+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
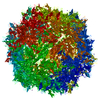
| Title | The Structure of AAV5 at 4 Degrees | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | temperature / genome / vector / icosahedron / VIRUS | |||||||||
| Function / homology | Phospholipase A2-like domain / Phospholipase A2-like domain / Parvovirus coat protein VP2 / Parvovirus coat protein VP1/VP2 / Parvovirus coat protein VP1/VP2 / Capsid/spike protein, ssDNA virus / T=1 icosahedral viral capsid / structural molecule activity / Capsid protein Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  adeno-associated virus 5 adeno-associated virus 5 | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.89 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Bennett AB / McKenna R | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Virol / Year: 2025 Journal: J Virol / Year: 2025Title: Biophysical and structural insights into AAV genome ejection. Authors: Keely Gliwa / Joshua Hull / Austin Kansol / Victoria Zembruski / Renuk Lakshmanan / Mario Mietzsch / Paul Chipman / Antonette Bennett / Robert McKenna /  Abstract: Recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) is comprised of non-enveloped capsids that can package a therapeutic transgene and are currently being developed and utilized as gene therapy vectors. The ...Recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) is comprised of non-enveloped capsids that can package a therapeutic transgene and are currently being developed and utilized as gene therapy vectors. The therapeutic efficiency of rAAV is dependent on successful cytoplasmic trafficking and transgene delivery to the nucleus. It is hypothesized that an increased understanding of the effects of the cellular environment and biophysical properties of the capsid as it traffics to the nucleus could provide insight to improve vector efficiency. The AAV capsid is exposed to increasing [H] during endo-lysosomal trafficking. Exposure to low pH facilitates the externalization of the viral protein 1 unique region (VP1u). This VP1u contains a phospholipase A2 domain required for endosomal escape and nuclear localization signals that facilitate nuclear targeting and entry. The viral genome is released either after total capsid disassembly or via a concerted DNA ejection mechanism in the nucleus. This study presents the characterization of genome ejection (GE) for two diverse serotypes, AAV2 and AAV5, using temperature. The temperature required to disassemble the virus capsid (T) is significantly higher than the temperature required to expose the transgene (T) for both serotypes. This was verified by quantitative PCR (qPCR) and transmission electron microscopy. Additionally, the absence of VP1/VP2 in the capsids and a decrease in pH increase the temperature of GE. Furthermore, cryo-electron microscopy structures of the AAV5 capsid pre- and post-GE reveal dynamics at the twofold, threefold, and fivefold regions of the capsid interior consistent with a concerted egress of the viral genome.IMPORTANCEThe development of recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) capsids has grown rapidly in recent years, with five of the eight established therapeutics gaining approval in the past 2 years alone. Clinical progression with AAV2 and AAV5 represents a growing need to further characterize the molecular biology of these viruses. The goal of AAV-based gene therapy is to treat monogenic disorders with a vector-delivered transgene to provide wild-type protein function. A better understanding of the dynamics and conditions enabling transgene release may improve therapeutic efficiency. In addition to their clinical importance, AAV2 and 5 were chosen in this study for their diverse antigenic and biophysical properties compared to more closely related serotypes. Characterization of a shared genome ejection process may imply a conserved mechanism for all rAAV therapies. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_46748.map.gz emd_46748.map.gz | 234.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-46748-v30.xml emd-46748-v30.xml emd-46748.xml emd-46748.xml | 17.2 KB 17.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_46748.png emd_46748.png | 240.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-46748.cif.gz emd-46748.cif.gz | 6.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_46748_half_map_1.map.gz emd_46748_half_map_1.map.gz emd_46748_half_map_2.map.gz emd_46748_half_map_2.map.gz | 442.1 MB 442.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-46748 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-46748 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-46748 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-46748 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9dcbMC  9dc7C  9dccC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_46748.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 476.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_46748.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 476.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.935 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_46748_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_46748_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : adeno-associated virus 5
| Entire | Name:  adeno-associated virus 5 adeno-associated virus 5 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: adeno-associated virus 5
| Supramolecule | Name: adeno-associated virus 5 / type: virus / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all / Details: Baculovirus expression / NCBI-ID: 82300 / Sci species name: adeno-associated virus 5 / Virus type: VIRION / Virus isolate: SEROTYPE / Virus enveloped: No / Virus empty: No |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 4 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Capsid protein
| Macromolecule | Name: Capsid protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 60 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  adeno-associated virus 5 adeno-associated virus 5 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 80.497414 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSFVDHPPDW LEEVGEGLRE FLGLEAGPPK PKPNQQHQDQ ARGLVLPGYN YLGPGNGLDR GEPVNRADEV AREHDISYNE QLEAGDNPY LKYNHADAEF QEKLADDTSF GGNLGKAVFQ AKKRVLEPFG LVEEGAKTAP TGKRIDDHFP KRKKARTEED S KPSTSSDA ...String: MSFVDHPPDW LEEVGEGLRE FLGLEAGPPK PKPNQQHQDQ ARGLVLPGYN YLGPGNGLDR GEPVNRADEV AREHDISYNE QLEAGDNPY LKYNHADAEF QEKLADDTSF GGNLGKAVFQ AKKRVLEPFG LVEEGAKTAP TGKRIDDHFP KRKKARTEED S KPSTSSDA EAGPSGSQQL QIPAQPASSL GADTMSAGGG GPLGDNNQGA DGVGNASGDW HCDSTWMGDR VVTKSTRTWV LP SYNNHQY REIKSGSVDG SNANAYFGYS TPWGYFDFNR FHSHWSPRDW QRLINNYWGF RPRSLRVKIF NIQVKEVTVQ DST TTIANN LTSTVQVFTD DDYQLPYVVG NGTEGCLPAF PPQVFTLPQY GYATLNRDNT ENPTERSSFF CLEYFPSKML RTGN NFEFT YNFEEVPFHS SFAPSQNLFK LANPLVDQYL YRFVSTNNTG GVQFNKNLAG RYANTYKNWF PGPMGRTQGW NLGSG VNRA SVSAFATTNR MELEGASYQV PPQPNGMTNN LQGSNTYALE NTMIFNSQPA NPGTTATYLE GNMLITSESE TQPVNR VAY NVGGQMATNN QSSTTAPATG TYNLQEIVPG SVWMERDVYL QGPIWAKIPE TGAHFHPSPA MGGFGLKHPP PMMLIKN TP VPGNITSFSD VPVSSFITQY STGQVTVEME WELKKENSKR WNPEIQYTNN YNDPQFVDFA PDSTGEYRTT RPIGTRYL T RPL UniProtKB: Capsid protein |
-Macromolecule #2: DNA (5'-D(P*AP*A)-3')
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (5'-D(P*AP*A)-3') / type: dna / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 60 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  adeno-associated virus 5 adeno-associated virus 5 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 581.456 Da |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DA) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 / Component - Concentration: 1.0 mM / Component - Formula: PBS-MK / Component - Name: TD Details: 10 mM Na2HPO4, 2 mM KH2PO4, 135 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, pH 7.4 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 45.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.967 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.289 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.89 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 23000 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: COMMON LINE |
| Final angle assignment | Type: COMMON LINE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)