[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-36607: Cryo-EM structure of the glucagon receptor bound to glucagon and ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the glucagon receptor bound to glucagon and beta-arrestin 1 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Complex structure / glucagon receptor / beta-arrestin 1 / glucagon / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationactivated protein C (thrombin-activated peptidase) / positive regulation of establishment of endothelial barrier / negative regulation of coagulation / glucagon receptor binding / renal water retention / Defective AVP does not bind AVPR2 and causes neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus (NDI) / Vasopressin-like receptors / regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure by vasopressin / vasopressin receptor activity / regulation of glycogen metabolic process ...activated protein C (thrombin-activated peptidase) / positive regulation of establishment of endothelial barrier / negative regulation of coagulation / glucagon receptor binding / renal water retention / Defective AVP does not bind AVPR2 and causes neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus (NDI) / Vasopressin-like receptors / regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure by vasopressin / vasopressin receptor activity / regulation of glycogen metabolic process / glucagon receptor activity / hemostasis / : / telencephalon development / negative regulation of execution phase of apoptosis / feeding behavior / response to starvation / positive regulation of calcium ion import / positive regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure / peptide hormone binding / positive regulation of intracellular signal transduction / positive regulation of vasoconstriction / negative regulation of blood coagulation / Synthesis, secretion, and deacylation of Ghrelin / endocytic vesicle / Transport of gamma-carboxylated protein precursors from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus / Gamma-carboxylation of protein precursors / Common Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation / positive regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / Removal of aminoterminal propeptides from gamma-carboxylated proteins / activation of adenylate cyclase activity / cellular response to hormone stimulus / Intrinsic Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation / response to cytokine / response to nutrient / regulation of insulin secretion / cellular response to glucagon stimulus / positive regulation of gluconeogenesis / guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity / cellular response to starvation / viral budding from plasma membrane / response to activity / Cell surface interactions at the vascular wall / gluconeogenesis / generation of precursor metabolites and energy / Post-translational protein phosphorylation / clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane / hormone activity / Golgi lumen / negative regulation of inflammatory response / regulation of blood pressure / adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / Regulation of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) transport and uptake by Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) / adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / blood coagulation / Glucagon signaling in metabolic regulation / Synthesis, secretion, and inactivation of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) / Glucagon-type ligand receptors / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins / Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP1) regulates insulin secretion / Cargo recognition for clathrin-mediated endocytosis / glucose homeostasis / Clathrin-mediated endocytosis / secretory granule lumen / clathrin-dependent endocytosis of virus by host cell / G alpha (s) signalling events / G alpha (q) signalling events / cell surface receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / endosome / host cell surface receptor binding / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / endoplasmic reticulum lumen / receptor ligand activity / signaling receptor binding / negative regulation of cell population proliferation / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / serine-type endopeptidase activity / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / negative regulation of apoptotic process / virion attachment to host cell / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / endoplasmic reticulum / Golgi apparatus / proteolysis / extracellular space / extracellular region / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  Escherichia phage EcSzw-2 (virus) Escherichia phage EcSzw-2 (virus) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chen K / Zhang C / Lin S / Zhao Q / Wu B | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 2 items China, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2023 Journal: Nature / Year: 2023Title: Tail engagement of arrestin at the glucagon receptor. Authors: Kun Chen / Chenhui Zhang / Shuling Lin / Xinyu Yan / Heng Cai / Cuiying Yi / Limin Ma / Xiaojing Chu / Yuchen Liu / Ya Zhu / Shuo Han / Qiang Zhao / Beili Wu /  Abstract: Arrestins have pivotal roles in regulating G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signalling by desensitizing G protein activation and mediating receptor internalization. It has been proposed that the ...Arrestins have pivotal roles in regulating G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signalling by desensitizing G protein activation and mediating receptor internalization. It has been proposed that the arrestin binds to the receptor in two different conformations, 'tail' and 'core', which were suggested to govern distinct processes of receptor signalling and trafficking. However, little structural information is available for the tail engagement of the arrestins. Here we report two structures of the glucagon receptor (GCGR) bound to β-arrestin 1 (βarr1) in glucagon-bound and ligand-free states. These structures reveal a receptor tail-engaged binding mode of βarr1 with many unique features, to our knowledge, not previously observed. Helix VIII, instead of the receptor core, has a major role in accommodating βarr1 by forming extensive interactions with the central crest of βarr1. The tail-binding pose is further defined by a close proximity between the βarr1 C-edge and the receptor helical bundle, and stabilized by a phosphoinositide derivative that bridges βarr1 with helices I and VIII of GCGR. Lacking any contact with the arrestin, the receptor core is in an inactive state and loosely binds to glucagon. Further functional studies suggest that the tail conformation of GCGR-βarr governs βarr recruitment at the plasma membrane and endocytosis of GCGR, and provides a molecular basis for the receptor forming a super-complex simultaneously with G protein and βarr to promote sustained signalling within endosomes. These findings extend our knowledge about the arrestin-mediated modulation of GPCR functionalities. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
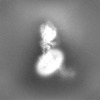
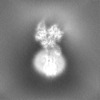
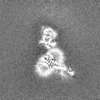
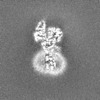
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_36607.map.gz emd_36607.map.gz | 57.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-36607-v30.xml emd-36607-v30.xml emd-36607.xml emd-36607.xml | 22.7 KB 22.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_36607.png emd_36607.png | 46.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-36607.cif.gz emd-36607.cif.gz | 7.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_36607_half_map_1.map.gz emd_36607_half_map_1.map.gz emd_36607_half_map_2.map.gz emd_36607_half_map_2.map.gz | 59.4 MB 59.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36607 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36607 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36607 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36607 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8jrvMC  8jruC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_36607.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_36607.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
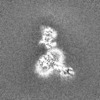
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.071 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_36607_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
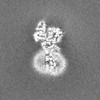
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
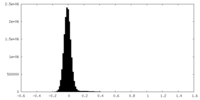
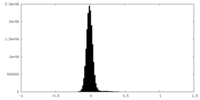
