[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-42839: Structure of UT14 Fab in complex with the head domain of H3 (A/Si... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of UT14 Fab in complex with the head domain of H3 (A/Singapore/INFIMH-16-0019/2016) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Complex / viral protein / immune system / Influenza / Hemagglutinin | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationclathrin-dependent endocytosis of virus by host cell / host cell surface receptor binding / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / virion attachment to host cell / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /   Influenza A virus Influenza A virus | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Park J / Georgiou G | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Lancet Microbe / Year: 2025 Journal: Lancet Microbe / Year: 2025Title: Molecular features of the serological IgG repertoire elicited by egg-based, cell-based, or recombinant haemagglutinin-based seasonal influenza vaccines: a comparative, prospective, observational cohort study. Authors: Juyeon Park / Foteini Bartzoka / Troy von Beck / Zhu-Nan Li / Margarita Mishina / Luke S Hebert / Jessica Kain / Feng Liu / Suresh Sharma / Weiping Cao / Devon J Eddins / Amrita Kumar / Jin ...Authors: Juyeon Park / Foteini Bartzoka / Troy von Beck / Zhu-Nan Li / Margarita Mishina / Luke S Hebert / Jessica Kain / Feng Liu / Suresh Sharma / Weiping Cao / Devon J Eddins / Amrita Kumar / Jin Eyun Kim / Justin S Lee / Yuanyuan Wang / Evan A Schwartz / Axel F Brilot / Ed Satterwhite / Dalton M Towers / Eric McKnight / Jan Pohl / Mark G Thompson / Manjusha Gaglani / Fatimah S Dawood / Allison L Naleway / James Stevens / Richard B Kennedy / Joshy Jacob / Jason J Lavinder / Min Z Levine / Shivaprakash Gangappa / Gregory C Ippolito / Suryaprakash Sambhara / George Georgiou /  Abstract: BACKGROUND: Egg-based inactivated quadrivalent seasonal influenza vaccine (eIIV4), cell culture-based inactivated quadrivalent seasonal influenza vaccine (ccIIV4), and recombinant haemagglutinin (HA) ...BACKGROUND: Egg-based inactivated quadrivalent seasonal influenza vaccine (eIIV4), cell culture-based inactivated quadrivalent seasonal influenza vaccine (ccIIV4), and recombinant haemagglutinin (HA)-based quadrivalent seasonal influenza vaccine (RIV4) have been licensed for use in the USA. In this study, we used antigen-specific serum proteomics analysis to assess how the molecular composition and qualities of the serological antibody repertoires differ after seasonal influenza immunisation by each of the three vaccines and how different vaccination platforms affect the HA binding affinity and breadth of the serum antibodies that comprise the polyclonal response. METHODS: In this comparative, prospective, observational cohort study, we included female US health-care personnel (mean age 47·6 years [SD 8]) who received a single dose of RIV4, eIIV4, or ccIIV4 ...METHODS: In this comparative, prospective, observational cohort study, we included female US health-care personnel (mean age 47·6 years [SD 8]) who received a single dose of RIV4, eIIV4, or ccIIV4 during the 2018-19 influenza season at Baylor Scott & White Health (Temple, TX, USA). Eligible individuals were selected based on comparable day 28 serum microneutralisation titres and similar vaccination history. Laboratory investigators were blinded to assignment until testing was completed. The preplanned exploratory endpoints were assessed by deconvoluting the serological repertoire specific to A/Singapore/INFIMH-16-0019/2016 (H3N2) HA before (day 0) and after (day 28) immunisation using bottom-up liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry proteomics (referred to as Ig-Seq) and natively paired variable heavy chain-variable light chain high-throughput B-cell receptor sequencing (referred to as BCR-Seq). Features of the antigen-specific serological repertoire at day 0 and day 28 for the three vaccine groups were compared. Antibodies identified with high confidence in sera were recombinantly expressed and characterised in depth to determine the binding affinity and breadth to time-ordered H3 HA proteins. FINDINGS: During September and October of the 2018-19 influenza season, 15 individuals were recruited and assigned to receive RIV4 (n=5), eIIV4 (n=5), or ccIIV4 (n=5). For all three cohorts, the ...FINDINGS: