[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-44184: Filament of Tau in complex with D-TLKIVWI, a D-peptide that disag... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Filament of Tau in complex with D-TLKIVWI, a D-peptide that disaggregates Alzheimer's Paired Helical Filaments, determined by Cryo-EM | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Alzheimer's disease / Tau / fibril / cryo-EM / helix / UNKNOWN FUNCTION / PROTEIN FIBRIL | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationplus-end-directed organelle transport along microtubule / histone-dependent DNA binding / negative regulation of establishment of protein localization to mitochondrion / neurofibrillary tangle / microtubule lateral binding / axonal transport / tubulin complex / positive regulation of protein localization to synapse / negative regulation of tubulin deacetylation / phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate binding ...plus-end-directed organelle transport along microtubule / histone-dependent DNA binding / negative regulation of establishment of protein localization to mitochondrion / neurofibrillary tangle / microtubule lateral binding / axonal transport / tubulin complex / positive regulation of protein localization to synapse / negative regulation of tubulin deacetylation / phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate binding / generation of neurons / rRNA metabolic process / axonal transport of mitochondrion / regulation of mitochondrial fission / axon development / regulation of chromosome organization / central nervous system neuron development / intracellular distribution of mitochondria / minor groove of adenine-thymine-rich DNA binding / lipoprotein particle binding / microtubule polymerization / negative regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential / dynactin binding / regulation of microtubule polymerization / apolipoprotein binding / main axon / protein polymerization / axolemma / glial cell projection / Caspase-mediated cleavage of cytoskeletal proteins / regulation of microtubule polymerization or depolymerization / negative regulation of mitochondrial fission / neurofibrillary tangle assembly / positive regulation of axon extension / regulation of cellular response to heat / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / synapse assembly / positive regulation of superoxide anion generation / regulation of long-term synaptic depression / positive regulation of protein localization / supramolecular fiber organization / cellular response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulus / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / positive regulation of microtubule polymerization / somatodendritic compartment / axon cytoplasm / astrocyte activation / stress granule assembly / phosphatidylinositol binding / nuclear periphery / regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization / protein phosphatase 2A binding / cellular response to reactive oxygen species / Hsp90 protein binding / microglial cell activation / cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus / synapse organization / protein homooligomerization / PKR-mediated signaling / regulation of synaptic plasticity / SH3 domain binding / response to lead ion / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / memory / cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule / neuron projection development / cell-cell signaling / single-stranded DNA binding / protein-folding chaperone binding / cellular response to heat / actin binding / microtubule cytoskeleton / cell body / growth cone / double-stranded DNA binding / protein-macromolecule adaptor activity / microtubule binding / dendritic spine / sequence-specific DNA binding / amyloid fibril formation / microtubule / learning or memory / neuron projection / regulation of autophagy / membrane raft / axon / negative regulation of gene expression / neuronal cell body / dendrite / DNA damage response / protein kinase binding / enzyme binding / mitochondrion / DNA binding / RNA binding / extracellular region / identical protein binding / nucleus / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hou K / Ge P / Sawaya MR / Eisenberg DS | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2025 Journal: Nature / Year: 2025Title: How short peptides disassemble tau fibrils in Alzheimer's disease. Authors: Ke Hou / Peng Ge / Michael R Sawaya / Liisa Lutter / Joshua L Dolinsky / Yuan Yang / Yi Xiao Jiang / David R Boyer / Xinyi Cheng / Justin Pi / Jeffrey Zhang / Jiahui Lu / Romany Abskharon / ...Authors: Ke Hou / Peng Ge / Michael R Sawaya / Liisa Lutter / Joshua L Dolinsky / Yuan Yang / Yi Xiao Jiang / David R Boyer / Xinyi Cheng / Justin Pi / Jeffrey Zhang / Jiahui Lu / Romany Abskharon / Shixin Yang / Zhiheng Yu / Juli Feigon / David S Eisenberg /  Abstract: Reducing fibrous aggregates of the protein tau is a possible strategy for halting the progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Previously, we found that in vitro, the D-enantiomeric peptide (D- ...Reducing fibrous aggregates of the protein tau is a possible strategy for halting the progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Previously, we found that in vitro, the D-enantiomeric peptide (D-peptide) D-TLKIVWC disassembles ultra-stable tau fibrils extracted from the autopsied brains of individuals with AD (hereafter, these tau fibrils are referred to as AD-tau) into benign segments, with no energy source other than ambient thermal agitation. To consider D-peptide-mediated disassembly as a potential route to therapeutics for AD, it is essential to understand the mechanism and energy source of the disassembly action. Here, we show that the assembly of D-peptides into amyloid-like ('mock-amyloid') fibrils is essential for AD-tau disassembly. These mock-amyloid fibrils have a right-handed twist but are constrained to adopt a left-handed twist when templated in complex with AD-tau. The release of strain that accompanies the conversion of left-twisted to right-twisted, relaxed mock-amyloid produces a torque that is sufficient to break the local hydrogen bonding between tau molecules, and leads to the fragmentation of AD-tau. This strain-relief mechanism seems to operate in other examples of amyloid fibril disassembly, and could inform the development of first-in-class therapeutics for amyloid diseases. