[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-41880: Cryo-EM structure of long form insulin receptor (IR-B) with three... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of long form insulin receptor (IR-B) with three IGF2 bound, asymmetric conformation. | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Cryo-EM structure of long form insulin receptor (IR-B) with three IGF2 bound, asymmetric conformation. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Insulin receptor / IGF2 / RTK / SIGNALING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationembryonic placenta morphogenesis / negative regulation of muscle cell differentiation / positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue growth / Signaling by Type 1 Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF1R) / regulation of muscle cell differentiation / IRS-related events triggered by IGF1R / regulation of female gonad development / positive regulation of meiotic cell cycle / positive regulation of organ growth / insulin-like growth factor II binding ...embryonic placenta morphogenesis / negative regulation of muscle cell differentiation / positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue growth / Signaling by Type 1 Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF1R) / regulation of muscle cell differentiation / IRS-related events triggered by IGF1R / regulation of female gonad development / positive regulation of meiotic cell cycle / positive regulation of organ growth / insulin-like growth factor II binding / positive regulation of developmental growth / transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activator activity / male sex determination / genomic imprinting / insulin receptor complex / positive regulation of protein-containing complex disassembly / insulin-like growth factor I binding / insulin receptor activity / positive regulation of multicellular organism growth / exocrine pancreas development / positive regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation / dendritic spine maintenance / cargo receptor activity / insulin binding / adrenal gland development / PTB domain binding / neuronal cell body membrane / Signaling by Insulin receptor / IRS activation / positive regulation of respiratory burst / amyloid-beta clearance / positive regulation of cell division / positive regulation of receptor internalization / positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation / insulin receptor substrate binding / regulation of embryonic development / epidermis development / positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process / Signal attenuation / protein kinase activator activity / positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway / embryonic placenta development / SHC-related events triggered by IGF1R / heart morphogenesis / transport across blood-brain barrier / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding / Insulin receptor recycling / insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / striated muscle cell differentiation / neuron projection maintenance / positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division / dendrite membrane / receptor-mediated endocytosis / insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway / Insulin receptor signalling cascade / platelet alpha granule lumen / positive regulation of glycolytic process / animal organ morphogenesis / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / positive regulation of D-glucose import across plasma membrane / learning / insulin receptor binding / growth factor activity / hormone activity / receptor protein-tyrosine kinase / caveola / receptor internalization / cellular response to growth factor stimulus / integrin binding / male gonad development / memory / Regulation of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) transport and uptake by Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) / cellular response to insulin stimulus / glucose metabolic process / positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process / osteoblast differentiation / insulin receptor signaling pathway / late endosome / Platelet degranulation / glucose homeostasis / amyloid-beta binding / protein autophosphorylation / PI5P, PP2A and IER3 Regulate PI3K/AKT Signaling / protein tyrosine kinase activity / in utero embryonic development / positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / lysosome / positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / receptor complex / positive regulation of MAPK cascade / endosome membrane / positive regulation of cell migration / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / receptor ligand activity / protein domain specific binding / axon / external side of plasma membrane / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / symbiont entry into host cell / regulation of DNA-templated transcription Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | An W / Hall C / Li J / Huang A / Wu J / Park J / Bai XC / Choi E | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Activation of the insulin receptor by insulin-like growth factor 2. Authors: Weidong An / Catherine Hall / Jie Li / Albert Hung / Jiayi Wu / Junhee Park / Liwei Wang / Xiao-Chen Bai / Eunhee Choi /  Abstract: Insulin receptor (IR) controls growth and metabolism. Insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) has different binding properties on two IR isoforms, mimicking insulin's function. However, the molecular ...Insulin receptor (IR) controls growth and metabolism. Insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) has different binding properties on two IR isoforms, mimicking insulin's function. However, the molecular mechanism underlying IGF2-induced IR activation remains unclear. Here, we present cryo-EM structures of full-length human long isoform IR (IR-B) in both the inactive and IGF2-bound active states, and short isoform IR (IR-A) in the IGF2-bound active state. Under saturated IGF2 concentrations, both the IR-A and IR-B adopt predominantly asymmetric conformations with two or three IGF2s bound at site-1 and site-2, which differs from that insulin saturated IR forms an exclusively T-shaped symmetric conformation. IGF2 exhibits a relatively weak binding to IR site-2 compared to insulin, making it less potent in promoting full IR activation. Cell-based experiments validated the functional importance of IGF2 binding to two distinct binding sites in optimal IR signaling and trafficking. In the inactive state, the C-terminus of α-CT of IR-B contacts FnIII-2 domain of the same protomer, hindering its threading into the C-loop of IGF2, thus reducing the association rate of IGF2 with IR-B. Collectively, our studies demonstrate the activation mechanism of IR by IGF2 and reveal the molecular basis underlying the different affinity of IGF2 to IR-A and IR-B. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_41880.map.gz emd_41880.map.gz | 102.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-41880-v30.xml emd-41880-v30.xml emd-41880.xml emd-41880.xml | 18.4 KB 18.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_41880.png emd_41880.png | 28.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-41880.cif.gz emd-41880.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_41880_half_map_1.map.gz emd_41880_half_map_1.map.gz emd_41880_half_map_2.map.gz emd_41880_half_map_2.map.gz | 141.6 MB 141.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41880 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41880 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41880 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41880 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8u4eMC  8u4bC  8u4cC  8vjbC  8vjcC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_41880.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_41880.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM structure of long form insulin receptor (IR-B) with three IGF2 bound, asymmetric conformation. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
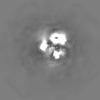
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
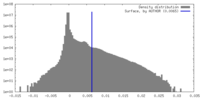
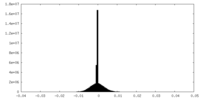
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Cryo-EM structure of long form insulin receptor (IR-B)...
