[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-46820: Cryo-EM structure of a SUR1/Kir6.2 ATP-sensitive potassium channe... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
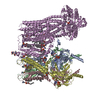
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of a SUR1/Kir6.2 ATP-sensitive potassium channel in the presence of Aekatperone in the closed conformation | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ATP-sensitive potassium channel / KATP channel / SUR1 / Kir6.2 / potassium transport / metabolic sensor / congenital hyperinsulinism / trafficking / pharmacochaperone / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRegulation of insulin secretion / ATP sensitive Potassium channels / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / ATP-activated inward rectifier potassium channel activity / response to resveratrol / inward rectifying potassium channel / sulfonylurea receptor activity / ventricular cardiac muscle tissue development / cell body fiber / CAMKK-AMPK signaling cascade ...Regulation of insulin secretion / ATP sensitive Potassium channels / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / ATP-activated inward rectifier potassium channel activity / response to resveratrol / inward rectifying potassium channel / sulfonylurea receptor activity / ventricular cardiac muscle tissue development / cell body fiber / CAMKK-AMPK signaling cascade / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / regulation of monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / ATPase-coupled monoatomic cation transmembrane transporter activity / inward rectifier potassium channel activity / nervous system process / : / ankyrin binding / Ion homeostasis / response to testosterone / response to ATP / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / response to stress / intercalated disc / action potential / axolemma / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / ABC-type transporter activity / heat shock protein binding / potassium ion transmembrane transport / cellular response to nutrient levels / T-tubule / regulation of insulin secretion / acrosomal vesicle / response to ischemia / determination of adult lifespan / positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / regulation of membrane potential / potassium ion transport / cellular response to glucose stimulus / negative regulation of insulin secretion / sarcolemma / cellular response to nicotine / glucose metabolic process / cellular response to tumor necrosis factor / response to estradiol / nuclear envelope / presynaptic membrane / transmembrane transporter binding / response to hypoxia / endosome / response to xenobiotic stimulus / neuronal cell body / apoptotic process / glutamatergic synapse / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / metal ion binding / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Mesocricetus auratus (golden hamster) Mesocricetus auratus (golden hamster) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Driggers CM / ElSheikh A / Shyng S-L | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2025 Journal: Elife / Year: 2025Title: AI-based discovery and cryoEM structural elucidation of a K channel pharmacochaperone. Authors: Assmaa Elsheikh / Camden M Driggers / Ha H Truong / Zhongying Yang / John Allen / Niel M Henriksen / Katarzyna Walczewska-Szewc / Show-Ling Shyng /    Abstract: Pancreatic K channel trafficking defects underlie congenital hyperinsulinism (CHI) cases unresponsive to the K channel opener diazoxide, the mainstay medical therapy for CHI. Current clinically used ...Pancreatic K channel trafficking defects underlie congenital hyperinsulinism (CHI) cases unresponsive to the K channel opener diazoxide, the mainstay medical therapy for CHI. Current clinically used K channel inhibitors have been shown to act as pharmacochaperones and restore surface expression of trafficking mutants; however, their therapeutic utility for K trafficking-impaired CHI is hindered by high affinity binding, which limits functional recovery of rescued channels. Recent structural studies of K channels employing cryo-electron