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_36607_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
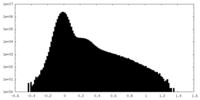
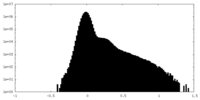
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : The glucagon receptor bound to glucagon and beta-arrestin 1
| Entire | Name: The glucagon receptor bound to glucagon and beta-arrestin 1 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: The glucagon receptor bound to glucagon and beta-arrestin 1
| Supramolecule | Name: The glucagon receptor bound to glucagon and beta-arrestin 1 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#4 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: HA signal peptide,HPC4 purification tag,Glucagon receptor,C-termi...
| Macromolecule | Name: HA signal peptide,HPC4 purification tag,Glucagon receptor,C-terminal tail of Vasopressin V2 receptor type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 54.163012 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MKTIIALSYI FCLVFAGAPE DQVDPRLIDG KGSGSAGSAG SQVMDFLFEK WKLYGDQCHH NLSLLPPPTE LVCNRTFDKY SCWPDTPAN TTANISCPWY LPWHHKVQHR FVFKRCGPDG QWVRGPRGQP WRDASQCQMD GEEIEVQKEV AKMYSSFQVM Y TVGYSLSL ...String: MKTIIALSYI FCLVFAGAPE DQVDPRLIDG KGSGSAGSAG SQVMDFLFEK WKLYGDQCHH NLSLLPPPTE LVCNRTFDKY SCWPDTPAN TTANISCPWY LPWHHKVQHR FVFKRCGPDG QWVRGPRGQP WRDASQCQMD GEEIEVQKEV AKMYSSFQVM Y TVGYSLSL GALLLALAIL GGLSKLHCTR NAIHANLFAS FVLKASSVLV IDGLLRTRYS QKIGDDLSVS TWLSDGAVAG CR VAAVFMQ YGIVANYCWL LVEGLYLHNL LGLATLPERS FFSLYLGIGW GAPMLFVVPW AVVKCLFENV QCWTSNDNMG FWW ILRFPV FLAILINFFI FVRIVQLLVA KLRARQMHHT DYKFRLAKST LTLIPLLGVH EVVFAFVTDE HAQGTLRSAK LFFD LFLSS FQGLLVAVLY CFLNKEVQSE LRRRWHRWRL GKVLWEERNT SNARGRTPPS LGPQDE(SEP)CT(TPO) A(SEP) (SEP)(SEP)LAKDT SS UniProtKB: Hemagglutinin, Vitamin K-dependent protein C, Glucagon receptor, Vasopressin V2 receptor |
-Macromolecule #2: Glucagon
| Macromolecule | Name: Glucagon / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 3.486781 KDa |
| Sequence | String: HSQGTFTSDY SKYLDSRRAQ DFVQWLMNT UniProtKB: Pro-glucagon |
-Macromolecule #3: Beta-arrestin 1 and single-chain fragment variable 30 (scFv30)
| Macromolecule | Name: Beta-arrestin 1 and single-chain fragment variable 30 (scFv30) type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 69.173891 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGDKGTRVFK KASPNGKLTV YLGKRDFVDH IDLVEPVDGV VLVDPEYLKE RRVYVTLTAA FRYGREDLDV LGLTFRKDLF VANVQSFPP APEDKKPLTR LQERLIKKLG EHAYPFTFEI PPNLPSSVTL QPGPEDTGKA IGVDYEVKAF VAENLEEKIH K RNSVRLVI ...String: MGDKGTRVFK KASPNGKLTV YLGKRDFVDH IDLVEPVDGV VLVDPEYLKE RRVYVTLTAA FRYGREDLDV LGLTFRKDLF VANVQSFPP APEDKKPLTR LQERLIKKLG EHAYPFTFEI PPNLPSSVTL QPGPEDTGKA IGVDYEVKAF VAENLEEKIH K RNSVRLVI EKVQYAPERP GPQPTAETTR QFLMSDKPLH LEASLDKEIY YHGEPISVNV HVTNNTNKTV KKIKISVRQY AD IVLFNTA QYKVPVAMEE ADDTVAPSST FSKVYTLTPF LANNREKRGL ALDGKLKHED TNLASSTLLR EGANREILGI IVS YKVKVK LVVSRGGLLG DLASSDVAVE LPFTLMHPKP KEEPPHREVP EHETPVDTNL SDIQMTQSPS SLSASVGDRV TITC RASQS VSSAVAWYQQ KPGKAPKLLI YSASSLYSGV PSRFSGSRSG TDFTLTISSL QPEDFATYYC QQYKYVPVTF GQGTK VEIK GTTAASGSSG GSSSGAEVQL VESGGGLVQP GGSLRLSCAA SGFNVYSSSI HWVRQAPGKG LEWVASISSY YGYTYY ADS VKGRFTISAD TSKNTAYLQM NSLRAEDTAV YYCARSRQFW YSGLDYWGQG TLVTVSSAHH HHHH |
-Macromolecule #4: Nanobody 32
| Macromolecule | Name: Nanobody 32 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Escherichia phage EcSzw-2 (virus) Escherichia phage EcSzw-2 (virus) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.867408 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAQVQLQESG GGLVQAGGSL RLSCVVSGFF FDTVTMAWYR RAPGKHRELV ASATAGGTTT YADSVKDRFT ISRDNAKNTV YLQMNSLKP EDTAVYYCNT FVRSLSWGQG TQVTVSSHHH HHHEPEA |
-Macromolecule #5: [(2R)-2-octanoyloxy-3-[oxidanyl-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-2,3,6-tris(o...
| Macromolecule | Name: [(2R)-2-octanoyloxy-3-[oxidanyl-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-2,3,6-tris(oxidanyl)-4,5-diphosphonooxy-cyclohexyl]oxy-phosphoryl]oxy-propyl] octanoate type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: PIO |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 746.566 Da |
| Chemical component information | 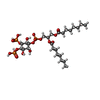 ChemComp-PIO: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 6 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 70.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)