+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: EMDB / ID: EMD-3564 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
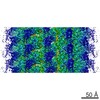
| タイトル | Subtomogram average of type VI secretion system (T6SS) contracted sheath | |||||||||
 マップデータ マップデータ | ||||||||||
 試料 試料 |
| |||||||||
| 機能・相同性 | Type VI secretion system TssC-like / TssC1, N-terminal / TssC1, C-terminal / EvpB/VC_A0108, tail sheath N-terminal domain / EvpB/VC_A0108, tail sheath gpW/gp25-like domain / Type VI secretion system sheath protein TssB1 / Type VI secretion system, VipA, VC_A0107 or Hcp2 / Type VI secretion protein / Type VI secretion system contractile sheath small subunit 機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報 | |||||||||
| 生物種 |  | |||||||||
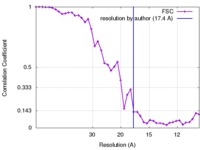
| 手法 | サブトモグラム平均法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 17.4 Å | |||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Wang J / Basler M | |||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Nat Microbiol / 年: 2017 ジャーナル: Nat Microbiol / 年: 2017タイトル: Cryo-EM structure of the extended type VI secretion system sheath-tube complex. 著者: Jing Wang / Maximilian Brackmann / Daniel Castaño-Díez / Mikhail Kudryashev / Kenneth N Goldie / Timm Maier / Henning Stahlberg / Marek Basler /   要旨: The bacterial type VI secretion system (T6SS) uses contraction of a long sheath to quickly thrust a tube with associated effectors across membranes of eukaryotic and bacterial cells . Only limited ...The bacterial type VI secretion system (T6SS) uses contraction of a long sheath to quickly thrust a tube with associated effectors across membranes of eukaryotic and bacterial cells . Only limited structural information is available about the inherently unstable precontraction state of the T6SS. Here, we obtain a 3.7 Å resolution structure of a non-contractile sheath-tube complex using cryo-electron microscopy and show that it resembles the extended T6SS inside Vibrio cholerae cells. We build a pseudo-atomic model of the complete sheath-tube assembly, which provides a mechanistic understanding of coupling sheath contraction with pushing and rotating the inner tube for efficient target membrane penetration. Our data further show that sheath contraction exposes a buried recognition domain to specifically trigger the disassembly and recycling of the T6SS sheath by the cognate ATP-dependent unfoldase ClpV. | |||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| ムービー |
 ムービービューア ムービービューア |
|---|---|
| 構造ビューア | EMマップ:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| 添付画像 |
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
-EMDBアーカイブ
| マップデータ |  emd_3564.map.gz emd_3564.map.gz | 3.5 MB |  EMDBマップデータ形式 EMDBマップデータ形式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ヘッダ (付随情報) |  emd-3564-v30.xml emd-3564-v30.xml emd-3564.xml emd-3564.xml | 9.3 KB 9.3 KB | 表示 表示 |  EMDBヘッダ EMDBヘッダ |
| FSC (解像度算出) |  emd_3564_fsc.xml emd_3564_fsc.xml | 4.3 KB | 表示 |  FSCデータファイル FSCデータファイル |
| 画像 |  emd_3564.png emd_3564.png | 114.3 KB | ||
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3564 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3564 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3564 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3564 | HTTPS FTP |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  emd_3564_validation.pdf.gz emd_3564_validation.pdf.gz | 268.2 KB | 表示 |  EMDB検証レポート EMDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  emd_3564_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_3564_full_validation.pdf.gz | 267.3 KB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  emd_3564_validation.xml.gz emd_3564_validation.xml.gz | 7 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-3564 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-3564 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-3564 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-3564 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
- リンク
リンク
| EMDBのページ |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- マップ
マップ
| ファイル |  ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_3564.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 4.2 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_3564.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 4.2 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 投影像・断面図 | 画像のコントロール
画像は Spider により作成 これらの図は立方格子座標系で作成されたものです | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ボクセルのサイズ | X=Y=Z: 5.2 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 密度 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 空間群: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | EMDB XML:
CCP4マップ ヘッダ情報:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-添付データ
- 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素
-全体 : Type VI secretion system contracted sheath
| 全体 | 名称: Type VI secretion system contracted sheath |
|---|---|
| 要素 |
|
-超分子 #1: Type VI secretion system contracted sheath
| 超分子 | 名称: Type VI secretion system contracted sheath / タイプ: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / 親要素: 0 / 含まれる分子: all |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  |
-分子 #1: vipA
| 分子 | 名称: vipA / タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / 光学異性体: LEVO |
|---|---|
| 配列 | 文字列: MSKEGSVAPK ERINIKYIPA TGDAQAEVEL PLKTLVVGDF KGHAEQTPLE ERATITVDKN NFEAVMRESE LKITATVKN KLTDDENAEL PVELNFKSLA DFAPDAVASQ VPELKKLIEL REALVALKGP LGNIPAFRER L QSLLNSEE SREKLLAELN LLSGQEEPQA |
-分子 #2: vipB
| 分子 | 名称: vipB / タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / 光学異性体: LEVO |
|---|---|
| 配列 | 文字列: MMSTTEKVLE RPQLAQGSLL DEIMAQTRIA PSEEGYDIAK KGVAAFIENL MGSQHSAEPV NKSLVDQMLV ELDKKISAQ MDEILHNSQF QAMESAWRGL KLFVDRTDFR ENNKVEILHV TKDELLEDFE FAPETAQSGL Y KHVYSAGY GQFGGEPVGA IIGNYAFTPS ...文字列: MMSTTEKVLE RPQLAQGSLL DEIMAQTRIA PSEEGYDIAK KGVAAFIENL MGSQHSAEPV NKSLVDQMLV ELDKKISAQ MDEILHNSQF QAMESAWRGL KLFVDRTDFR ENNKVEILHV TKDELLEDFE FAPETAQSGL Y KHVYSAGY GQFGGEPVGA IIGNYAFTPS TPDMKLLQYM GALGAMAHAP FISSVGPEFF GIDSFEELPN IK DLKSTFE SPKYTKWRSL RESEDARYLG LTAPRFLLRV PYDPIENPVK SFNYAENVSA SHEHYLWGNT AFA FATRLT DSFAKYRWCP NIIGPQSGGA VEDLPVHVFE SMGALQSKIP TEVLITDRKE FELAEEGFIA LTMR KGSDN AAFFSANSIQ KPKVFPNTKE GKEAETNYKL GTQLPYMMII NRLAHYVKVL QREQIGAWKE RQDLE RELN SWIKQYVADQ ENPPADVRSR RPLRAARIEV MDVEGNPGWY QVSLSVRPHF KYMGANFELS LVGRLD QA |
-実験情報
-構造解析
| 手法 | クライオ電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
 解析 解析 | サブトモグラム平均法 |
| 試料の集合状態 | helical array |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| 凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE |
- 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法
| 顕微鏡 | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| 撮影 | フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) 平均電子線量: 1.0 e/Å2 |
| 電子線 | 加速電圧: 300 kV / 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| 電子光学系 | 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM / 撮影モード: BRIGHT FIELD |
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー








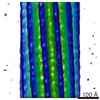
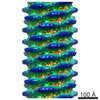
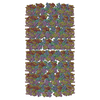


 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)