[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-37593: Vibrio vulnificus MARTX effector duet (RDTND-RID) complexed with ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | 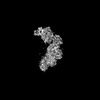 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Vibrio vulnificus MARTX effector duet (RDTND-RID) complexed with human Rac1 Q61L and calmodulin | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | pixel size: 0.66extraction box size: 500 pixel (500 x 0.66 = 330 A) | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MARTX toxin / RDTND-RID / NADase / N-fatty acyl transferase / CaM / Rac1 / TOXIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtransporter inhibitor activity / Ligases; Forming carbon-nitrogen bonds; Acid-amino-acid ligases (peptide synthases) / embryonic olfactory bulb interneuron precursor migration / anatomical structure arrangement / regulation of ERK5 cascade / angiotensin-activated signaling pathway involved in heart process / cerebral cortex GABAergic interneuron development / regulation of respiratory burst / positive regulation of ovarian follicle development / auditory receptor cell morphogenesis ...transporter inhibitor activity / Ligases; Forming carbon-nitrogen bonds; Acid-amino-acid ligases (peptide synthases) / embryonic olfactory bulb interneuron precursor migration / anatomical structure arrangement / regulation of ERK5 cascade / angiotensin-activated signaling pathway involved in heart process / cerebral cortex GABAergic interneuron development / regulation of respiratory burst / positive regulation of ovarian follicle development / auditory receptor cell morphogenesis / cerebral cortex radially oriented cell migration / erythrocyte enucleation / regulation of neutrophil migration / negative regulation of interleukin-23 production / localization within membrane / Activated NTRK2 signals through CDK5 / regulation of hydrogen peroxide metabolic process / kinocilium / regulation of cell adhesion involved in heart morphogenesis / interneuron migration / ruffle assembly / engulfment of apoptotic cell / NTRK2 activates RAC1 / Inactivation of CDC42 and RAC1 / NADPH oxidase complex / cochlea morphogenesis / regulation of neuron maturation / respiratory burst / WNT5:FZD7-mediated leishmania damping / cortical cytoskeleton organization / SEMA3A-Plexin repulsion signaling by inhibiting Integrin adhesion / positive regulation of skeletal muscle acetylcholine-gated channel clustering / GTP-dependent protein binding / midbrain dopaminergic neuron differentiation / epithelial cell morphogenesis / regulation of neuron migration / cell projection assembly / positive regulation of bicellular tight junction assembly / ruffle organization / thioesterase binding / regulation of lamellipodium assembly / regulation of stress fiber assembly / negative regulation of fibroblast migration / RHO GTPases activate CIT / cell-cell junction organization / motor neuron axon guidance / Nef and signal transduction / sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor signaling pathway / PCP/CE pathway / hepatocyte growth factor receptor signaling pathway / Activation of RAC1 / RHO GTPases activate KTN1 / regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process / DCC mediated attractive signaling / MET activates RAP1 and RAC1 / Azathioprine ADME / Sema4D mediated inhibition of cell attachment and migration / Ephrin signaling / CD28 dependent Vav1 pathway / hyperosmotic response / positive regulation of cell-substrate adhesion / positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis / positive regulation of ruffle assembly / Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway / superoxide anion generation / regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / lamellipodium assembly / host cell cytosol / NRAGE signals death through JNK / small GTPase-mediated signal transduction / dendrite morphogenesis / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor binding / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / acyltransferase activity / regulation of cell size / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / ligase activity / synaptic transmission, GABAergic / positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction / presynaptic endocytosis / positive regulation of dendritic spine development / pericentriolar material / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / positive regulation of actin filament polymerization / Rac protein signal transduction / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / calcineurin-mediated signaling / semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / adenylate cyclase binding / protein phosphatase activator activity / ficolin-1-rich granule membrane / Sema3A PAK dependent Axon repulsion / EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells / regulation of postsynapse assembly / positive regulation of focal adhesion assembly / RHO GTPases Activate NADPH Oxidases / regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Vibrio vulnificus (bacteria) / Vibrio vulnificus (bacteria) /  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