During September and October of the 2018-19 influenza season, 15 individuals were recruited and assigned to receive RIV4 (n=5), eIIV4 (n=5), or ccIIV4 (n=5). For all three cohorts, the serum antibody repertoire was dominated by back-boosted antibody lineages (median 98% [95% CI 88-99]) that were present in the serum before vaccination. Although vaccine platform-dependent differences were not evident in the repertoire diversity, somatic hypermutation, or heavy chain complementarity determining region 3 biochemical features, antibodies boosted by RIV4 showed substantially higher binding affinity to the vaccine H3/HA (median half-maximal effective concentration [EC50] to A/Singapore/INFIMH-16-0019/2016 HA: 0·037 μg/mL [95% CI 0·012-0·12] for RIV4; 4·43 μg/mL [0·030-100·0] for eIIV4; and 18·50 μg/mL [0·99-100·0] μg/mL for ccIIV4) and also the HAs from contemporary H3N2 strains than did those elicited by eIIV4 or ccIIV4 (median EC50 to A/Texas/50/2012 HA: 0·037 μg/mL [0·017-0·32] for RIV4; 1·10 μg/mL [0·045-100] for eIIV4; and 12·6 μg/mL [1·8-100] for ccIIV4). Comparison of B-cell receptor sequencing repertoires on day 7 showed that eIIV4 increased the median frequency of canonical egg glycan-targeting B cells (0·20% [95% CI 0·067-0·37] for eIIV4; 0·058% [0·050-0·11] for RIV4; and 0·035% [0-0·062] for ccIIV4), whereas RIV4 vaccination decreased the median frequency of B-cell receptors displaying stereotypical features associated with membrane proximal anchor-targeting antibodies (0·062% [95% CI 0-0·084] for RIV4; 0·12% [0·066-0·16] for eIIV4; and 0·18% [0·016-0·20] for ccIIV4). In exploratory analysis, we characterised the structure of a highly abundant monoclonal antibody that binds to both group 1 and 2 HAs and recognises the HA trimer interface, despite its sequence resembling the stereotypical sequence motif found in membrane-proximal anchor binding antibodies. INTERPRETATION: Although all three licensed seasonal influenza vaccines elicit serological antibody repertoires with indistinguishable features shaped by heavy imprinting, the RIV4 vaccine ...INTERPRETATION: Although all three licensed seasonal influenza vaccines elicit serological antibody repertoires with indistinguishable features shaped by heavy imprinting, the RIV4 vaccine selectively boosts higher affinity monoclonal antibodies to contemporary strains and elicits greater serum binding potency and breadth, possibly as a consequence of the multivalent structural features of the HA immunogen in this vaccine formulation. Collectively, our findings show advantages of RIV4 vaccines and more generally highlight the benefits of multivalent HA immunogens in promoting higher affinity serum antibody responses. FUNDING: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Institutes of Health, and Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_42839.map.gz emd_42839.map.gz | 59.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-42839-v30.xml emd-42839-v30.xml emd-42839.xml emd-42839.xml | 23.9 KB 23.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_42839_fsc.xml emd_42839_fsc.xml | 8.5 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_42839.png emd_42839.png | 33.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-42839.cif.gz emd-42839.cif.gz | 7.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_42839_half_map_1.map.gz emd_42839_half_map_1.map.gz emd_42839_half_map_2.map.gz emd_42839_half_map_2.map.gz | 59.5 MB 59.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42839 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42839 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42839 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42839 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 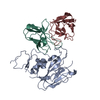 8uzcMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_42839.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_42839.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.0415 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_42839_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_42839_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Structure of UT14 Fab in complex with the head domain of H3 (A/Si...
| Entire | Name: Structure of UT14 Fab in complex with the head domain of H3 (A/Singapore/INFIMH-16-0019/2016) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Structure of UT14 Fab in complex with the head domain of H3 (A/Si...