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_44184.map.gz emd_44184.map.gz | 184.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-44184-v30.xml emd-44184-v30.xml emd-44184.xml emd-44184.xml | 24.9 KB 24.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_44184_fsc.xml emd_44184_fsc.xml | 15.3 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_44184.png emd_44184.png | 86.1 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_44184_msk_1.map emd_44184_msk_1.map | 307.5 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-44184.cif.gz emd-44184.cif.gz | 7.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_44184_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44184_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44184_half_map_2.map.gz emd_44184_half_map_2.map.gz | 57 MB 57 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44184 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44184 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44184 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44184 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_44184_validation.pdf.gz emd_44184_validation.pdf.gz | 674.7 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_44184_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_44184_full_validation.pdf.gz | 674.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_44184_validation.xml.gz emd_44184_validation.xml.gz | 23.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_44184_validation.cif.gz emd_44184_validation.cif.gz | 31.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44184 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44184 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44184 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44184 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9b4lMC  9b4iC  9b4jC  9b4kC  9b4mC  9b4nC  9b4oC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_44184.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 307.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_44184.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 307.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.94 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_44184_msk_1.map emd_44184_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_44184_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_44184_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Tau PHF - D-TLKIVWI Complex
| Entire | Name: Tau PHF - D-TLKIVWI Complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Tau PHF - D-TLKIVWI Complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Tau PHF - D-TLKIVWI Complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: Tau PHF
| Supramolecule | Name: Tau PHF / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #3: D-TLKIVWI
| Supramolecule | Name: D-TLKIVWI / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) / Synthetically produced: Yes |
-Macromolecule #1: Microtubule-associated protein tau
| Macromolecule | Name: Microtubule-associated protein tau / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 12 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 79.041617 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MAEPRQEFEV MEDHAGTYGL GDRKDQGGYT MHQDQEGDTD AGLKESPLQT PTEDGSEEPG SETSDAKSTP TAEDVTAPLV DEGAPGKQA AAQPHTEIPE GTTAEEAGIG DTPSLEDEAA GHVTQEPESG KVVQEGFLRE PGPPGLSHQL MSGMPGAPLL P EGPREATR ...String: MAEPRQEFEV MEDHAGTYGL GDRKDQGGYT MHQDQEGDTD AGLKESPLQT PTEDGSEEPG SETSDAKSTP TAEDVTAPLV DEGAPGKQA AAQPHTEIPE GTTAEEAGIG DTPSLEDEAA GHVTQEPESG KVVQEGFLRE PGPPGLSHQL MSGMPGAPLL P EGPREATR QPSGTGPEDT EGGRHAPELL KHQLLGDLHQ EGPPLKGAGG KERPGSKEEV DEDRDVDESS PQDSPPSKAS PA QDGRPPQ TAAREATSIP GFPAEGAIPL PVDFLSKVST EIPASEPDGP SVGRAKGQDA PLEFTFHVEI TPNVQKEQAH SEE HLGRAA FPGAPGEGPE ARGPSLGEDT KEADLPEPSE KQPAAAPRGK PVSRVPQLKA RMVSKSKDGT GSDDKKAKTS TRSS AKTLK NRPCLSPKHP TPGSSDPLIQ PSSPAVCPEP PSSPKYVSSV TSRTGSSGAK EMKLKGADGK TKIATPRGAA PPGQK GQAN ATRIPAKTPP APKTPPSSGE PPKSGDRSGY SSPGSPGTPG SRSRTPSLPT PPTREPKKVA VVRTPPKSPS SAKSRL QTA PVPMPDLKNV KSKIGSTENL KHQPGGGKVQ IINKKLDLSN VQSKCGSKDN IKHVPGGGSV QIVYKPVDLS KVTSKCG SL GNIHHKPGGG QVEVKSEKLD FKDRVQSKIG SLDNITHVPG GGNKKIETHK LTFRENAKAK TDHGAEIVYK SPVVSGDT S PRHLSNVSST GSIDMVDSPQ LATLADEVSA SLAKQGL UniProtKB: Microtubule-associated protein tau |
-Macromolecule #2: DTH-DLE-DLY-DIL-DVA-DTR-DIL
| Macromolecule | Name: DTH-DLE-DLY-DIL-DVA-DTR-DIL / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 24 / Enantiomer: DEXTRO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 872.106 Da |
| Sequence | String: (DTH)(DLE)(DLY)(DIL)(DVA)(DTR)(DIL) |
-Macromolecule #3: {[-(BIS-CARBOXYMETHYL-AMINO)-ETHYL]-CARBOXYMETHYL-AMINO}-ACETIC ACID
| Macromolecule | Name: {[-(BIS-CARBOXYMETHYL-AMINO)-ETHYL]-CARBOXYMETHYL-AMINO}-ACETIC ACID type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: EDT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 292.243 Da |
| Chemical component information | 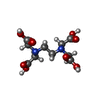 ChemComp-EDT: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE | |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.8 µm / Nominal magnification: 130000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model |
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT | |||||||||
| Output model |  PDB-9b4l: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














 Y (Sec.)
Y (Sec.) X (Row.)
X (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)















