| File | emd_41880_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM structure of long form insulin receptor (IR-B) with three IGF2 bound, asymmetric conformation. Half map 1. | ||||||||||||
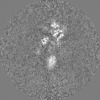
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
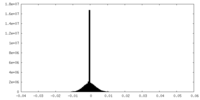
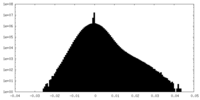
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Cryo-EM structure of long form insulin receptor (IR-B)...
| File | emd_41880_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM structure of long form insulin receptor (IR-B) with three IGF2 bound, asymmetric conformation. Half map 2. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Long form insulin receptor (IR-B) with three IGF2 bound, asymmetr...
| Entire | Name: Long form insulin receptor (IR-B) with three IGF2 bound, asymmetric conformation. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Long form insulin receptor (IR-B) with three IGF2 bound, asymmetr...
| Supramolecule | Name: Long form insulin receptor (IR-B) with three IGF2 bound, asymmetric conformation. type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Insulin receptor
| Macromolecule | Name: Insulin receptor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 156.518328 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MATGGRRGAA AAPLLVAVAA LLLGAAGHLY PGEVCPGMDI RNNLTRLHEL ENCSVIEGHL QILLMFKTRP EDFRDLSFPK LIMITDYLL LFRVYGLESL KDLFPNLTVI RGSRLFFNYA LVIFEMVHLK ELGLYNLMNI TRGSVRIEKN NELCYLATID W SRILDSVE ...String: MATGGRRGAA AAPLLVAVAA LLLGAAGHLY PGEVCPGMDI RNNLTRLHEL ENCSVIEGHL QILLMFKTRP EDFRDLSFPK LIMITDYLL LFRVYGLESL KDLFPNLTVI RGSRLFFNYA LVIFEMVHLK ELGLYNLMNI TRGSVRIEKN NELCYLATID W SRILDSVE DNYIVLNKDD NEECGDICPG TAKGKTNCPA TVINGQFVER CWTHSHCQKV CPTICKSHGC TAEGLCCHSE CL GNCSQPD DPTKCVACRN FYLDGRCVET CPPPYYHFQD WRCVNFSFCQ DLHHKCKNSR RQGCHQYVIH NNKCIPECPS GYT MNSSNL LCTPCLGPCP KVCHLLEGEK TIDSVTSAQE LRGCTVINGS LIINIRGGNN LAAELEANLG LIEEISGYLK IRRS YALVS LSFFRKLRLI RGETLEIGNY SFYALDNQNL RQLWDWSKHN LTITQGKLFF HYNPKLCLSE IHKMEEVSGT KGRQE RNDI ALKTNGDQAS CENELLKFSY IRTSFDKILL RWEPYWPPDF RDLLGFMLFY KEAPYQNVTE FDGQDACGSN SWTVVD IDP PLRSNDPKSQ NHPGWLMRGL KPWTQYAIFV KTLVTFSDER RTYGAKSDII YVQTDATNPS VPLDPISVSN SSSQIIL KW KPPSDPNGNI THYLVFWERQ AEDSELFELD YCLKGLKLPS RTWSPPFESE DSQKHNQSEY EDSAGECCSC PKTDSQIL K ELEESSFRKT FEDYLHNVVF VPRKTSSGTG AEDPRPSRKR RSLGDVGNVT VAVPTVAAFP NTSSTSVPTS PEEHRPFEK VVNKESLVIS GLRHFTGYRI ELQACNQDTP EERCSVAAYV SARTMPEAKA DDIVGPVTHE IFENNVVHLM WQEPKEPNGL IVLYEVSYR RYGDEELHLC VSRKHFALER GCRLRGLSPG NYSVRIRATS LAGNGSWTEP TYFYVTDYLD VPSNIAKIII G PLIFVFLF SVVIGSIYLF LRKRQPDGPL GPLYASSNPE YLSASDVFPC SVYVPDEWEV SREKITLLRE LGQGSFGMVY EG NARDIIK GEAETRVAVK TVNESASLRE RIEFLNEASV MKGFTCHHVV RLLGVVSKGQ PTLVVMELMA HGDLKSYLRS LRP EAENNP GRPPPTLQEM IQMAAEIADG MAYLNAKKFV HRDLAARNCM VAHDFTVKIG DFGMTRDIYE TDYYRKGGKG LLPV RWMAP ESLKDGVFTT SSDMWSFGVV LWEITSLAEQ PYQGLSNEQV LKFVMDGGYL DQPDNCPERV TDLMRMCWQF NPKMR PTFL EIVNLLKDDL HPSFPEVSFF HSEENKAPES EELEMEFEDM ENVPLDRSSH CQREEAGGRD GGSSLGFKRS YEEHIP YTH MNGGKKNGRI LTLPRSNPS UniProtKB: Insulin receptor |
-Macromolecule #2: Insulin-like growth factor II
| Macromolecule | Name: Insulin-like growth factor II / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 20.170398 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGIPMGKSML VLLTFLAFAS CCIAAYRPSE TLCGGELVDT LQFVCGDRGF YFSRPASRVS RRSRGIVEEC CFRSCDLALL ETYCATPAK SERDVSTPPT VLPDNFPRYP VGKFFQYDTW KQSTQRLRRG LPALLRARRG HVLAKELEAF REAKRHRPLI A LPTQDPAH GGAPPEMASN RK UniProtKB: Insulin-like growth factor 2 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.6 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.6 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-8u4e: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)