[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
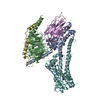
Yorodumi- EMDB-37237: Cryo-EM structure of the GPR174-Gs complex bound to endogenous lysoPS -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the GPR174-Gs complex bound to endogenous lysoPS | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GPCR / Gs / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationbioactive lipid receptor activity / negative regulation of interleukin-2 production / T cell homeostasis / PKA activation in glucagon signalling / developmental growth / hair follicle placode formation / intracellular transport / D1 dopamine receptor binding / vascular endothelial cell response to laminar fluid shear stress / activation of adenylate cyclase activity ...bioactive lipid receptor activity / negative regulation of interleukin-2 production / T cell homeostasis / PKA activation in glucagon signalling / developmental growth / hair follicle placode formation / intracellular transport / D1 dopamine receptor binding / vascular endothelial cell response to laminar fluid shear stress / activation of adenylate cyclase activity / renal water homeostasis / Hedgehog 'off' state / adenylate cyclase-activating adrenergic receptor signaling pathway / regulation of insulin secretion / cellular response to glucagon stimulus / adenylate cyclase activator activity / trans-Golgi network membrane / negative regulation of inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus / bone development / G protein-coupled receptor activity / platelet aggregation / cognition / centriolar satellite / G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding / adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / Olfactory Signaling Pathway / Activation of the phototransduction cascade / G beta:gamma signalling through PLC beta / Presynaptic function of Kainate receptors / Thromboxane signalling through TP receptor / G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway / Activation of G protein gated Potassium channels / Inhibition of voltage gated Ca2+ channels via Gbeta/gamma subunits / G-protein activation / G beta:gamma signalling through CDC42 / Prostacyclin signalling through prostacyclin receptor / Glucagon signaling in metabolic regulation / G beta:gamma signalling through BTK / Synthesis, secretion, and inactivation of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 12 / photoreceptor disc membrane / Glucagon-type ligand receptors / Sensory perception of sweet, bitter, and umami (glutamate) taste / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / sensory perception of smell / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins / Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP1) regulates insulin secretion / G alpha (z) signalling events / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 1 / ADORA2B mediated anti-inflammatory cytokines production / cellular response to catecholamine stimulus / G beta:gamma signalling through PI3Kgamma / adenylate cyclase-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway / Cooperation of PDCL (PhLP1) and TRiC/CCT in G-protein beta folding / GPER1 signaling / G-protein beta-subunit binding / cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus / heterotrimeric G-protein complex / G alpha (12/13) signalling events / Inactivation, recovery and regulation of the phototransduction cascade / extracellular vesicle / sensory perception of taste / positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / signaling receptor complex adaptor activity / retina development in camera-type eye / G protein activity / GTPase binding / Ca2+ pathway / fibroblast proliferation / High laminar flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and PECAM1:CDH5:KDR in endothelial cells / G alpha (i) signalling events / G alpha (s) signalling events / phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / G alpha (q) signalling events / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / Ras protein signal transduction / Extra-nuclear estrogen signaling / cell population proliferation / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / lysosomal membrane / GTPase activity / synapse / GTP binding / protein-containing complex binding / signal transduction / extracellular exosome / metal ion binding / membrane / plasma membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.83 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Nie Y / Qiu Z / Zheng S / Chen S | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Specific binding of GPR174 by endogenous lysophosphatidylserine leads to high constitutive G signaling. Authors: Yingying Nie / Zeming Qiu / Sijia Chen / Zhao Chen / Xiaocui Song / Yan Ma / Niu Huang / Jason G Cyster / Sanduo Zheng /   Abstract: Many orphan G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) remain understudied because their endogenous ligands are unknown. Here, we show that a group of class A/rhodopsin-like orphan GPCRs including GPR61, ...Many orphan G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) remain understudied because their endogenous ligands are unknown. Here, we show that a group of class A/rhodopsin-like orphan GPCRs including GPR61, GPR161 and GPR174 increase the cAMP level similarly to fully activated D1 dopamine receptor (D1R). We report cryo-electron microscopy structures of the GPR61‒G, GPR161‒G and GPR174‒G complexes without any exogenous ligands. The GPR174 structure reveals that endogenous lysophosphatidylserine (lysoPS) is copurified. While GPR174 fails to respond to exogenous lysoPS, likely owing to its maximal activation by the endogenous ligand, GPR174 mutants with lower ligand binding affinities can be specifically activated by lysoPS but not other lipids, in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, GPR174 adopts a non-canonical G coupling mode. The structures of GPR161 and GPR61 reveal that the second extracellular loop (ECL2) penetrates into the orthosteric pocket, possibly contributing to constitutive activity. Our work definitively confirms lysoPS as an endogenous GPR174 ligand and suggests that high constitutive activity of some orphan GPCRs could be accounted for by their having naturally abundant ligands. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_37237.map.gz emd_37237.map.gz | 20.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-37237-v30.xml emd-37237-v30.xml emd-37237.xml emd-37237.xml | 24.5 KB 24.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_37237.png emd_37237.png | 79.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-37237.cif.gz emd-37237.cif.gz | 7.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_37237_half_map_1.map.gz emd_37237_half_map_1.map.gz emd_37237_half_map_2.map.gz emd_37237_half_map_2.map.gz | 20.7 MB 20.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37237 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37237 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37237 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37237 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8kh5MC  8kgkC  8kh4C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_37237.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 22.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_37237.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 22.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
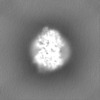
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
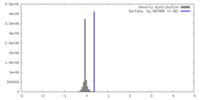
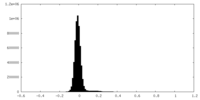
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_37237_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
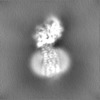
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
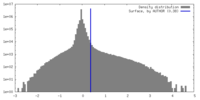
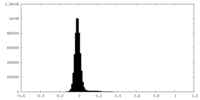
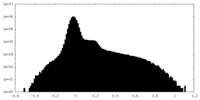
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_37237_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
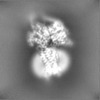
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Cryo-EM structure of the GPR174 and mini-Gs complex with Nb35
+Supramolecule #1: Cryo-EM structure of the GPR174 and mini-Gs complex with Nb35
+Supramolecule #2: GPR174
+Supramolecule #3: Gs complex
+Supramolecule #4: Nb35
+Macromolecule #1: Probable G-protein coupled receptor 174
+Macromolecule #2: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(s) subunit alpha isoforms short
+Macromolecule #3: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-1
+Macromolecule #4: Nanobody 35
+Macromolecule #5: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-2
+Macromolecule #6: CHOLESTEROL
+Macromolecule #7: O-{HYDROXY[((2R)-2-HYDROXY-3-{[(1S)-1-HYDROXYPENTADECYL]OXY}PROPY...
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 7.0 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 281 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Number real images: 2943 / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.7800000000000002 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.3900000000000001 µm / Nominal magnification: 64000 |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)