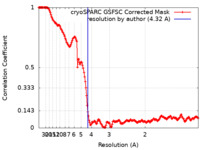
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.32 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lee Y / Choi S / Jang SY / Hwang J / Kim MH | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Korea, Republic Of, 2 items Korea, Republic Of, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Dissemination of pathogenic bacteria is reinforced by a MARTX toxin effector duet. Authors: Sanghyeon Choi / Youngjin Lee / Shinhye Park / Song Yee Jang / Jongbin Park / Do Won Oh / Su-Man Kim / Tae-Hwan Kim / Ga Seul Lee / Changyi Cho / Byoung Sik Kim / Donghan Lee / Eun-Hee Kim / ...Authors: Sanghyeon Choi / Youngjin Lee / Shinhye Park / Song Yee Jang / Jongbin Park / Do Won Oh / Su-Man Kim / Tae-Hwan Kim / Ga Seul Lee / Changyi Cho / Byoung Sik Kim / Donghan Lee / Eun-Hee Kim / Hae-Kap Cheong / Jeong Hee Moon / Ji-Joon Song / Jungwon Hwang / Myung Hee Kim /  Abstract: Multiple bacterial genera take advantage of the multifunctional autoprocessing repeats-in-toxin (MARTX) toxin to invade host cells. Secretion of the MARTX toxin by Vibrio vulnificus, a deadly ...Multiple bacterial genera take advantage of the multifunctional autoprocessing repeats-in-toxin (MARTX) toxin to invade host cells. Secretion of the MARTX toxin by Vibrio vulnificus, a deadly opportunistic pathogen that causes primary septicemia, the precursor of sepsis, is a major driver of infection; however, the molecular mechanism via which the toxin contributes to septicemia remains unclear. Here, we report the crystal and cryo-electron microscopy (EM) structures of a toxin effector duet comprising the domain of unknown function in the first position (DUF1)/Rho inactivation domain (RID) complexed with human targets. These structures reveal how the duet is used by bacteria as a potent weapon. The data show that DUF1 acts as a RID-dependent transforming NADase domain (RDTND) that disrupts NAD homeostasis by hijacking calmodulin. The cryo-EM structure of the RDTND-RID duet complexed with calmodulin and Rac1, together with immunological analyses in vitro and in mice, provide mechanistic insight into how V. vulnificus uses the duet to suppress ROS generation by depleting NAD(P) and modifying Rac1 in a mutually-reinforcing manner that ultimately paralyzes first line immune responses, promotes dissemination of invaders, and induces sepsis. These data may allow development of tools or strategies to combat MARTX toxin-related human diseases. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_37593.map.gz emd_37593.map.gz | 448.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-37593-v30.xml emd-37593-v30.xml emd-37593.xml emd-37593.xml | 21 KB 21 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_37593_fsc.xml emd_37593_fsc.xml | 16.5 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
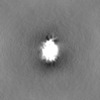
| Images |  emd_37593.png emd_37593.png | 73 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-37593.cif.gz emd-37593.cif.gz | 6.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_37593_half_map_1.map.gz emd_37593_half_map_1.map.gz emd_37593_half_map_2.map.gz emd_37593_half_map_2.map.gz | 442.3 MB 442.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37593 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37593 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37593 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37593 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8k9zC  8ka0C  8ka1C  8ka2C C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_37593.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 476.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_37593.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 476.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | pixel size: 0.66extraction box size: 500 pixel (500 x 0.66 = 330 A) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
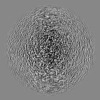
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.66 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
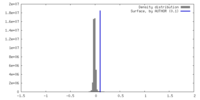
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
