPase activity / GTP binding / metal ion binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Taheri A / Al-bassam J | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025Title: Cryo-EM structures of the tubulin cofactors reveal the molecular basis of alpha/beta-tubulin biogenesis. Authors: Aryan Taheri / Zhoaqian Wang / Bharti Singal / Fei Guo / Jawdat Al-Bassam /  Abstract: Microtubule polarity and dynamic polymerization arise from the self-association properties of the αβ-tubulin heterodimer. For decades, it has remained unclear how the tubulin cofactors TBCD, TBCE, ...Microtubule polarity and dynamic polymerization arise from the self-association properties of the αβ-tubulin heterodimer. For decades, it has remained unclear how the tubulin cofactors TBCD, TBCE, TBCC, and the Arl2 GTPase mediate the biogenesis of αβ-tubulin from individual α- and β-tubulins. Here, we use cryo-electron microscopy to determine structures of tubulin cofactors bound to αβ-tubulin. TBCD, TBCE, and Arl2 form a heterotrimeric cage-like assembly, we term TBC-DEG, around the αβ-tubulin heterodimer. The TBC-DEG-αβ-tubulin structures show that TBC-DEG wraps around β-tubulin while TBCE extends along α-tubulin. The TBC-DEG/TBCC-αβ-tubulin structures reveal that TBCC forms multi-domain interactions with Arl2 and TBCD to engage the αβ-tubulin intradimer-interface, promoting TBCE rotation while TBCD holds β-tubulin. TBCC engages the GTP-bound Arl2, multiple sites of TBCD, and the native αβ-tubulin intradimer interface near the α-tubulin N-site GTP. Together, these structures uncover transition states for αβ-tubulin biogenesis and degradation, suggesting a vise-like, GTP-hydrolysis-dependent mechanism in which TBCC binding to TBC-DEG modulates αβ-tubulin interfaces. Our studies provide structural evidence that tubulin cofactors act as enzymatic regulators that assemble the invariant αβ-tubulin architecture. By catalyzing α- and β-tubulin biogenesis and degradation, the TBC-DEG and TBCC assemblies regulate the polymerization competency of αβ-tubulin for microtubule formation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_47954.map.gz emd_47954.map.gz | 217.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-47954-v30.xml emd-47954-v30.xml emd-47954.xml emd-47954.xml | 20.6 KB 20.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_47954.png emd_47954.png | 135.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-47954.cif.gz emd-47954.cif.gz | 7.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47954 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47954 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47954 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47954 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9eebMC  9edrC  9edsC  9edtC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_47954.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_47954.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.324 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Tubulin cofactors D,E,G in complex with tubulin dimer
| Entire | Name: Tubulin cofactors D,E,G in complex with tubulin dimer |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Tubulin cofactors D,E,G in complex with tubulin dimer
