[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-44979: human sodium chloride cotransporter NCC S344E in the phosphorylat... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | human sodium chloride cotransporter NCC S344E in the phosphorylation state and in complex with hydrochlorothiazide | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | human sodium chloride cotransporter NCC S344E in the phosphorylation state and in complex with hydrochlorothiazide | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | sodium chloride cotransporter / phosphorylation / thiazide diuretics / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsodium:chloride symporter activity / apical plasma membrane / ATP binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Cao EH / Zhao YX | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Structural bases for Na-Cl cotransporter inhibition by thiazide diuretic drugs and activation by kinases. Authors: Yongxiang Zhao / Heidi Schubert / Alan Blakely / Biff Forbush / Micholas Dean Smith / Jesse Rinehart / Erhu Cao /   Abstract: The Na-Cl cotransporter (NCC) drives salt reabsorption in the kidney and plays a decisive role in balancing electrolytes and blood pressure. Thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics inhibit NCC-mediated ...The Na-Cl cotransporter (NCC) drives salt reabsorption in the kidney and plays a decisive role in balancing electrolytes and blood pressure. Thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics inhibit NCC-mediated renal salt retention and have been cornerstones for treating hypertension and edema since the 1950s. Here we determine NCC co-structures individually complexed with the thiazide drug hydrochlorothiazide, and two thiazide-like drugs chlorthalidone and indapamide, revealing that they fit into an orthosteric site and occlude the NCC ion translocation pathway. Aberrant NCC activation by the WNKs-SPAK kinase cascade underlies Familial Hyperkalemic Hypertension, but it remains unknown whether/how phosphorylation transforms the NCC structure to accelerate ion translocation. We show that an intracellular amino-terminal motif of NCC, once phosphorylated, associates with the carboxyl-terminal domain, and together, they interact with the transmembrane domain. These interactions suggest a phosphorylation-dependent allosteric network that directly influences NCC ion translocation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_44979.map.gz emd_44979.map.gz | 168 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-44979-v30.xml emd-44979-v30.xml emd-44979.xml emd-44979.xml | 20.3 KB 20.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_44979.png emd_44979.png | 26.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-44979.cif.gz emd-44979.cif.gz | 6.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_44979_additional_1.map.gz emd_44979_additional_1.map.gz emd_44979_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44979_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44979_half_map_2.map.gz emd_44979_half_map_2.map.gz | 89.4 MB 165.4 MB 165.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44979 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44979 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44979 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44979 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9bwtMC  8vpnC  8vppC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_44979.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_44979.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | human sodium chloride cotransporter NCC S344E in the phosphorylation state and in complex with hydrochlorothiazide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.825 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Additional Map
| File | emd_44979_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Additional Map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half Map A
| File | emd_44979_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half Map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half Map B
| File | emd_44979_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half Map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Phosphorylated SLC12A3 transporter in complex with hydrochlorothiazide
| Entire | Name: Phosphorylated SLC12A3 transporter in complex with hydrochlorothiazide |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Phosphorylated SLC12A3 transporter in complex with hydrochlorothiazide
| Supramolecule | Name: Phosphorylated SLC12A3 transporter in complex with hydrochlorothiazide type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Solute carrier family 12 member 3
| Macromolecule | Name: Solute carrier family 12 member 3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 113.40668 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MAELPTTETP GDATLCSGRF TISTLLSSDE PSPPAAYDSS HPSHLTHSST FCMR(TPO)FGYN(TPO) IDVVPTYEHY AN (SEP)TQPGEP RKVRPTLADL HSFLKEGRHL HALAFDSRPS HEMTDGLVEG EAGTSSEKNP EEPVRFGWVK GVMIRCMLN IWGVILYLRL ...String: MAELPTTETP GDATLCSGRF TISTLLSSDE PSPPAAYDSS HPSHLTHSST FCMR(TPO)FGYN(TPO) IDVVPTYEHY AN (SEP)TQPGEP RKVRPTLADL HSFLKEGRHL HALAFDSRPS HEMTDGLVEG EAGTSSEKNP EEPVRFGWVK GVMIRCMLN IWGVILYLRL PWITAQAGIV LTWIIILLSV TVTSITGLSI SAISTNGKVK SGGTYFLISR SLGPELGGSI GLIFAFANAV GVAMHTVGF AETVRDLLQE YGAPIVDPIN DIRIIAVVSV TVLLAISLAG MEWESKAQVL FFLVIMVSFA NYLVGTLIPP S EDKASKGF FSYRADIFVQ NLVPDWRGPD GTFFGMFEIF FPSATGILAG ANISGDLKDP AIAIPKGTLM AIFWTTISYL AI SATIGSC VVRDASGVLN DTVTPGWGAC EGLACSYGWN FTECTQQHSC HYGLINYYQT MSMVSGFAPL ITAGIFGATL SSA LACLVS AAKVFQCLCE DQLYPLIGFF GKGYGKNKEP VRGYLLAYAI AVAFIIIAEL NTIAPIISNF FLCSYALINF SCFH ASITN SPGWRPSFQY YNKWAALFGA IISVVIMFLL TWWAALIAIG VVLFLLLYVI YKKPEVNWGS SVQAGSYNLA LSYSV GLNE VEDHIKNYRP QCLVLTGPPN FRPALVDFVG TFTRNLSLMI CGHVLIGPHK QRMPELQLIA NGHTKWLNKR KIKAFY SDV IAEDLRRGVQ ILMQAAGLGR MKPNILVVGF KKNWQSAHPA TVEDYIGILH DAFDFNYGVC VMRMREGLNV SKMMQAH IN PVFDPAEDGK EASARVDPKA LVKEEQATTI FQSEQGKKTI DIYWLFDDGG LTLLIPYLLG RKRRWSKCKI RVFVGGQI N RMDQERKAII SLLSKFRLGF HEVHILPDIN QNPRAEHTKR FEDMIAPFRL NDGFKDEATV NEMRRDCPWK ISDEEITKN RVKSLRQVRL NEIVLDYSRD AALIVITLPI GRKGKCPSSL YMAWLETLSQ DLRPPVILIR GNQENVLTFY CQ UniProtKB: Solute carrier family 12 member 3 |
-Macromolecule #2: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Macromolecule #3: 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-...
| Macromolecule | Name: 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: HCZ |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 297.739 Da |
| Chemical component information | 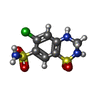 ChemComp-HCZ: |
-Macromolecule #4: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 4 K |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)












































