+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the PEA-bound mTAAR9-Golf complex | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PEA / mTAAR9 / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationAdenylate cyclase activating pathway / Amine ligand-binding receptors / trace-amine receptor activity / G alpha (s) signalling events / sensory perception of chemical stimulus / response to caffeine / adenylate cyclase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of protein localization to cell cortex / T cell migration / Adenylate cyclase inhibitory pathway ...Adenylate cyclase activating pathway / Amine ligand-binding receptors / trace-amine receptor activity / G alpha (s) signalling events / sensory perception of chemical stimulus / response to caffeine / adenylate cyclase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of protein localization to cell cortex / T cell migration / Adenylate cyclase inhibitory pathway / response to prostaglandin E / D2 dopamine receptor binding / G protein-coupled serotonin receptor binding / adenylate cyclase regulator activity / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting serotonin receptor signaling pathway / cellular response to forskolin / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / response to amphetamine / Regulation of insulin secretion / positive regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process / negative regulation of insulin secretion / G protein-coupled receptor binding / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / response to peptide hormone / adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / centriolar satellite / G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding / adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / Olfactory Signaling Pathway / Activation of the phototransduction cascade / G beta:gamma signalling through PLC beta / Presynaptic function of Kainate receptors / Thromboxane signalling through TP receptor / G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway / Activation of G protein gated Potassium channels / Inhibition of voltage gated Ca2+ channels via Gbeta/gamma subunits / G-protein activation / G beta:gamma signalling through CDC42 / Prostacyclin signalling through prostacyclin receptor / Glucagon signaling in metabolic regulation / G beta:gamma signalling through BTK / Synthesis, secretion, and inactivation of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 12 / photoreceptor disc membrane / Glucagon-type ligand receptors / Sensory perception of sweet, bitter, and umami (glutamate) taste / GDP binding / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / sensory perception of smell / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins / Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP1) regulates insulin secretion / G alpha (z) signalling events / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 1 / ADORA2B mediated anti-inflammatory cytokines production / cellular response to catecholamine stimulus / G beta:gamma signalling through PI3Kgamma / adenylate cyclase-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway / Cooperation of PDCL (PhLP1) and TRiC/CCT in G-protein beta folding / GPER1 signaling / G-protein beta-subunit binding / cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus / heterotrimeric G-protein complex / G alpha (12/13) signalling events / Inactivation, recovery and regulation of the phototransduction cascade / extracellular vesicle / sensory perception of taste / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / signaling receptor complex adaptor activity / retina development in camera-type eye / G protein activity / GTPase binding / Ca2+ pathway / fibroblast proliferation / midbody / cell cortex / High laminar flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and PECAM1:CDH5:KDR in endothelial cells / G alpha (i) signalling events / G alpha (s) signalling events / phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / G alpha (q) signalling events / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / Ras protein signal transduction / Extra-nuclear estrogen signaling / cell population proliferation / ciliary basal body / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / cell division / lysosomal membrane / GTPase activity / synapse / centrosome / GTP binding / protein-containing complex binding / nucleolus / magnesium ion binding / Golgi apparatus / signal transduction / extracellular exosome / nucleoplasm / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Sun JP / Li Q / Yang F / Xu YF / Guo LL / Lian S / Zhang MH / Rong NK | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2023 Journal: Nature / Year: 2023Title: Structural