[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-4303: Cryo-EM subtomogram average of IFT complex B and inhibited dynein... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-4303 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
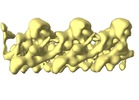
| Title | Cryo-EM subtomogram average of IFT complex B and inhibited dynein-1b in anterograde IFT trains (Chlamydomonas reinhardtii) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Cryo-EM stubtomogram average of IFT complex B and inhibited dynein-1b in anterograde IFT trains (Chlamydomonas reinhardtii) | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationintraciliary transport involved in cilium assembly / perinuclear theca / nitric-oxide synthase inhibitor activity / sperm annulus / deoxyribonuclease inhibitor activity / negative regulation of DNA strand resection involved in replication fork processing / negative regulation of phosphorylation / intraciliary retrograde transport / methylated-DNA-[protein]-cysteine S-methyltransferase / methylated-DNA-[protein]-cysteine S-methyltransferase activity ...intraciliary transport involved in cilium assembly / perinuclear theca / nitric-oxide synthase inhibitor activity / sperm annulus / deoxyribonuclease inhibitor activity / negative regulation of DNA strand resection involved in replication fork processing / negative regulation of phosphorylation / intraciliary retrograde transport / methylated-DNA-[protein]-cysteine S-methyltransferase / methylated-DNA-[protein]-cysteine S-methyltransferase activity / visual behavior / intraciliary transport / regulation of cilium assembly / dynein light chain binding / dynein heavy chain binding / embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis / Activation of BIM and translocation to mitochondria / motile cilium assembly / Intraflagellar transport / negative regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process / cell projection organization / ciliary plasm / dynein complex / ciliary transition zone / determination of left/right symmetry / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / microtubule motor activity / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / cytoplasmic dynein complex / dynein light intermediate chain binding / motile cilium / microtubule-based movement / Macroautophagy / ciliary base / ciliary tip / pericentriolar material / dynein intermediate chain binding / tertiary granule membrane / ficolin-1-rich granule membrane / cilium assembly / spermatid development / axoneme / positive regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / axon cytoplasm / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / centriole / MHC class II antigen presentation / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / substantia nigra development / enzyme inhibitor activity / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / sperm principal piece / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / filopodium / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / kinetochore / apical part of cell / HCMV Early Events / Aggrephagy / mitotic spindle / Separation of Sister Chromatids / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / sperm midpiece / site of double-strand break / scaffold protein binding / methylation / nuclear membrane / microtubule / cytoskeleton / cilium / nuclear speck / nuclear body / ciliary basal body / DNA repair / apoptotic process / DNA damage response / Neutrophil degranulation / centrosome / protein-containing complex binding / nucleolus / enzyme binding / Golgi apparatus / mitochondrion / extracellular space / DNA binding / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / metal ion binding / identical protein binding / membrane / nucleus / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | subtomogram averaging / cryo EM / Resolution: 37.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Pigino G / Jordan MA | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Cell Biol / Year: 2018 Journal: Nat Cell Biol / Year: 2018Title: The cryo-EM structure of intraflagellar transport trains reveals how dynein is inactivated to ensure unidirectional anterograde movement in cilia. Authors: Mareike A Jordan / Dennis R Diener / Ludek Stepanek / Gaia Pigino /  Abstract: Movement of cargos along microtubules plays key roles in diverse cellular processes, from signalling to mitosis. In cilia, rapid movement of ciliary components along the microtubules to and from the ...Movement of cargos along microtubules plays key roles in diverse cellular processes, from signalling to mitosis. In cilia, rapid movement of ciliary components along the microtubules to and from the assembly site is essential for the assembly and disassembly of the structure itself. This bidirectional transport, known as intraflagellar transport (IFT), is driven by the anterograde motor kinesin-2 and the retrograde motor dynein-1b (dynein-2 in mammals). However, to drive retrograde transport, dynein-1b must first be delivered to the ciliary tip by anterograde IFT. Although, the presence of opposing motors in bidirectional transport processes often leads to periodic stalling and slowing of cargos, IFT is highly processive. Using cryo-electron tomography, we show that a tug-of-war between kinesin-2 and dynein-1b is prevented by loading dynein-1b onto anterograde IFT trains in an autoinhibited form and by positioning it away from the microtubule track to prevent binding. Once at the ciliary tip, dynein-1b must transition into an active form and engage microtubules to power retrograde trains. These findings provide a striking example of how coordinated structural changes mediate the behaviour of complex cellular machinery. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_4303.map.gz emd_4303.map.gz | 168.2 KB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-4303-v30.xml emd-4303-v30.xml emd-4303.xml emd-4303.xml | 8.9 KB 8.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_4303_1.png emd_4303_1.png emd_4303_2.png emd_4303_2.png | 284.4 KB 188 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4303 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4303 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4303 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4303 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6sc2M  4304C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_4303.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 306.6 KB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_4303.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 306.6 KB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM stubtomogram average of IFT complex B and inhibited dynein-1b in anterograde IFT trains (Chlamydomonas reinhardtii) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 14.13 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Intraflagellar transport complex B and inhibited dynein-1b
| Entire | Name: Intraflagellar transport complex B and inhibited dynein-1b |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Intraflagellar transport complex B and inhibited dynein-1b
| Supramolecule | Name: Intraflagellar transport complex B and inhibited dynein-1b type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | subtomogram averaging |
| Aggregation state | 2D array |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R3.5/1 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: LEICA EM GP |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Quantum LS |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average electron dose: 2.1 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 37.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: PEET (ver. 1.11.0) / Number subtomograms used: 750 |
|---|---|
| Extraction | Number tomograms: 15 / Number images used: 750 / Software - Name:  IMOD (ver. 4.9.2) IMOD (ver. 4.9.2) |
| CTF correction | Software - Name: CTFPHASEFLIP |
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