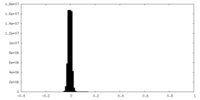
-Half map: pixel size: 0.66extraction box size: 500 pixel (500 x 0.66 = 330 A)
| File | emd_37593_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | pixel size: 0.66extraction box size: 500 pixel (500 x 0.66 = 330 A) | ||||||||||||
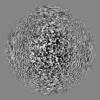
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
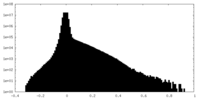
-Half map: pixel size: 0.66extraction box size: 500 pixel (500 x 0.66 = 330 A)
| File | emd_37593_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | pixel size: 0.66extraction box size: 500 pixel (500 x 0.66 = 330 A) | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : RDTND-RID effector duet complexed with Ca2+CaM and Rac1Q61L
| Entire | Name: RDTND-RID effector duet complexed with Ca2+CaM and Rac1Q61L |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: RDTND-RID effector duet complexed with Ca2+CaM and Rac1Q61L
| Supramolecule | Name: RDTND-RID effector duet complexed with Ca2+CaM and Rac1Q61L type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: RDTND-RID
| Supramolecule | Name: RDTND-RID / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 / Details: single mutation, C2838A |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Vibrio vulnificus (bacteria) Vibrio vulnificus (bacteria) |
-Supramolecule #3: Calmodulin
| Supramolecule | Name: Calmodulin / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 / Details: Sequence conflict, Q124E |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #4: Rac1
| Supramolecule | Name: Rac1 / type: complex / ID: 4 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #3 / Details: single muatation, Q61L |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: RDTND-RID
| Macromolecule | Name: RDTND-RID / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Details: single mutant C2838A / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Vibrio vulnificus (bacteria) Vibrio vulnificus (bacteria) |
| Sequence | String: MGEASHDSAE SLVAARAEKV ANLYRWLDTD NDVATDKYVP VPGFERVDVD VSDEVKQRMI QSMSGYIEHT DNQVPKDQAE ALATLFVEST LDYDWDKRVE FLTKLESYGY SFEAPHAEKS IVSFWSGKNF KQYRDILDNA QTDGKKVVYD IDVKGNAFAI DLNKHLMRWG ...String: MGEASHDSAE SLVAARAEKV ANLYRWLDTD NDVATDKYVP VPGFERVDVD VSDEVKQRMI QSMSGYIEHT DNQVPKDQAE ALATLFVEST LDYDWDKRVE FLTKLESYGY SFEAPHAEKS IVSFWSGKNF KQYRDILDNA QTDGKKVVYD IDVKGNAFAI DLNKHLMRWG GLFLDPDNAE QNQLKSSIDA ATFSNTGFWS SVYATGAQND VYVIAEGGVR LGNYFWNVEL PALRQLQREG LVGEIRLLDK PVSEYKDLPA DQIGRRLTDA GVAVKVRFDA LSHERQAELL ADNPDGYKAD TLVELDVKLS AIDSMLRESL PFYSLRTERN LLVQEGEEGF EVRSWPGIDG KSKTILLDNP EDAAQQKSIE RFILANFDNF EQMPDELFLV DNKVLSHHDG RTRIIAQKED GAWTYNTNVE LMSVTELLDA AHVNGKVRGD SYQQVIDALT EYHASTVEHA DYELESVEKL LNLRKQIEGY VLGHPDSGRV EAMNSLLNQV NSRLEEVSVL AVSEQSIKAH DSFSRLYDQL DNANLKESKH LYLDGNGDFV TKGKGNLATI DQLGGSDAVL EKVKAAVTHE YGQVVADTIF ARLSANDLAK DGKGIDIAGL NKVHQAIEQH MSPVSATMYI WKPSDHSTLG HAALQIGQGR TQLEGQAAAD FNKQNYVSWW PLGSKSSNIR NIFNVATEDQ PDLKLRWSDF SQPAHQNDTL EHDMASEEND GFGLKDGETK LKRFIEKLNA AKGIDASYKD ASEGYASVLL GNPDMLASTG IPAHVFQPFV DQWNDTSYDM MDVANRFAEE LQKQAQASGD PALVEKRIDN VVRLFAERAL EEIEAFKASQ ADEGRVFRIN LEGLDVAAMQ AEWKRLSNDP DARYQLLTKN ASSTVAKVLK AGGADKLIGH TWRPKFGVWT PTELFNFGQA LQEAQLEIAA KKQSHQVTDV LDAL UniProtKB: Multifunctional-autoprocessing repeats-in-toxin |
-Macromolecule #2: Calmodulin
| Macromolecule | Name: Calmodulin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Details: Q124E, "sequence conflict" / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: GAMADQLTEE QIAEFKEAFS LFDKDGDGTI TTKELGTVMR SLGQNPTEAE LQDMINEVDA DGNGTIDFPE FLTMMARKMK DTDSEEEIRE AFRVFDKDGN GYISAAELRH VMTNLGEKLT DEEVDQMIRE ADIDGDGQVN YEEFVQMMTA K UniProtKB: Calmodulin-2 |
-Macromolecule #3: Rac1
| Macromolecule | Name: Rac1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Details: single mutation, Q61L / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: GHMQAIKCVV VGDGAVGKTC LLISYTTNAF PGEYIPTVFD NYSANVMVDG KPVNLGLWDT AGLEDYDRLR PLSYPQTDVF LICFSLVSPA SFENVRAKWY PEVRHHCPNT PIILVGTKLD LRDDKDTIEK LKEKKLTPIT YPQGLAMAKE IGAVKYLECS ALTQRGLKTV FDEAIRAVL UniProtKB: Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.75 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
Details: 50 mM HEPES-NaOH (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl, and 1% (v/v) glycerol | ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 297 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV | ||||||||||||
| Details | This sample was monodisperse |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.4000000000000001 µm |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)