basis of amine odorant perception by a mammal olfactory receptor. Authors: Lulu Guo / Jie Cheng / Shuo Lian / Qun Liu / Yan Lu / Yuan Zheng / Kongkai Zhu / Minghui Zhang / Yalei Kong / Chao Zhang / Naikang Rong / Yuming Zhuang / Guoxing Fang / Jingjing Jiang / ...Authors: Lulu Guo / Jie Cheng / Shuo Lian / Qun Liu / Yan Lu / Yuan Zheng / Kongkai Zhu / Minghui Zhang / Yalei Kong / Chao Zhang / Naikang Rong / Yuming Zhuang / Guoxing Fang / Jingjing Jiang / Tianyao Zhang / Xiang Han / Zili Liu / Ming Xia / Shangming Liu / Lei Zhang / Stephen D Liberles / Xiao Yu / Yunfei Xu / Fan Yang / Qian Li / Jin-Peng Sun /   Abstract: Odorants are detected as smell in the nasal epithelium of mammals by two G-protein-coupled receptor families, the odorant receptors and the trace amine-associated receptors (TAARs). TAARs emerged ...Odorants are detected as smell in the nasal epithelium of mammals by two G-protein-coupled receptor families, the odorant receptors and the trace amine-associated receptors (TAARs). TAARs emerged following the divergence of jawed and jawless fish, and comprise a large monophyletic family of receptors that recognize volatile amine odorants to elicit both intraspecific and interspecific innate behaviours such as attraction and aversion. Here we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of mouse TAAR9 (mTAAR9) and mTAAR9-G or mTAAR9-G trimers in complex with β-phenylethylamine, N,N-dimethylcyclohexylamine or spermidine. The mTAAR9 structures contain a deep and tight ligand-binding pocket decorated with a conserved DWY motif, which is essential for amine odorant recognition. In the mTAAR9 structure, a unique disulfide bond connecting the N terminus to ECL2 is required for agonist-induced receptor activation. We identify key structural motifs of TAAR family members for detecting monoamines and polyamines and the shared sequence of different TAAR members that are responsible for recognition of the same odour chemical. We elucidate the molecular basis of mTAAR9 coupling to G and G by structural characterization and mutational analysis. Collectively, our results provide a structural basis for odorant detection, receptor activation and G coupling of an amine olfactory receptor. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_35761.map.gz emd_35761.map.gz | 27 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-35761-v30.xml emd-35761-v30.xml emd-35761.xml emd-35761.xml | 20.7 KB 20.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
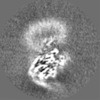
| Images |  emd_35761.png emd_35761.png | 82.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-35761.cif.gz emd-35761.cif.gz | 6.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_35761_half_map_1.map.gz emd_35761_half_map_1.map.gz emd_35761_half_map_2.map.gz emd_35761_half_map_2.map.gz | 26.3 MB 26.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35761 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35761 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35761 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35761 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8iw1MC  8itfC  8iw4C  8iw7C  8iw9C  8iweC  8iwmC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_35761.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_35761.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.85 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
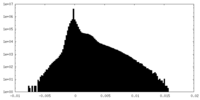
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_35761_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
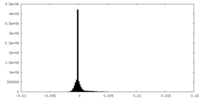
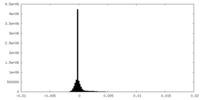
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_35761_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
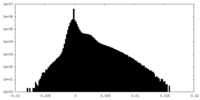
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Cryo-EM structure of the PEA-bound mTAAR9-Golf complex
| Entire | Name: Cryo-EM structure of the PEA-bound mTAAR9-Golf complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Cryo-EM structure of the PEA-bound mTAAR9-Golf complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Cryo-EM structure of the PEA-bound mTAAR9-Golf complex type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-1,Guanine n...
