+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
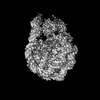
| Title | Structure of H1.2 bound to the nucleosome | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Nucleosome / Chromatin / DNA / H1.2 / Complex / DNA BINDING PROTEIN | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhistone H3K27me3 reader activity / facultative heterochromatin formation / negative regulation of DNA recombination / Apoptosis induced DNA fragmentation / regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome / chromosome condensation / nucleosomal DNA binding / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation ...histone H3K27me3 reader activity / facultative heterochromatin formation / negative regulation of DNA recombination / Apoptosis induced DNA fragmentation / regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome / chromosome condensation / nucleosomal DNA binding / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / heterochromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / telomere organization / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Interleukin-7 signaling / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / innate immune response in mucosa / Defective pyroptosis / Negative Regulation of CDH1 Gene Transcription / HDACs deacetylate histones / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / lipopolysaccharide binding / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / euchromatin / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / HDMs demethylate histones / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / chromatin DNA binding / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Metalloprotease DUBs / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / RMTs methylate histone arginines / HCMV Early Events / structural constituent of chromatin / UCH proteinases / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / nucleosome assembly / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / antibacterial humoral response / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / HATs acetylate histones / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / chromatin organization / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / double-stranded DNA binding / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / killing of cells of another organism / defense response to Gram-negative bacterium / chromosome, telomeric region / Ub-specific processing proteases / defense response to Gram-positive bacterium / cadherin binding / Amyloid fiber formation / protein heterodimerization activity / negative regulation of cell population proliferation / nucleolus / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein-containing complex / extracellular space / DNA binding / RNA binding / extracellular exosome Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.0 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kujirai T / Echigoya K / Takizawa Y / Kurumizaka H | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 8 items Japan, 8 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2025Title: Structural insights into how DEK nucleosome binding facilitates H3K27 trimethylation in chromatin. Authors: Tomoya Kujirai / Kenta Echigoya / Yusuke Kishi / Mai Saeki / Tomoko Ito / Junko Kato / Lumi Negishi / Hiroshi Kimura / Hiroshi Masumoto / Yoshimasa Takizawa / Yukiko Gotoh / Hitoshi Kurumizaka /  Abstract: Structural diversity of the nucleosome affects chromatin conformations and regulates eukaryotic genome functions. Here we identify DEK, whose function is unknown, as a nucleosome-binding protein. In ...Structural diversity of the nucleosome affects chromatin conformations and regulates eukaryotic genome functions. Here we identify DEK, whose function is unknown, as a nucleosome-binding protein. In embryonic neural progenitor cells, DEK colocalizes with H3 K27 trimethylation (H3K27me3), the facultative heterochromatin mark. DEK stimulates the methyltransferase activity of Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2), which is responsible for H3K27me3 deposition in vitro. Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the DEK-nucleosome complexes reveal that DEK binds the nucleosome by its tripartite DNA-binding mode on the dyad and linker DNAs and interacts with the nucleosomal acidic patch by its newly identified histone-binding region. The DEK-nucleosome interaction mediates linker DNA reorientation and induces chromatin compaction, which may facilitate PRC2 activation. These findings provide mechanistic insights into chromatin structure-mediated gene regulation by DEK. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_37149.map.gz emd_37149.map.gz | 2.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-37149-v30.xml emd-37149-v30.xml emd-37149.xml emd-37149.xml | 23.8 KB 23.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_37149_fsc.xml emd_37149_fsc.xml | 7.2 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_37149.png emd_37149.png | 76.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-37149.cif.gz emd-37149.cif.gz | 6.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_37149_half_map_1.map.gz emd_37149_half_map_1.map.gz emd_37149_half_map_2.map.gz emd_37149_half_map_2.map.gz | 23.4 MB 23.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37149 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37149 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37149 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37149 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8ke0MC  8kcyC  8kd1C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_37149.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_37149.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.05 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_37149_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_37149_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : H1.2 bound to the nucleosome