| Supramolecule | Name: Structure of UT14 Fab in complex with the head domain of H3 (A/Singapore/INFIMH-16-0019/2016) type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 113 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: UT14 Fab heavy chain
| Macromolecule | Name: UT14 Fab heavy chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.28108 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: QVQLVESGGG VVQPGRSLRL SCATSGFTFS SYGIHWVRQA PGKGLGWVAM ISFDGSKTYY ADSVRGRFTI SRDNSKNTLS LQMNSLRTE DTAVYYCAKE RDRDGYNEGI YDYWGQGTLV TVSSASTKGP SVFPLAPSSK STSGGTAALG CLVKDYFPEP V TVSWNSGA ...String: QVQLVESGGG VVQPGRSLRL SCATSGFTFS SYGIHWVRQA PGKGLGWVAM ISFDGSKTYY ADSVRGRFTI SRDNSKNTLS LQMNSLRTE DTAVYYCAKE RDRDGYNEGI YDYWGQGTLV TVSSASTKGP SVFPLAPSSK STSGGTAALG CLVKDYFPEP V TVSWNSGA LTSGVHTFPA VLQSSGLYSL SSVVTVPSSS LGTQTYICNV NHKPSNTKVD KKVEPKSCD |
-Macromolecule #2: UT14 Fab light chain
| Macromolecule | Name: UT14 Fab light chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 23.687346 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: EIVMTQSPAT LSLSPGERAT LSCRASQSAG FYLAWYQQKP GQAPRLLIYD TSNRATGIPA RFSGRGSGTD FTLTINSLEP EDFAVYYCQ QRYNWPITFG QGTRLEIKRT VAAPSVFIFP PSDEQLKSGT ASVVCLLNNF YPREAKVQWK VDNALQSGNS Q ESVTEQDS ...String: EIVMTQSPAT LSLSPGERAT LSCRASQSAG FYLAWYQQKP GQAPRLLIYD TSNRATGIPA RFSGRGSGTD FTLTINSLEP EDFAVYYCQ QRYNWPITFG QGTRLEIKRT VAAPSVFIFP PSDEQLKSGT ASVVCLLNNF YPREAKVQWK VDNALQSGNS Q ESVTEQDS KDSTYSLSST LTLSKADYEK HKVYACEVTH QGLSSPVTKS FNRGEC |
-Macromolecule #3: Hemagglutinin
| Macromolecule | Name: Hemagglutinin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Influenza A virus / Strain: H3N2 (A/Singapore/INFIMH-16-0019/2016) Influenza A virus / Strain: H3N2 (A/Singapore/INFIMH-16-0019/2016) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.679719 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MKTIIALSYI LCLVFAQKIP GNDNSTATLC LGHHAVPNGT IVKTITNDRI EVTNATELVQ NSSIGEICDS PHQILDGENC TLIDALLGD PQCDGFQNKK WDLFVERSKA YSNCYPYDVP DYASLRSLVA SSGTLEFKNE SFNWTGVTQN GTSSACIRGS S SSFFSRLN ...String: MKTIIALSYI LCLVFAQKIP GNDNSTATLC LGHHAVPNGT IVKTITNDRI EVTNATELVQ NSSIGEICDS PHQILDGENC TLIDALLGD PQCDGFQNKK WDLFVERSKA YSNCYPYDVP DYASLRSLVA SSGTLEFKNE SFNWTGVTQN GTSSACIRGS S SSFFSRLN WLTHLNYTYP ALNVTMPNKE QFDKLYIWGV HHPGTDKDQI FLYAQSSGRI TVSTKRSQQA VIPNIGSRPR IR DIPSRIS IYWTIVKPGD ILLINSTGNL IAPRGYFKIR SGKSSIMRSD APIGKCKSEC ITPNGSIPND KPFQNVNRIT YGA CPRYVK HSTLKLATGM RNVPEKQTRG IFGAIAGFIE NGWEGMVDGW YGFRHQNSEG RGQAADLKST QAAIDQINGK LNRL IGKTN EKFHQIEKEF SEVEGRVQDL EKYVEDTKID LWSYNAELLV ALENQHTIDL TDSEMNKLFE KTKKQLRENA EDMGN GCFK IYHKCDNACI ESIRNETYDH NVYRDEALNN RFQIKGVELK SGYKDGSGYI PEAPRDGQAY VRKDGEWVLL STFLGS GLN DIFEAQKIEW HEGSHHHHHH UniProtKB: Hemagglutinin |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
Details: 2 mM Tris pH 8.0, 200 mM NaCl, 0.02% NaN3 | ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Au-flat 1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Pretreatment - Type: PLASMA CLEANING / Pretreatment - Time: 240 sec. Details: A total of 3ul of the specimen was applied to Au-flat 1.2/1.3-hole pattern 300 mesh grids (Electron Microscopy Sciences, PA; Cat. AUFT313-50) that had been plasma cleaned in a PELCO easiGlow ...Details: A total of 3ul of the specimen was applied to Au-flat 1.2/1.3-hole pattern 300 mesh grids (Electron Microscopy Sciences, PA; Cat. AUFT313-50) that had been plasma cleaned in a PELCO easiGlow plasma cleaner (Ted Pella Inc., CA) for 4 min and were plunge-frozen into liquid ethane using Thermo Fisher/FEI Vitrobot Mark IV at 4 celsius under 100% humidity. Excess liquid was blotted for 4-6 sec. | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 10 eV Details: The grids were imaged using a FEI Titan Krios G3 300kV cryo-TEM (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA) equipped with a K3 direct electron detection camera (Gatan, CA) with a slit width 10eV Gatan ...Details: The grids were imaged using a FEI Titan Krios G3 300kV cryo-TEM (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA) equipped with a K3 direct electron detection camera (Gatan, CA) with a slit width 10eV Gatan BioContinuum Imaging Filter. |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 80.0 e/Å2 Details: The calibrated pixel sizes were 0.83A/pixel with a total dose of 80e/A^2. |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.9 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





