| Macromolecule | Name: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-1,Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(olf) subunit alpha type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: Author stated: We buide a chimera based on wide type Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(olf) subunit alpha and deleted GaAH domain (V67-L190) according to the Articles (Nehme, Rony et al. ...Details: Author stated: We buide a chimera based on wide type Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(olf) subunit alpha and deleted GaAH domain (V67-L190) according to the Articles (Nehme, Rony et al. "Mini-G proteins: Novel tools for studying GPCRs in their active conformation." PloS one vol. 12,4 e0175642. 20 Apr. 2017). Those residues (A236, S239, L259, I359, V362) are dominant negative mutant during G protein modification to increase stability and affinity. A modified Gaolf chimera (Chain A) was generated on the basis of the mini-Golf scaffold with its N terminus replaced by the N terminus of Golf (residue M1 to residue K27) with Gai1 (residue M1 to residue M18) to facilitate the binding of scFv16. Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 29.528566 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGCTLSAEDK AAVERSKMIE KQLQKERLAY KATHRLLLLG ADNSGKSTIV KQMRILHGGS GGSGGTSGIF ETRFQVDKVN FHMFDVGGQ RDERRKWIQC FNDVTAIIYV ADCSDYNMVI REDNNTNRLR ESLDDFESIW NNRWLRTISI ILFLNKQDML A EKVLAGKS ...String: MGCTLSAEDK AAVERSKMIE KQLQKERLAY KATHRLLLLG ADNSGKSTIV KQMRILHGGS GGSGGTSGIF ETRFQVDKVN FHMFDVGGQ RDERRKWIQC FNDVTAIIYV ADCSDYNMVI REDNNTNRLR ESLDDFESIW NNRWLRTISI ILFLNKQDML A EKVLAGKS KIEDYFPEYA NYTVPEDATP DAGEDPKVTR AKFFIRDLFL RISTATGDGK HYCYPHFTCA VDTENARRIF ND CRDIIQR MHLKQYELL UniProtKB: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-1, Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(olf) subunit alpha, Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(olf) subunit alpha |
-Macromolecule #2: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 Details: Author stated: residues (-9) - (-4) is His Tag, residues 341-355 is Linker, residues 356-366 is Small Bit. Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.055867 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MHHHHHHGSL LQSELDQLRQ EAEQLKNQIR DARKACADAT LSQITNNIDP VGRIQMRTRR TLRGHLAKIY AMHWGTDSRL LVSASQDGK LIIWDSYTTN KVHAIPLRSS WVMTCAYAPS GNYVACGGLD NICSIYNLKT REGNVRVSRE LAGHTGYLSC C RFLDDNQI ...String: MHHHHHHGSL LQSELDQLRQ EAEQLKNQIR DARKACADAT LSQITNNIDP VGRIQMRTRR TLRGHLAKIY AMHWGTDSRL LVSASQDGK LIIWDSYTTN KVHAIPLRSS WVMTCAYAPS GNYVACGGLD NICSIYNLKT REGNVRVSRE LAGHTGYLSC C RFLDDNQI VTSSGDTTCA LWDIETGQQT TTFTGHTGDV MSLSLAPDTR LFVSGACDAS AKLWDVREGM CRQTFTGHES DI NAICFFP NGNAFATGSD DATCRLFDLR ADQELMTYSH DNIICGITSV SFSKSGRLLL AGYDDFNCNV WDALKADRAG VLA GHDNRV SCLGVTDDGM AVATGSWDSF LKIWNGSSGG GGSGGGGSSG VSGWRLFKKI S UniProtKB: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-1 |
-Macromolecule #3: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-2
| Macromolecule | Name: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-2 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 6.504446 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: NTASIAQARK LVEQLKMEAN IDRIKVSKAA ADLMAYCEAH AKEDPLLTPV PASENPFRE UniProtKB: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-2 |
-Macromolecule #4: Trace amine-associated receptor 9
| Macromolecule | Name: Trace amine-associated receptor 9 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 38.928238 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MTSDFSPEPP MELCYENVNG SCIKSSYAPW PRAILYGVLG LGALLAVFGN LLVIIAILHF KQLHTPTNFL VASLACADFL VGVTVMPFS TVRSVESCWY FGESYCKFHT CFDTSFCFAS LFHLCCISID RYIAVTDPLT YPTKFTVSVS GLCIALSWFF S VTYSFSIF ...String: MTSDFSPEPP MELCYENVNG SCIKSSYAPW PRAILYGVLG LGALLAVFGN LLVIIAILHF KQLHTPTNFL VASLACADFL VGVTVMPFS TVRSVESCWY FGESYCKFHT CFDTSFCFAS LFHLCCISID RYIAVTDPLT YPTKFTVSVS GLCIALSWFF S VTYSFSIF YTGANEEGIE ELVVALTCVG GCQAPLNQNW VLLCFLLFFL PTVVMVFLYG RIFLVAKYQA RKIEGTANQA QA SSESYKE RVAKRERKAA KTLGIAMAAF LVSWLPYIID AVIDAYMNFI TPAYVYEILV WCVYYNSAMN PLIYAFFYPW FRK AIKLIV SGKVFRADSS TTNLFSEEAG AG UniProtKB: Trace amine-associated receptor 9 |
-Macromolecule #5: scFv16
| Macromolecule | Name: scFv16 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 30.363043 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MLLVNQSHQG FNKEHTSKMV SAIVLYVLLA AAAHSAFAVQ LVESGGGLVQ PGGSRKLSCS ASGFAFSSFG MHWVRQAPEK GLEWVAYIS SGSGTIYYAD TVKGRFTISR DDPKNTLFLQ MTSLRSEDTA MYYCVRSIYY YGSSPFDFWG QGTTLTVSAG G GGSGGGGS ...String: MLLVNQSHQG FNKEHTSKMV SAIVLYVLLA AAAHSAFAVQ LVESGGGLVQ PGGSRKLSCS ASGFAFSSFG MHWVRQAPEK GLEWVAYIS SGSGTIYYAD TVKGRFTISR DDPKNTLFLQ MTSLRSEDTA MYYCVRSIYY YGSSPFDFWG QGTTLTVSAG G GGSGGGGS GGGGSADIVM TQATSSVPVT PGESVSISCR SSKSLLHSNG NTYLYWFLQR PGQSPQLLIY RMSNLASGVP DR FSGSGSG TAFTLTISRL EAEDVGVYYC MQHLEYPLTF GAGTKLEL |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 1.875 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: DIFFRACTION / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 749097 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
| Final angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)