| Supramolecule | Name: Tubulin cofactors D,E,G in complex with tubulin dimer / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#6 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Protein PAC2
| Macromolecule | Name: Protein PAC2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: Chain E contains a well-resolved C-terminal region that was modeled with full side-chain identities. Density for the LRR and CAP-Gly domains is weaker and discontinuous, consistent with ...Details: Chain E contains a well-resolved C-terminal region that was modeled with full side-chain identities. Density for the LRR and CAP-Gly domains is weaker and discontinuous, consistent with flexibility of this portion of the protein in the complex. Therefore, residues in these regions are modeled as poly-alanine to represent the backbone trace and overall topology only (listed as UNK in the entry). Side-chain identities are not asserted in these low-density regions. The sequence register is anchored by the well-resolved C-terminal domain and supported by the AlphaFold prediction. Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 32.341963 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) ...String: (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)SLVL KIKIRAGKKP SSDLDYWVLP S FTVRYVKS VICRKLNFDI LNVKLFHENS EGMINEIKYN FRPISDFNVV NGDIIHVSSP VNNKSIQKVN SPS UniProtKB: Protein PAC2 |
-Macromolecule #2: GTP-binding protein CIN4
| Macromolecule | Name: GTP-binding protein CIN4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 22.096717 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGLLSIIRKQ KLRDKEIRCL ILGLDNSGKS TIVNKLLPKD EQNNDGIMPT VGFQIHSLMI KDVTISLWDI GGQRTLRPFW DNYFDKTQA MIWCIDVSLS MRFDETLQEL KELINRDENR IGYECAVIVV LNKIDLVEDK SELHRRCLLV ESELKCLFKP D IRIELVKC SGVTGEGIDN LRDRLVESCH FTQ UniProtKB: GTP-binding protein CIN4 |
-Macromolecule #3: Tubulin beta chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin beta chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 49.90777 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MREIVHIQAG QCGNQIGAKF WEVISDEHGI DPTGSYHGDS DLQLERINVY YNEAAGNKYV PRAILVDLEP GTMDSVRSGP FGQIFRPDN FVFGQSGAGN NWAKGHYTEG AELVDSVLDV VRKESESCDC LQGFQLTHSL GGGTGSGMGT LLISKIREEY P DRIMNTFS ...String: MREIVHIQAG QCGNQIGAKF WEVISDEHGI DPTGSYHGDS DLQLERINVY YNEAAGNKYV PRAILVDLEP GTMDSVRSGP FGQIFRPDN FVFGQSGAGN NWAKGHYTEG AELVDSVLDV VRKESESCDC LQGFQLTHSL GGGTGSGMGT LLISKIREEY P DRIMNTFS VVPSPKVSDT VVEPYNATLS VHQLVENTDE TYCIDNEALY DICFRTLKLT TPTYGDLNHL VSATMSGVTT CL RFPGQLN ADLRKLAVNM VPFPRLHFFM PGFAPLTSRG SQQYRALTVP ELTQQMFDAK NMMAACDPRH GRYLTVAAVF RGR MSMKEV DEQMLNVQNK NSSYFVEWIP NNVKTAVCDI PPRGLKMSAT FIGNSTAIQE LFKRISEQFT AMFRRKAFLH WYTG EGMDE MEFTEAESNM NDLVSEYQQY QDATADEQGE FEEEGEEDEA UniProtKB: Tubulin beta chain |
-Macromolecule #4: DESIGNED ANKYRIN REPEAT PROTEIN -- DARPin
| Macromolecule | Name: DESIGNED ANKYRIN REPEAT PROTEIN -- DARPin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 17.955262 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MRGSHHHHHH GSDLGKKLLE AARAGQDDEV RVLMANGADV NATDASGLTP LHLAATYGHL EIVEVLLKHG ADVSASDLMG STPLHLAAL IGHLEIVEVL LKHGADVNAV DTWGDTPLRL AAVMGHLKIV EALLKHGADV NAQDKFGKTA YDTSIDNGSE D LAEILQKL N |