| Entire | Name: H1.2 bound to the nucleosome |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: H1.2 bound to the nucleosome
| Supramolecule | Name: H1.2 bound to the nucleosome / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#7 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Histone H3.1
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H3.1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.719445 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GSHMARTKQT ARKSTGGKAP RKQLATKAAR KSAPATGGVK KPHRYRPGTV ALREIRRYQK STELLIRKLP FQRLVREIAQ DFKTDLRFQ SSAVMALQEA CEAYLVGLFE DTNLCAIHAK RVTIMPKDIQ LARRIRGERA UniProtKB: Histone H3.1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Histone H4
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.676703 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GSHMSGRGKG GKGLGKGGAK RHRKVLRDNI QGITKPAIRR LARRGGVKRI SGLIYEETRG VLKVFLENVI RDAVTYTEHA KRKTVTAMD VVYALKRQGR TLYGFGG UniProtKB: Histone H4 |
-Macromolecule #3: Histone H2A type 1-B/E
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2A type 1-B/E / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.447825 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GSHMSGRGKQ GGKARAKAKT RSSRAGLQFP VGRVHRLLRK GNYSERVGAG APVYLAAVLE YLTAEILELA GNAARDNKKT RIIPRHLQL AIRNDEELNK LLGRVTIAQG GVLPNIQAVL LPKKTESHHK AKGK UniProtKB: Histone H2A type 1-B/E |
-Macromolecule #4: Histone H2B type 1-J
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2B type 1-J / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.217516 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GSHMPEPAKS APAPKKGSKK AVTKAQKKDG KKRKRSRKES YSIYVYKVLK QVHPDTGISS KAMGIMNSFV NDIFERIAGE ASRLAHYNK RSTITSREIQ TAVRLLLPGE LAKHAVSEGT KAVTKYTSAK UniProtKB: Histone H2B type 1-J |
-Macromolecule #7: Histone H1.2
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H1.2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 22.15684 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSETAPAAPA AAPPAEKAPV KKKAAKKAGG TPRKASGPPV SELITKAVAA SKERSGVSLA ALKKALAAAG YDVEKNNSRI KLGLKSLVS KGTLVQTKGT GASGSFKLNK KAASGEAKPK VKKAGGTKPK KPVGAAKKPK KAAGGATPKK SAKKTPKKAK K PAAATVTK ...String: MSETAPAAPA AAPPAEKAPV KKKAAKKAGG TPRKASGPPV SELITKAVAA SKERSGVSLA ALKKALAAAG YDVEKNNSRI KLGLKSLVS KGTLVQTKGT GASGSFKLNK KAASGEAKPK VKKAGGTKPK KPVGAAKKPK KAAGGATPKK SAKKTPKKAK K PAAATVTK KVAKSPKKAK VAKPKKAAKS AAKAVKPKAA KPKVVKPKKA APKKKLEVLF Q UniProtKB: Histone H1.2 |
-Macromolecule #5: DNA (193-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (193-MER) / type: dna / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 59.589984 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DT) (DA)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC) (DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG) (DC) (DC)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DC) ...String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DT) (DA)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC) (DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG) (DC) (DC)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG) (DC)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT) (DC)(DG) (DT)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG) (DC)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC) (DG)(DC)(DT) (DT)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DG) (DC)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DA) (DA)(DT)(DC)(DC) (DG)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DG) (DT)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DG) (DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG) (DC)(DT)(DA)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DC) (DG)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DA) (DT)(DT)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DA) (DT)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DT) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DC) (DA) (DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DG) (DA)(DT) |
-Macromolecule #6: DNA (193-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (193-MER) / type: dna / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 59.580969 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DT) (DA)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC) (DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG) (DC) (DC)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DC) ...String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DT) (DA)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC) (DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG) (DC) (DC)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG) (DC)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT) (DC)(DG) (DT)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG) (DC)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC) (DG)(DC)(DT) (DT)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DG) (DC)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DA) (DT)(DT)(DC)(DC) (DG)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DG) (DT)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DG) (DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG) (DC)(DT)(DA)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DC) (DG)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DA) (DT)(DT)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DA) (DT)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DT) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DC) (DA) (DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DG) (DA)(DT) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 56.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





































