+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | CryoEM structure of ADP-DNA-MuB conformation1 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | CryoEM structure of ADP-DNA-MuB conformation1 with D9 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MuB / MuB-ADP / Ring / VIRAL PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationDNA transposition / viral DNA genome replication / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; In phosphorus-containing anhydrides / DNA integration / host cell cytoplasm / DNA replication / ATP hydrolysis activity / DNA binding / ATP binding / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Escherichia phage Mu (virus) Escherichia phage Mu (virus) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.32 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhao X / Zhang K / Li S | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Elucidating the Architectural dynamics of MuB filaments in bacteriophage Mu DNA transposition. Authors: Xiaolong Zhao / Yongxiang Gao / Qingguo Gong / Kaiming Zhang / Shanshan Li /  Abstract: MuB is a non-specific DNA-binding protein and AAA+ ATPase that significantly influences the DNA transposition process of bacteriophage Mu, especially in target DNA selection for transposition. While ...MuB is a non-specific DNA-binding protein and AAA+ ATPase that significantly influences the DNA transposition process of bacteriophage Mu, especially in target DNA selection for transposition. While studies have established the ATP-dependent formation of MuB filament as pivotal to this process, the high-resolution structure of a full-length MuB protomer and the underlying molecular mechanisms governing its oligomerization remain elusive. Here, we use cryo-EM to obtain a 3.4-Å resolution structure of the ATP(+)-DNA(+)-MuB helical filament, which encapsulates the DNA substrate within its axial channel. The structure categorizes MuB within the initiator clade of the AAA+ protein family and precisely locates the ATP and DNA binding sites. Further investigation into the oligomeric states of MuB show the existence of various forms of the filament. These findings lead to a mechanistic model where MuB forms opposite helical filaments along the DNA, exposing potential target sites on the bare DNA and then recruiting MuA, which stimulates MuB's ATPase activity and disrupts the previously formed helical structure. When this happens, MuB generates larger ring structures and dissociates from the DNA. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_38696.map.gz emd_38696.map.gz | 202.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-38696-v30.xml emd-38696-v30.xml emd-38696.xml emd-38696.xml | 21.1 KB 21.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_38696.png emd_38696.png | 54.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-38696.cif.gz emd-38696.cif.gz | 5.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_38696_additional_1.map.gz emd_38696_additional_1.map.gz emd_38696_additional_2.map.gz emd_38696_additional_2.map.gz emd_38696_half_map_1.map.gz emd_38696_half_map_1.map.gz emd_38696_half_map_2.map.gz emd_38696_half_map_2.map.gz | 203 MB 101.9 MB 199.7 MB 199.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-38696 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-38696 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-38696 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-38696 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8xvcMC  8xvbC  8xvdC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_38696.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_38696.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | CryoEM structure of ADP-DNA-MuB conformation1 with D9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
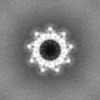
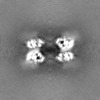
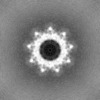
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.82 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
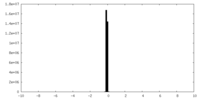
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: CryoEM structure of ADP-DNA-MuB conformation1 monomer
| File | emd_38696_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | CryoEM structure of ADP-DNA-MuB conformation1 monomer | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
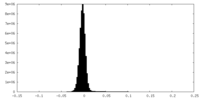
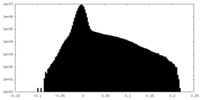
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: CryoEM structure of ADP-DNA-MuB conformation1 with D9
| File | emd_38696_additional_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | CryoEM structure of ADP-DNA-MuB conformation1 with D9 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: CryoEM structure of ADP-DNA-MuB conformation1 with D9
| File | emd_38696_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | CryoEM structure of ADP-DNA-MuB conformation1 with D9 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: CryoEM structure of ADP-DNA-MuB conformation1 with D9
| File | emd_38696_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | CryoEM structure of ADP-DNA-MuB conformation1 with D9 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : ADP-DNA-MuB conformation1
| Entire | Name: ADP-DNA-MuB conformation1 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: ADP-DNA-MuB conformation1
| Supramolecule | Name: ADP-DNA-MuB conformation1 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Escherichia phage Mu (virus) Escherichia phage Mu (virus) |
-Macromolecule #1: ATP-dependent target DNA activator B
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP-dependent target DNA activator B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 18 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number: Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; In phosphorus-containing anhydrides |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Escherichia phage Mu (virus) Escherichia phage Mu (virus) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 35.153133 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MNISDIRAGL RTLVENEETT FKQIALESGL STGTISSFIN DKYNGDNERV SQMLQRWLEK YHAVAELPEP PRFVETQTVK QIWTSMRFA SLTESIAVVC GNPGVGKTEA AREYRRTNNN VWMITITPSC ASVLECLTEL AFELGMNDAP RRKGPLSRAL R RRLEGTQG ...String: MNISDIRAGL RTLVENEETT FKQIALESGL STGTISSFIN DKYNGDNERV SQMLQRWLEK YHAVAELPEP PRFVETQTVK QIWTSMRFA SLTESIAVVC GNPGVGKTEA AREYRRTNNN VWMITITPSC ASVLECLTEL AFELGMNDAP RRKGPLSRAL R RRLEGTQG LVIIDEADHL GAEVLEELRL LQESTRIGLV LMGNHRVYSN MTGGNRTVEF ARLFSRIAKR TAINKTKKAD VK AIADAWQ INGEKELELL QQIAQKPGAL RILNHSLRLA AMTAHGKGER VNEDYLRQAF RELDLDVDIS TLLRN UniProtKB: ATP-dependent target DNA activator B |
-Macromolecule #2: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 18 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Number real images: 9510 / Average electron dose: 60.9 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 2.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)