+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human KCNQ2(F104A)-CaM-PIP2-CBD complex in state I | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | potassium voltage-gated channel / CBD / PIP2 / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationaxon initial segment / Voltage gated Potassium channels / node of Ranvier / voltage-gated monoatomic cation channel activity / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / ankyrin binding / Calmodulin induced events ...axon initial segment / Voltage gated Potassium channels / node of Ranvier / voltage-gated monoatomic cation channel activity / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / ankyrin binding / Calmodulin induced events / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / PKA activation / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / autophagosome membrane docking / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / presynaptic endocytosis / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / calcineurin-mediated signaling / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / action potential / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Long-term potentiation / protein phosphatase activator activity / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / DARPP-32 events / Smooth Muscle Contraction / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / catalytic complex / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / cellular response to interferon-beta / Protein methylation / calcium channel inhibitor activity / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / presynaptic cytosol / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / Ion homeostasis / eNOS activation / titin binding / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / sperm midpiece / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / potassium ion transmembrane transport / calcium channel complex / FCERI mediated Ca+2 mobilization / substantia nigra development / regulation of heart rate / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor / FCGR3A-mediated IL10 synthesis / Antigen activates B Cell Receptor (BCR) leading to generation of second messengers / calyx of Held / adenylate cyclase activator activity / sarcomere / VEGFR2 mediated cell proliferation / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / regulation of cytokinesis / spindle microtubule / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / calcium channel regulator activity / RAF activation / Transcriptional activation of mitochondrial biogenesis / response to calcium ion / cellular response to type II interferon / Stimuli-sensing channels / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / long-term synaptic potentiation / spindle pole / RAS processing / calcium-dependent protein binding / Signaling by RAF1 mutants / Signaling by moderate kinase activity BRAF mutants / Paradoxical activation of RAF signaling by kinase inactive BRAF / Signaling downstream of RAS mutants / Signaling by BRAF and RAF1 fusions / Platelet degranulation / Inactivation, recovery and regulation of the phototransduction cascade Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.7 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ma D / Li D / Guo J | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 4 items China, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Ligand activation mechanisms of human KCNQ2 channel. Authors: Demin Ma / Yueming Zheng / Xiaoxiao Li / Xiaoyu Zhou / Zhenni Yang / Yan Zhang / Long Wang / Wenbo Zhang / Jiajia Fang / Guohua Zhao / Panpan Hou / Fajun Nan / Wei Yang / Nannan Su / ...Authors: Demin Ma / Yueming Zheng / Xiaoxiao Li / Xiaoyu Zhou / Zhenni Yang / Yan Zhang / Long Wang / Wenbo Zhang / Jiajia Fang / Guohua Zhao / Panpan Hou / Fajun Nan / Wei Yang / Nannan Su / Zhaobing Gao / Jiangtao Guo /  Abstract: The human voltage-gated potassium channel KCNQ2/KCNQ3 carries the neuronal M-current, which helps to stabilize the membrane potential. KCNQ2 can be activated by analgesics and antiepileptic drugs but ...The human voltage-gated potassium channel KCNQ2/KCNQ3 carries the neuronal M-current, which helps to stabilize the membrane potential. KCNQ2 can be activated by analgesics and antiepileptic drugs but their activation mechanisms remain unclear. Here we report cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of human KCNQ2-CaM in complex with three activators, namely the antiepileptic drug cannabidiol (CBD), the lipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP), and HN37 (pynegabine), an antiepileptic drug in the clinical trial, in an either closed or open conformation. The activator-bound structures, along with electrophysiology analyses, reveal the binding modes of two CBD, one PIP, and two HN37 molecules in each KCNQ2 subunit, and elucidate their activation mechanisms on the KCNQ2 channel. These structures may guide the development of antiepileptic drugs and analgesics that target KCNQ2. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_35882.map.gz emd_35882.map.gz | 48.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-35882-v30.xml emd-35882-v30.xml emd-35882.xml emd-35882.xml | 16.3 KB 16.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_35882.png emd_35882.png | 47.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-35882.cif.gz emd-35882.cif.gz | 5.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_35882_half_map_1.map.gz emd_35882_half_map_1.map.gz emd_35882_half_map_2.map.gz emd_35882_half_map_2.map.gz | 37 MB 37 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35882 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35882 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35882 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35882 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_35882_validation.pdf.gz emd_35882_validation.pdf.gz | 840.5 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_35882_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_35882_full_validation.pdf.gz | 840.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_35882_validation.xml.gz emd_35882_validation.xml.gz | 11.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_35882_validation.cif.gz emd_35882_validation.cif.gz | 13.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-35882 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-35882 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-35882 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-35882 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8j03MC  8izyC  8j00C  8j01C  8j02C  8j04C  8j05C  8w4uC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_35882.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_35882.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
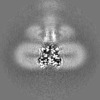
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.93 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
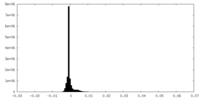
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_35882_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
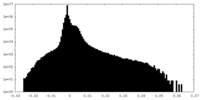
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_35882_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
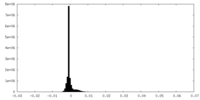
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : human KCNQ2(F104A)-CaM-PIP2-CBD complex in state I
| Entire | Name: human KCNQ2(F104A)-CaM-PIP2-CBD complex in state I |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: human KCNQ2(F104A)-CaM-PIP2-CBD complex in state I
| Supramolecule | Name: human KCNQ2(F104A)-CaM-PIP2-CBD complex in state I / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 2 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 73.551719 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MAGKPPKRNA FYRKLQNFLY NVLERPRGWA FIYHAYVFLL VASCLVLSVF STIKEYEKSS EGALYILEIV TIVVFGVEYF VRIWAAGCC CRYRGWRGRL KFARKPFCVI DIMVLIASIA VLAAGSQGNV FATSALRSLR FLQILRMIRM DRRGGTWKLL G SVVYAHSK ...String: MAGKPPKRNA FYRKLQNFLY NVLERPRGWA FIYHAYVFLL VASCLVLSVF STIKEYEKSS EGALYILEIV TIVVFGVEYF VRIWAAGCC CRYRGWRGRL KFARKPFCVI DIMVLIASIA VLAAGSQGNV FATSALRSLR FLQILRMIRM DRRGGTWKLL G SVVYAHSK ELVTAWYIGF LCLILASFLV YLAEKGENDH FDTYADALWW GLITLTTIGY GDKYPQTWNG RLLAATFTLI GV SFFALPA GILGSGFALK VQEQHRQKHF EKRRNPAAGL IQSAWRFYAT NLSRTDLHST WQYYERTVTV PMYSSQTQTY GAS RLIPPL NQLELLRNLK SKSGLAFRKD PPPEPSPSKG SPCRGPLCGC CPGRSSQKVS LKDRVFSSPR GVAAKGKGSP QAQT VRRSP SADQSLEDSP SKVPKSWSFG DRSRARQAFR IKGAASRQNS EEASLPGEDI VDDKSCPCEF VTEDLTPGLK VSIRA VCVM RFLVSKRKFK ESLRPYDVMD VIEQYSAGHL DMLSRIKSLQ SRVDQIVGRG PAITDKDRTK GPAEAELPED PSMMGR LGK VEKQVLSMEK KLDFLVNIYM QRMGIPPTET EAYFGAKEPE PAPPYHSPED SREHVDRHGC IVKIVRSSSS TGQKNFS VE GGSSGGWSHP QFEK UniProtKB: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 2 |
-Macromolecule #2: Calmodulin-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Calmodulin-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 19.615445 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MADQLTEEQI AEFKEAFSLF DKDGDGTITT KELGTVMRSL GQNPTEAELQ DMINEVDADG NGTIDFPEFL TMMARKMKDT DSEEEIREA FRVFDKDGNG YISAAELRHV MTNLGEKLTD EEVDEMIREA DIDGDGQVNY EEFVQMMTAK LEGGSSGGLV P RGSGGSSG GHHHHHHHH UniProtKB: Calmodulin-1 |
-Macromolecule #3: cannabidiol
| Macromolecule | Name: cannabidiol / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: P0T |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 314.462 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-P0T: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 52.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 147292 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)