+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | ion channel | |||||||||
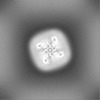
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ion channel / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology | Voltage-gated cation channel calcium and sodium / voltage-gated sodium channel complex / voltage-gated sodium channel activity / Voltage-dependent channel domain superfamily / Ion transport domain / Ion transport protein / Ion transport domain-containing protein Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chen HW / Jiang D | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Structural mechanism of voltage-gated sodium channel slow inactivation. Authors: Huiwen Chen / Zhanyi Xia / Jie Dong / Bo Huang / Jiangtao Zhang / Feng Zhou / Rui Yan / Yiqiang Shi / Jianke Gong / Juquan Jiang / Zhuo Huang / Daohua Jiang /  Abstract: Voltage-gated sodium (Na) channels mediate a plethora of electrical activities. Na channels govern cellular excitability in response to depolarizing stimuli. Inactivation is an intrinsic property of ...Voltage-gated sodium (Na) channels mediate a plethora of electrical activities. Na channels govern cellular excitability in response to depolarizing stimuli. Inactivation is an intrinsic property of Na channels that regulates cellular excitability by controlling the channel availability. The fast inactivation, mediated by the Ile-Phe-Met (IFM) motif and the N-terminal helix (N-helix), has been well-characterized. However, the molecular mechanism underlying Na channel slow inactivation remains elusive. Here, we demonstrate that the removal of the N-helix of NaEh (NaEh) results in a slow-inactivated channel, and present cryo-EM structure of NaEh in a potential slow-inactivated state. The structure features a closed activation gate and a dilated selectivity filter (SF), indicating that the upper SF and the inner gate could serve as a gate for slow inactivation. In comparison to the NaEh structure, NaEh undergoes marked conformational shifts on the intracellular side. Together, our results provide important mechanistic insights into Na channel slow inactivation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_36039.map.gz emd_36039.map.gz | 118.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-36039-v30.xml emd-36039-v30.xml emd-36039.xml emd-36039.xml | 18.1 KB 18.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_36039.png emd_36039.png | 37.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-36039.cif.gz emd-36039.cif.gz | 6.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_36039_half_map_1.map.gz emd_36039_half_map_1.map.gz emd_36039_half_map_2.map.gz emd_36039_half_map_2.map.gz | 115.9 MB 115.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36039 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36039 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36039 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36039 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8j7fMC  8j7hC  8j7mC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_36039.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_36039.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
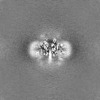
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.04 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
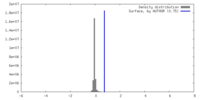
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_36039_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
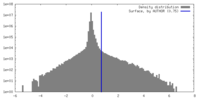
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_36039_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
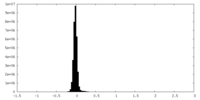
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : ion channel complex
| Entire | Name: ion channel complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: ion channel complex
| Supramolecule | Name: ion channel complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: ion channel,Voltage dependent ion channel,Green fluorescent prote...
| Macromolecule | Name: ion channel,Voltage dependent ion channel,Green fluorescent protein (Fragment),Voltage dependent ion channel,Green fluorescent protein (Fragment),Ion transport domain-containing protein type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 33.237289 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: WLPHQRKVFD FYASQGVQYF TAFLIVSNFI FNCAEKEWDP YTDQLYQGLW RWGEFAFNTM FLIELLINFY GIAFCFWRYN WAWNTFDLV VVAIGTLTMA EAIGGNFMPP SMALIRNLRA FRIFRLFKRI KSLNKIIVSL GKAIPGVANA FVIMVIIMCI Y AILGVEFY ...String: WLPHQRKVFD FYASQGVQYF TAFLIVSNFI FNCAEKEWDP YTDQLYQGLW RWGEFAFNTM FLIELLINFY GIAFCFWRYN WAWNTFDLV VVAIGTLTMA EAIGGNFMPP SMALIRNLRA FRIFRLFKRI KSLNKIIVSL GKAIPGVANA FVIMVIIMCI Y AILGVEFY HMTGSDGTYV TYNDNVKRGL CTGDEVELGQ CSLNQTVSSE TARGYTYGEE YYGTFFRALY TLFQVLTGES WS EAVARPA VFESHYDSFG PVLFYVSFII ICQIVLINVV VAVLLDKMVE ED UniProtKB: Ion transport domain-containing protein |
-Macromolecule #2: ILE-ALA-ALA-ILE-HIS-ASN-ALA-ARG-ARG-LYS-LYS-ARG-GLU-ALA-ALA-ALA-A...
| Macromolecule | Name: ILE-ALA-ALA-ILE-HIS-ASN-ALA-ARG-ARG-LYS-LYS-ARG-GLU-ALA-ALA-ALA-ALA-HIS-LYS-ALA type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 2.191584 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: IAAIHNARRK KREAAAAHKA |
-Macromolecule #3: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: (2S)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]propyl 2-(tri...
| Macromolecule | Name: (2S)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]propyl 2-(trimethylammonio)ethyl phosphate type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: POV |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 760.076 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-POV: |
-Macromolecule #5: CHOLESTEROL
| Macromolecule | Name: CHOLESTEROL / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 12 / Formula: CLR |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 386.654 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-CLR: |
-Macromolecule #6: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 10 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)