+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Arabinosyltransferase AftB in complex with Fab_B3 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Arabinosyltransferase / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology | : / : / : / AftB family C-terminal domain / Terminal beta-(1->2)-arabinofuranosyltransferase C-terminal domain-containing protein Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Mycolicibacterium chubuense (bacteria) / Mycolicibacterium chubuense (bacteria) /  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.85 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Liu Y / Mancia F | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025Title: Mechanistic studies of mycobacterial glycolipid biosynthesis by the mannosyltransferase PimE. Authors: Yaqi Liu / Chelsea M Brown / Nuno Borges / Rodrigo N Nobre / Satchal Erramilli / Meagan Belcher Dufrisne / Brian Kloss / Sabrina Giacometti / Ana M Esteves / Cristina G Timóteo / Piotr ...Authors: Yaqi Liu / Chelsea M Brown / Nuno Borges / Rodrigo N Nobre / Satchal Erramilli / Meagan Belcher Dufrisne / Brian Kloss / Sabrina Giacometti / Ana M Esteves / Cristina G Timóteo / Piotr Tokarz / Rosemary J Cater / Todd L Lowary / Yasu S Morita / Anthony A Kossiakoff / Helena Santos / Phillip J Stansfeld / Rie Nygaard / Filippo Mancia /        Abstract: Tuberculosis (TB), a leading cause of death among infectious diseases globally, is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). The pathogenicity of Mtb is largely attributed to its complex cell ...Tuberculosis (TB), a leading cause of death among infectious diseases globally, is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). The pathogenicity of Mtb is largely attributed to its complex cell envelope, which includes a class of glycolipids called phosphatidyl-myo-inositol mannosides (PIMs). These glycolipids maintain the integrity of the cell envelope, regulate permeability, and mediate host-pathogen interactions. PIMs comprise a phosphatidyl-myo-inositol core decorated with one to six mannose residues and up to four acyl chains. The mannosyltransferase PimE catalyzes the transfer of the fifth PIM mannose residue from a polyprenyl phosphate-mannose (PPM) donor. This step contributes to the proper assembly and function of the mycobacterial cell envelope; however, the structural basis for substrate recognition and the catalytic mechanism of PimE remain poorly understood. Here, we present the cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of PimE from Mycobacterium abscessus in its apo and product-bound form. The structures reveal a distinctive binding cavity that accommodates both donor and acceptor substrates/products. Key residues involved in substrate coordination and catalysis were identified and validated via in vitro assays and in vivo complementation, while molecular dynamics simulations delineated access pathways and binding dynamics. Our integrated approach provides comprehensive insights into PimE function and informs potential strategies for anti-TB therapeutics. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_46976.map.gz emd_46976.map.gz | 168 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-46976-v30.xml emd-46976-v30.xml emd-46976.xml emd-46976.xml | 17.4 KB 17.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_46976.png emd_46976.png | 38.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-46976.cif.gz emd-46976.cif.gz | 6.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_46976_half_map_1.map.gz emd_46976_half_map_1.map.gz emd_46976_half_map_2.map.gz emd_46976_half_map_2.map.gz | 165.1 MB 165.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-46976 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-46976 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-46976 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-46976 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9dlfMC  9dlhC  9dm5C  9dm7C  9mjbC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_46976.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_46976.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.87 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_46976_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_46976_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Arabinosyltransferase AftB in complex with Fab_B3
| Entire | Name: Arabinosyltransferase AftB in complex with Fab_B3 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Arabinosyltransferase AftB in complex with Fab_B3
| Supramolecule | Name: Arabinosyltransferase AftB in complex with Fab_B3 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Mycolicibacterium chubuense (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium chubuense (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: Arabinosyltransferase AftB
| Macromolecule | Name: Arabinosyltransferase AftB / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Mycolicibacterium chubuense (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium chubuense (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 72.830609 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MPQSSSADRL SRPFTEAAAT RLNRWPAFPY HVWVRVSLWV SVVTVAALFG WGAWQRRWIA DDGLIVLRTV RNLLAGNGPV FNAGERVEA NTSTVWSYLV TLGGFVAGSA RLEYVALVLA LTLSVLGVVL VMFGTARLYA PGLTGRRAVF LPAGALVYIA I PPARDFAT ...String: MPQSSSADRL SRPFTEAAAT RLNRWPAFPY HVWVRVSLWV SVVTVAALFG WGAWQRRWIA DDGLIVLRTV RNLLAGNGPV FNAGERVEA NTSTVWSYLV TLGGFVAGSA RLEYVALVLA LTLSVLGVVL VMFGTARLYA PGLTGRRAVF LPAGALVYIA I PPARDFAT SGLENGLVLA YLGLLWWMMV CWSQGLRRPD GERTSRGFDA TLAVVAGMSV LVRPELALIG GLALVMMLVA AP TWRRRLA LVVVGGLIPV AYQIFRMGYY GLLVPGTALA KDASGAKWDQ GLVYLANFNQ PYLLWAPAVL LIGLGLMVLL LRG RPSWGD RGARKESGWI ARTVQSPPAV VAFMLISGLL QAVYWIRQGG DFMHGRVLLT PLFCLLAPVA VIPLLLPDRS RMAR GAGYL YAGATAVLWL AVAGWALWAA NSPGMGADAT RVTYSGIVDE RRFYSQATGH AHPLTAADYL DYPRMRAVLT AIENT PDGA LLLPSGDYDR WDVVPALPPP PDVRAAAVGG YVGPHTVFFT NLGMLGMNVG LDVRVIDQIG LANPLAAHTA RLTDGR IGH DKNLFPDWAV AEGPFLKEPP WIPQYLDEDW IRQAEAALKC PETDKVLDAI RAPMGFRRFL SNVMHAAEYT RYRIDRV PL YELARCGLPV PEPVDPPYTG LPPTGPA UniProtKB: Terminal beta-(1->2)-arabinofuranosyltransferase C-terminal domain-containing protein |
-Macromolecule #2: Fab_B3 light chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Fab_B3 light chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.677979 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: DIQMTQSPSS LSASVGDRVT ITCRASQSVS SSAVAWYQQK PGKAPKLLIY SASSLYSGVP SRFSGSRSGT DFTLTISSLQ PEDFATYYC QQSPPYGPIT FGQGTKVELK |
-Macromolecule #3: Fab_B3 heavy chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Fab_B3 heavy chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.713124 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: EVQLVESGGG LVQPGGSLRL SCAASGFNVS SSYIHWVRQA PGKGLEWVAS ISSYYGYTSY ADSVKGRFTI SADTSKNTAY LQMNSLRAE DTAVYYCARG YMYSHWVYSY GAIDYWGQGT LVTVSSA |
-Macromolecule #4: [(2~{R})-1-[2-azanylethoxy(oxidanyl)phosphoryl]oxy-3-hexadecanoyl...
| Macromolecule | Name: [(2~{R})-1-[2-azanylethoxy(oxidanyl)phosphoryl]oxy-3-hexadecanoyloxy-propan-2-yl] (~{Z})-octadec-9-enoate type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: 6OU |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 717.996 Da |
| Chemical component information | 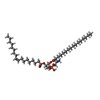 ChemComp-6OU: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 58.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)




