-Macromolecule #5: Chromosome instability protein 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Chromosome instability protein 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 117.608211 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MHHHHHHNNI RALLDSIQSG VQTVSPEKHQ QTIAAINKFQ DDPALLDTIL PRCVPLLTKS FFCMSQRDQK LVAELFYNLD KISHSKVLK SLDTSIFRLN EILNYLQDRA SPSSFSDVLC VYLNLSWLSV ILLSPYAFKD KFNKTLQVSS RFENYPICIP P INKIKAVL ...String: MHHHHHHNNI RALLDSIQSG VQTVSPEKHQ QTIAAINKFQ DDPALLDTIL PRCVPLLTKS FFCMSQRDQK LVAELFYNLD KISHSKVLK SLDTSIFRLN EILNYLQDRA SPSSFSDVLC VYLNLSWLSV ILLSPYAFKD KFNKTLQVSS RFENYPICIP P INKIKAVL YFKNFTDAFD QLPEREQANV PFLNQFLKLF IQSSEKANYY FSNENLRHLQ QVALSNDGIK LLPKLFQISF NH GSHDILD AIVEFFHDHL SSNSTDTRFQ LAHSFAKIAK FLHQADPASF IELIDYTIEN TVSLLQAPCD SIDSNELHTS LLI IAEVAL AKILPIDLVD RVLTLIIPKT CHFQKSHFQI IKGHHIRDST NFIIWSVIRS NRSNSLSPQV LQSLLSHLLI NAFF DPELI IRYSSFAALQ ELLGRSNKSL ALNQNDIALI LQANWKDLPR SFEENSGLIR RLFNPENTSK SAVCVWKVFR DWSFN WNLL ENLHLTTMKL NIDYNLVPLI KSKLSSPALL QEVLNKAGSS VTQNCQILYL YLKLFENDVN CPKISEICID IYQKKI KFQ LTTQAKRQFN DNSPELFQIF VILKYWQLTG QNDFNQELFW KFVDIVSPQK KLNLYNEFIP IIQQIISQCV SLNYTRI VQ LIKSDNELTC RSICHMPDQE KMCSLFFSQF PLLSPQSRSL LIGELDHHWD VRISLLPSNS YRKFRNIIIN CLDDYTIT Q QGDVGRLVRI QALKLMQSHP DFLSGDCDSI NPKLTRLLAE PVPEIRKLSY QLLASATSQI TVLSDSSILN FRHKQGLSE EFWKGYAVSA GAIHFTDSQL TSSIDSFIVY YRSLSPSQQL ELCHDLIRII PSAKQIAESR IRDRNKDPLT GGMRFDTIKF TIHCVKFWT RIMESGLVVL HPNFNFQGVF AKFYNLHLLD CTTLRVSVIK FFPFLAISCY HTMRENADQK NLSNIILKRL L VLVKREYA ATKSKFMTDQ NVALQGMFQI FLELGVTRQL QALQVACQKH ELANILESDI TL UniProtKB: Chromosome instability protein 1 |
-Macromolecule #6: Tubulin alpha-1A chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin alpha-1A chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 50.121266 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MRECISIHVG QAGVQIGNAC WELYCLEHGI QPDGQMPSDK TIGGGDDSFN TFFSETGAGK HVPRAVFVDL EPTVIDEVRT GTYRQLFHP EQLITGKEDA ANNYARGHYT IGKEIIDLVL DRIRKLADQC TGLQGFSVFH SFGGGTGSGF TSLLMERLSV D YGKKSKLE ...String: MRECISIHVG QAGVQIGNAC WELYCLEHGI QPDGQMPSDK TIGGGDDSFN TFFSETGAGK HVPRAVFVDL EPTVIDEVRT GTYRQLFHP EQLITGKEDA ANNYARGHYT IGKEIIDLVL DRIRKLADQC TGLQGFSVFH SFGGGTGSGF TSLLMERLSV D YGKKSKLE FSIYPAPQVS TAVVEPYNSI LTTHTTLEHS DCAFMVDNEA IYDICRRNLD IERPTYTNLN RLIGQIVSSI TA SLRFDGA LNVDLTEFQT NLVPYPRAHF PLATYAPVIS AEKAYHEQLS VAEITNACFE PANQMVKCDP RHGKYMACCL LYR GDVVPK DVNAAIATIK TKRTIQFVDW CPTGFKVGIN YEPPTVVPGG DLAKVQRAVC MLSNTTAIAE AWARLDHKFD LMYA KRAFV HWYVGEGMEE GEFSEAREDM AALEKDYEEV GVDSVEGEGE EEGEEY UniProtKB: Tubulin alpha-1A chain |
-Macromolecule #7: GUANOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: GUANOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: GTP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 523.18 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-GTP: |
-Macromolecule #8: GUANOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: GUANOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: GDP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 443.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-GDP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 BASE (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.1 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.9 µm |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)




