microscopy (cryoEM) have revealed a promiscuous pocket where several known K pharmacochaperones bind. The structural knowledge provides a framework for discovering K channel pharmacochaperones with desired reversible inhibitory effects to permit functional recovery of rescued channels. Using an AI-based virtual screening technology AtomNet followed by functional validation, we identified a novel compound, termed Aekatperone, which exhibits chaperoning effects on K channel trafficking mutations. Aekatperone reversibly inhibits K channel activity with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC) ~9 μM. Mutant channels rescued to the cell surface by Aekatperone showed functional recovery upon washout of the compound. CryoEM structure of K bound to Aekatperone revealed distinct binding features compared to known high affinity inhibitor pharmacochaperones. Our findings unveil a K pharmacochaperone enabling functional recovery of rescued channels as a promising therapeutic for CHI caused by K trafficking defects. #1:  Journal: Elife / Year: 2024 Journal: Elife / Year: 2024Title: AI-Based Discovery and CryoEM Structural Elucidation of a KATP Channel Pharmacochaperone Authors: ElSheikh A / Driggers CM / Truong HH / Yang Z / Allen J / Henriksen N / Walczewska-Szewc K / Shyng SL | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_46820.map.gz emd_46820.map.gz | 255.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-46820-v30.xml emd-46820-v30.xml emd-46820.xml emd-46820.xml | 25.3 KB 25.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_46820_fsc.xml emd_46820_fsc.xml | 17 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_46820.png emd_46820.png | 75.5 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_46820_msk_1.map emd_46820_msk_1.map | 512 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-46820.cif.gz emd-46820.cif.gz | 8.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_46820_half_map_1.map.gz emd_46820_half_map_1.map.gz emd_46820_half_map_2.map.gz emd_46820_half_map_2.map.gz | 475.7 MB 475.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-46820 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-46820 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-46820 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-46820 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9dfxMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_46820.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_46820.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.0515 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_46820_msk_1.map emd_46820_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_46820_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_46820_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Kir6.2/SUR1 closed channel in complex with Aekatperone
| Entire | Name: Kir6.2/SUR1 closed channel in complex with Aekatperone |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Kir6.2/SUR1 closed channel in complex with Aekatperone
| Supramolecule | Name: Kir6.2/SUR1 closed channel in complex with Aekatperone type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 Details: Kir6.2/SUR1 KATP channel in the closed conformation in complex with ATP and Aekatperone |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 880 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 11
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 11 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 43.661762 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MLSRKGIIPE EYVLTRLAED PTEPRYRTRE RRARFVSKKG NCNVAHKNIR EQGRFLQDVF TTLVDLKWPH TLLIFTMSFL CSWLLFAMV WWLIAFAHGD LAPGEGTNVP CVTSIHSFSS AFLFSIEVQV TIGFGGRMVT EECPLAILIL IVQNIVGLMI N AIMLGCIF ...String: MLSRKGIIPE EYVLTRLAED PTEPRYRTRE RRARFVSKKG NCNVAHKNIR EQGRFLQDVF TTLVDLKWPH TLLIFTMSFL CSWLLFAMV WWLIAFAHGD LAPGEGTNVP CVTSIHSFSS AFLFSIEVQV TIGFGGRMVT EECPLAILIL IVQNIVGLMI N AIMLGCIF MKTAQAHRRA ETLIFSKHAV ITLRHGRLCF MLRVGDLRKS MIISATIHMQ VVRKTTSPEG EVVPLHQVDI PM ENGVGGN SIFLVAPLII YHVIDSNSPL YDLAPSDLHH HQDLEIIVIL EGVVETTGIT TQARTSYLAD EILWGQRFVP IVA EEDGRY SVDYSKFGNT VKVPTPLCTA RQLDEDRSLL DALTLASSRG PLRKRSVAVA KAKPKFSISP DSLS UniProtKB: ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 11 |
-Macromolecule #2: SUR1
| Macromolecule | Name: SUR1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Mesocricetus auratus (golden hamster) / Organ: pancreas / Cell: Beta Cell Mesocricetus auratus (golden hamster) / Organ: pancreas / Cell: Beta Cell |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 177.296578 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MPLAFCGTEN HSAAYRVDQG VLNNGCFVDA LNVVPHVFLL FITFPILFIG WGSQSSKVHI HHSTWLHFPG HNLRWILTFI LLFVLVCEI AEGILSDGVT ESRHLHLYMP AGMAFMAAIT SVVYYHNIET SNFPKLLIAL LIYWTLAFIT KTIKFVKFYD H AIGFSQLR ...String: MPLAFCGTEN HSAAYRVDQG VLNNGCFVDA LNVVPHVFLL FITFPILFIG WGSQSSKVHI HHSTWLHFPG HNLRWILTFI LLFVLVCEI AEGILSDGVT ESRHLHLYMP AGMAFMAAIT SVVYYHNIET SNFPKLLIAL LIYWTLAFIT KTIKFVKFYD H AIGFSQLR FCLTGLLVIL YGMLLLVEVN VIRVRRYIFF KTPREVKPPE DLQDLGVRFL QPFVNLLSKG TYWWMNAFIK TA HKKPIDL RAIGKLPIAM RALTNYQRLC VAFDAQARKD TQSPQGARAI WRALCHAFGR RLILSSTFRI LADLLGFAGP LCI FGIVDH LGKENHVFQP KTQFLGVYFV SSQEFLGNAY VLAVLLFLAL LLQRTFLQAS YYVAIETGIN LRGAIQTKIY NKIM HLSTS NLSMGEMTAG QICNLVAIDT NQLMWFFFLC PNLWAMPVQI IVGVILLYYI LGVSALIGAA VIILLAPVQY FVATK LSQA QRSTLEHSNE RLKQTNEMLR GMKLLKLYAW ESIFCSRVEV TRRKEMTSLR AFAVYTSISI FMNTAIPIAA VLITFV GHV SFFKESDLSP SVAFASLSLF HILVTPLFLL SSVVRSTVKA LVSVKKLSEF LSSAEIREEQ CAPREPAPQG QAGKYQA VP LKVVNRKRPA REEVRDLLGP LQRLAPSMDG DADNFCVQII GGFFTWTPDG IPTLSNITIR IPRGQLTMIV GQVGCGKS S LLLATLGEMQ KVSGAVFWNS NLPDSEGEDP SSPERETAAG SDIRSRGPVA YASQKPWLLN ATVEENITFE SPFNKQRYK MVIEACSLQP DIDILPHGDQ TQIGERGINL SGGQRQRISV ARALYQQTNV VFLDDPFSAL DVHLSDHLMQ AGILELLRDD KRTVVLVTH KLQYLPHADW IIAMKDGTIQ REGTLKDFQR SECQLFEHWK TLMNRQDQEL EKETVMERKA SEPSQGLPRA M SSRDGLLL DEEEEEEEAA ESEEDDNLSS VLHQRAKIPW RACTKYLSSA GILLLSLLVF SQLLKHMVLV AIDYWLAKWT DS ALVLSPA ARNCSLSQEC DLDQSVYAMV FTLLCSLGIV LCLVTSVTVE WTGLKVAKRL HRSLLNRIIL APMRFFETTP LGS ILNRFS SDCNTIDQHI PSTLECLSRS TLLCVSALTV ISYVTPVFLV ALLPLAVVCY FIQKYFRVAS RDLQQLDDTT QLPL LSHFA ETVEGLTTIR AFRYEARFQQ KLLEYTDSNN IASLFLTAAN RWLEVRMEYI GACVVLIAAA TSISNSLHRE LSAGL VGLG LTYALMVSNY LNWMVRNLAD MEIQLGAVKR IHALLKTEAE SYEGLLAPSL IPKNWPDQGK IQIQNLSVRY DSSLKP VLK HVNALISPGQ KIGICGRTGS GKSSFSLAFF RMVDMFEGRI IIDGIDIAKL PLHTLRSRLS IILQDPVLFS GTIRFNL DP EKKCSDSTLW EALEIAQLKL VVKALPGGLD AIITEGGENF SQGQRQLFCL ARAFVRKTSI FIMDEATASI DMATENIL Q KVVMTAFADR TVVTIAHRVH TILSADLVMV LKRGAILEFD KPETLLSQKD SVFASFVRAD K UniProtKB: ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 8 |
-Macromolecule #3: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Macromolecule #4: POTASSIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: POTASSIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: K |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.098 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: N-[3-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl]-2-[(1H-imidazol-1-yl)met...
| Macromolecule | Name: N-[3-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl]-2-[(1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]benzene-1-sulfonamide type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: A1A4F |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 399.51 Da |
-Macromolecule #6: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.15 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
Details: MSB with GDN, ATP and AKP | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: EMS Lacey Carbon / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: LACEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 279 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | Three microliters of purified Kir6.2-Q52R/FLAG-SUR1 were loaded onto Quantifoil R 1.2/1.3 Au 300 grids prepared with a fresh graphene oxide surface. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Details | Titan Krios with Falcon K3 at the Pacific Northwest National Lab |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 2 / Number real images: 21012 / Average exposure time: 3.2 sec. / Average electron dose: 55.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 81000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)